Class 9 Science Sample Paper (Term 1) - 4 (with solutions): Part - 2 | Extra Documents & Tests for Class 9 PDF Download
Ques 23: What will happen if cells are not organized in tissue?
Ans: Organisms whether it is unicellular or multicellular need to perform a lots of functions like respiration, digestion, locomotion, etc. Cells that are present in group and specialize in one particular function forms tissues. Some tissue helps in growth, while others in locomotion and some in body movement. So, if tissues are not present in bodies of living organism then these kinds of highly organized and specialized process will become disorganised. There will be no coordination in the functioning of cells and body.
Ques 24: (a) If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapours appear on the wall of the glass jar. Explain.
(b) What is the function of cardiac muscle fibre?
(c) Name the cells of bone and cartilage.
Ans: (a) Water vapour released through the stomatal aperture during transpiration, accumulate on the wall of glass jar.
(b) These muscles are found only in heart. They help in beating of heart and work 24 hours a day till death.
(c) Bone: Osteocytes
Cartilage: Chondrocytes.
Ques 25: Starting from a stationary position, Anil paddles his bicycle to attain a velocity of in 25 s. Then, heapplies brakes such that he again comes to rest after next 50 s. Calculate the acceleration of the bicycle in both cases. Also find the total distance covered by Anil.
Ans: In first case, initial velocity u1 = 0, time t1 = 25s and final velocity, v1 = 10 ms-1 ∴ acceleration 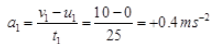 and distance covered in time t1 is
and distance covered in time t1 is 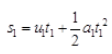
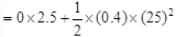 = 0+125 = 125m After applying the brakes in second case, Initial velocity, u2 = 10 ms-1 Time, t2 = 50s Final velocity, v2 = 0
= 0+125 = 125m After applying the brakes in second case, Initial velocity, u2 = 10 ms-1 Time, t2 = 50s Final velocity, v2 = 0
∴ acceleration, 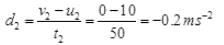 and distance covered in time t2 is
and distance covered in time t2 is
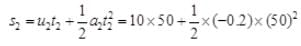 =500 + 250 = 250m So, total distance covered by Anil = s = s1 + s2 = 125 + 250 + 375m
=500 + 250 = 250m So, total distance covered by Anil = s = s1 + s2 = 125 + 250 + 375m
Ques 26: Describe an activity to demonstrate Newton's third law of motion.
Ans: Describe an activity to demonstrate Newton's third law of motion. Take a rubber balloon and inflate it. Attach it to a straw and connect it between two rigid supports as shown in the figure. Prick the balloon with a pin. The balloon moves in opposite direction of escaped air. This shows that the force with which air is pushed out, is exerted in opposite direction by a iron the balloon.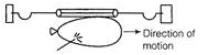
Ques 27: Glass and china wares are wrapped in straw or paper before packing. Briefly explain why?
Ans: Glass and china wares are wrapped in straw or paper before packing. If during loading or unloading in transit, packing gets some jerk, then straw or paper, being compressible increases the time of jerk. As a result for given change inmomentum, the force of jerk will be less and chances of breakage of glass and china wares will be reduced.
Ques 28: Shikha buys a few grams of precious stones in Delhi. She takes them to equator and is surprised to see that their weight is reduced. She thinks that she has been cheated. She goes back to the seller and claims the exchange amount. The shopkeeper explains her how weight differs due tovalue of g. Satisfied Shikha goes back.
(a) List few values of Shikha.
(b) What are the values of shopkeeper?
(c) How does g vary with distance?
Ans: (a) Shikha jumps to conclusion without thinking twice
(b) Shopkeeper is logical, patient and scientific.
(c) at equators, g is minimum and at poles, is maximum.
Ques 29: Two objects of masses m1 and m2, when separated by a distance d, exertsa force F on each other. What happens when (a) value of mass of first is doubled? (b) masses of both objects are doubled? (c) masses are brought so closer that distance between them becomes d/2? (d) the space between the two objects has no air, i.e., it is complete vacuum
Ans: We know that initial value of gravitational force between two objects,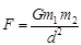
(a) If the mass of first object is doubled, then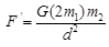
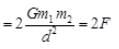 Hence, the force is doubled.
Hence, the force is doubled.
(b) If the masses of both objects are doubled, then 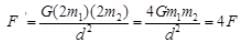 Hence, the force is quadrapled.
Hence, the force is quadrapled.
(c) If distance between the objects is reduced to onehalf of its original value, then 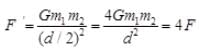 Hence, the force is quadrapled.
Hence, the force is quadrapled.
(d) There is no effect on force when air medium is removed.
Ques 30: (a) What is vermicompost?
(b) Name two crops used for preparinggreen manure.
(c) What are the characteristics of storage structure for grains?
(d) Name two nitrogen fixing bacteria.
(e) Which type of crop is generally grown between two cereal crops to restore soil fertility?
Or
Figure shows the two crop fields [plots A and B] have been treated by manures and chemical fertilisers respectively, keeping other environmental factors same. 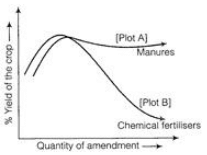
Observe the graph and answer the following questions
(a) Why does plot B show sudden increase and then gradual decrease in yield?
(b) Why is the highest peak in plot A graph slightly delayed?
(c) What is the reason for the different pattern of the two graphs?
Ans: (a) The process of preparation of compost by using earth worms, which hasten the process of decomposition of plant and animal refuse is called vermi-compost.
(b) (a) Sunhemp (b) Dhaincha
(c) Storage structures for grains should be air-tight, easy to clean, moisture proof and rodent proof.
(d) Rhizobium and Nitrosomonas
(e) Leguminous crop.
Or
(a) With the addition of chemical fertilisers there is sudden increase in yield due to release of nutrients N, P, K, etc in high quantity. The gradual decline inthe graph may be due to continuous use and highquantity of chemicals which kills microbes usefulfor replenishing the organic matter in the soil. This decreases the soil fertility.
(b) Manures supply small quantities of nutrients to the soil slowly as it contains large amounts of organic matter. It enriches soil with nutrients; there by increasing soil fertility continuously.
(c) The differences in the two graphs indicate that use of manure is beneficial for long duration incropping as the yield tends to remain high when the quantity of manure increases. In case of plot B the chemical fertilizers may cause various problems when used continuously for long time. Loss of microbial activity reduces decomposition of organic matter and as a result, soil fertility is lost that affects the yield.
Ques 31: (a) Why do solids have fixed shape and fixed volume?
(b) Why is air dense at the sea level?
(c) On melting of ice, there is decrease involume instead of increase. Why?
(d) What is the binding force between molecules if a substance is a gas under ordinary conditions of temperature and pressure?
(e) Why are average kinetic energies of hydrogen, carbon dioxide and ethane the same at the same temperature?
Or
(a) When we light an incense stick (agarbatti) in a corner of our room, why does its fragrance spread in the whole room quickly?
(b) Liquid A has higher vapour pressure than liquid B. Which liquid out of A and B will have lower boiling point?
(c) Name the five states of matter, which the scientists are now talking of?
(d) What do you understand by plasma?
(e) Name the Indian physicist, who worked for a fifth state of matter.
Ans: (a) In solids, the particles are closely packed and their positions are fixed due to strong forces of attraction existing between them. So, solids have fixed shape. Since, the space between the particles are also fixed, the solids have fixed volume.
(b) Air at sea level is compressed by the mass of air above it. Hence, air is more dense at sea level than atan altitude.
(c) There are empty spaces in the packing of water molecules in ice. On heating, different strings of hydrogen bonded water molecules break and water molecules come closer to each other. Hence, the volume decreases on melting of ice.
(d) The binding force between the molecules of a gas is van der Waals' force.
(e) Average kinetic energy of any gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. Since, all the gases are at the same temperature, their average kinetic energies will also be the same.
Or
(a) The fragrance of 'agarbatti' spreads all around due to diffusion of its smoke into the air. The particles of gas produced on burning of incense stick move rapidly inall the directions. They mix with air and reach the whole room very quickly.
(b) The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapour pressure becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure. The vapour pressure of liquid A is higher than liquid B. So, vapour pressure of A will become equal to atmospheric pressure at alower temperature than liquid B. Consequently boiling point of liquid A is lower than that of liquid B.
(c) The five states of matter are solid, liquid, gas, plasma and Bose-Einstein condensate.
(d) Plasma is the state, which consists of super energetic and super excited particles in the form of ionised gases. The non-sign bulbs and the fluorescent tube consist of plasma. The plasma glows with a special colour depending on the nature of the gas, when electric energy flows through it. The sun and stars glow due to the presence of plasma in them at very high temperature.
(e) In 1920, Indian physicist Satyendra Nath Bose did some calculations for the fifth state of matter.
Ques 32: How will you separate a mixture containing kerosene and petrol (difference in their boiling points is more than 25°C), which are miscible with each other? Or Benzoic acid is used as a food preservative. The graph below shows the heating curve for benzoic acid. Study the graph and answer the following questions
(i) At what time does benzoic acid begin to (a) melt? (b) boil?
(ii) What is the melting point of benzoic acid?
(iii) What happens to the temperature while benzoic acid melts?
(iv) What is the physical state of benzoic acid during the time interval of 35-45 min?
Ans: A mixture of kerosene and petrol (b.p. differ by more than 25oC) can be separated by the process of simple distillation. Method In a distillation flask, a mixture of kerosene and petrol is taken as shown in figure. The mixture is heated slowly and the temperature is noted with the help of thermometer. Petrol (b.p. = 70°C to 120°C) vaporizes first and the temperature becomes constant for some time (till all petrol evaporates from the mixture).
Vapours of petrol are condensed and collected in another container, while the kerosene remains in the distillation flask. Again the temperature starts rising and the heating is stopped and both the components are collected separately. This is shown in the diagram below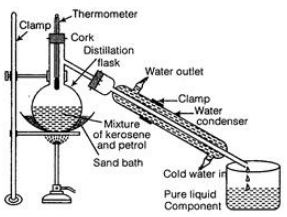
Or
(i) (a) Benzoic acid begin to melt at 20 min.
(b) Benzoic acid begin to boil at 52 min.
(ii) The melting point of benzoic acid is 120° C
(iii) The temperature remains constant at 120°C un till all the benzoic acid has melted.
(iv) The physical state of benzoic acid is liquidduring the time interval of 35-45 min.
Ques 33: Name the protective tissue of animal body. State the types of this tissue. Or List the characteristics of cork. How is it formed? Mention its role.
Ans: Epithelial tissue is the protective tissue of animal body.Depending upon the shape and function of the cells, they are of following types
(i) Squamous epithelium Simple squamous epithelium consists of extremely thin and flatcells forming delicate lining, e.g., the oesophagus and lining of mouth.
(ii) Cuboidal epitheliumIt consists of cube-likecells with rounded nuclei and forms the lining of kidney tubules and duct of salivary glands, where it provides mechanical support.
(iii) Columnar epitheliumIt consists of pillar-like cells having elongated nuclei. It is found in inner lining of intestine where absorption and secretion occur.
(iv) Ciliated epithelium The columnar epithelium tissue also has cilia, which are hair-like projections on the outer surface of epithelial cells.
(v) Glandular epithelium The columnar epithelium is often modified to form glands, which secrete chemicals.
Or
(i) It is the outer protective tissue of older stem and roots.
(ii) It is formed by secondary lateral meristem called cork cambium.
(iii) The mature cork become dead and filled with tannin, resin and air.
(iv) The cells are arranged compactly without intercellular spaces.
(v) The cells become several layers thick, which are impermeable due to deposition of suberin in their wall.
Formation of Cork As plant grow older, the outer protective tissue undergoes certain changes. A strip of secondary meristem replaces the epidermis of stem. Cells on the outside are cut-off from this layer. This form several layers thick cork or bark of theno overlap.
Role of Cork
(i) It prevents loss of water by evaporation.
(ii) It protects plant from the invasion of parasites and other harmful microorganisms.
(iii) It is used for manufacture of insulation boards, sport goods, shock absorber, etc.
|
1 videos|228 docs|21 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|

















