Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Climate Characteristics
Climate Characteristics | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Equatorial Climate Characteristics
World climate distribution
Climates vary worldwide due to various factors:
- Latitude: As you move away from the equator, both temperatures and sunshine hours decrease. This is because solar radiation is more dispersed at the poles and has to pass through a greater amount of atmosphere.
- Altitude: Increasing altitude results in lower temperatures. For example, as you climb a mountain, the temperature drops steadily.
- Continentality: Areas further inland experience rapid heating in summer and quick cooling in winter. This is noticeable in regions like central Asia.
- Ocean Currents: The circulation of warm and cold currents in oceans influences the temperature of adjacent land. For instance, the Gulf Stream warms the western coast of Europe.
- Aspect: In the northern hemisphere, south-facing slopes receive more sunlight and are therefore warmer. This can be observed in valleys or mountain ranges.
- Prevailing Winds: Winds from warmer regions bring higher temperatures. An example is the Foehn wind in the Alps, which warms as it descends.
- Pressure Systems: Areas affected by low pressure, such as the equator, experience rising air, condensation, and cloud formation leading to increased precipitation. Conversely, regions under high pressure have dry conditions due to descending air.
Equatorial climate distribution

Equatorial climate characteristics


Factors influencing the equatorial climate
- The position of the midday sun: When the sun is directly overhead, it maximizes the amount of solar energy received, impacting temperature and weather patterns in the region.
- Constant low pressure: Persistent low pressure systems contribute to the continuous rise of warm air, leading to cloud formation and precipitation. For example, regions near the equator often experience this phenomenon.
- Dense vegetation cover: Areas with lush vegetation experience high rates of evaporation and transpiration, adding moisture to the air and influencing local climate. The Amazon Rainforest is a prime example of this effect.
- Temperature variations: Warm air can hold a large amount of water vapor. When this warm air cools in the late afternoon, the water vapor condenses and results in heavy, localized rainfall. This process is evident in tropical regions like Southeast Asia.
Question for Climate CharacteristicsTry yourself: What is one factor that influences the temperature of a region?View Solution
Hot Desert Climate Characteristics
Hot desert climate distribution

Hot desert climate characteristics
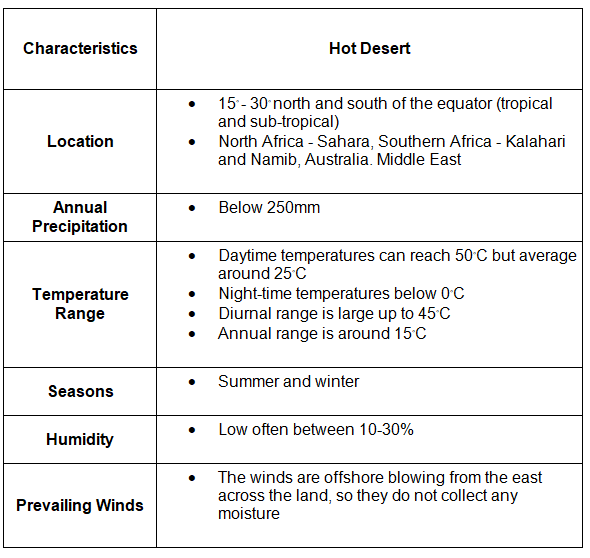

Factors influencing the hot desert climate
- Throughout the year, there is consistent high pressure, causing the air to descend and warm, which inhibits precipitation formation since the air doesn't rise.
- The prevailing winds often originate from land areas, carrying minimal moisture content.
- Certain desert regions are situated in a rain shadow, experiencing scant rainfall as a result.
- Cold ocean currents along the western coastlines of continents can lead to decreased summer temperatures, influenced by the cooling effect of the ocean.
Influence of pressure systems
- Hot deserts are located between 15° to 30° north and south of the equator, influenced by atmospheric pressure patterns.
- Air ascends at the equator and then diverges towards the northern and southern latitudes in the upper atmosphere.
- As the air travels away from the equator, it cools and descends back towards the Earth's surface.
- This descending air creates regions of high pressure approximately 30° north and south of the equator.
- Because of the downward movement of air, the warm air remains unable to rise, preventing condensation and cloud formation, resulting in significant aridity.
Atmospheric Pressure Systems:
Question for Climate CharacteristicsTry yourself: What is the main reason for the lack of precipitation in hot desert climates?View Solution
The document Climate Characteristics | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
57 videos|70 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Climate Characteristics - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are the main characteristics of an equatorial climate? |  |
Ans. An equatorial climate is characterized by high temperatures, heavy rainfall throughout the year, and high humidity levels. It experiences little variation in temperature and remains warm all year round.
| 2. How does the equatorial climate differ from other climate types? |  |
Ans. The equatorial climate differs from other climate types in terms of its consistent high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and high humidity levels. It is also characterized by dense vegetation and a lack of distinct seasons.
| 3. What are some regions of the world that have an equatorial climate? |  |
Ans. Some regions of the world that have an equatorial climate include the Amazon Rainforest in South America, the Congo Basin in Africa, and parts of Southeast Asia such as Indonesia and Malaysia.
| 4. How does the equatorial climate impact the biodiversity of an area? |  |
Ans. The equatorial climate's consistent warmth, abundant rainfall, and high humidity create ideal conditions for a diverse range of plant and animal species to thrive. This leads to high levels of biodiversity in equatorial regions.
| 5. How do people adapt to living in an equatorial climate? |  |
Ans. People living in equatorial climates often adapt by wearing light and breathable clothing, building homes with good ventilation, and relying on agriculture that is suited to the high levels of rainfall and humidity.
Related Searches

















