Collisions | Physics for Grade 10 PDF Download
Introduction
- Examples of momentum in an event are collisions
- Objects will either:
- Collide and move in opposite directions - this is an elastic colision
- Collide and move in the same direction together - this is an inelastic collision
- When the objects move in opposite directions:
- Each object will have a different velocity depending on its mass and initial momentum of the system
- When the objects move in the same direction together:
- They will have a combined mass and velocity
- Momentum is always conserved in a collision
 Types of collisions
Types of collisions
Exam Tips: If an exam question asks you to analyse a collision, follow these tips for full marks:
- Always consider the motion before and after the collision and state:
- The velocities of each object
- The direction each object moves
- State whether the collision was elastic or inelastic and explain your reasoning
- In a perfectly elastic collision, the kinetic energy is the same before and after
- In a perfectly inelastic collision, the two objects stick together after colliding
- Describe any energy transfers that occur if kinetic energy is not conserved
- For example, it may be converted into heat, sound, elastic potential energy etc
Calculations Involving Collisions
- Calculations involving collisions use the conservation of momentum to determine the velocity of an object (or objects) before or after the collision
- This means the momentum before the collision must equal the momentum after the collision for momentum to be conserved
Solved Example
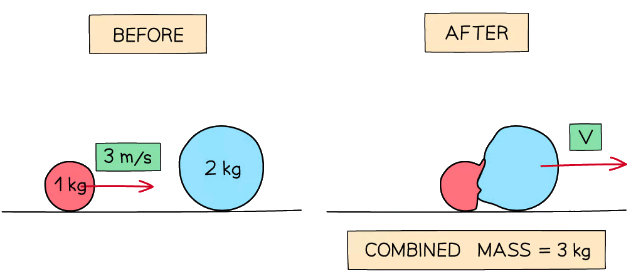
Example: An object of mass 1 kg is travelling at 3 m/s when it collides with a heavier object of mass 2 kg. The two objects stick together and travel off as one.Calculate the combined velocity of the objects after the collision.
Step 1: Draw a diagram
Step 2: State the principle of conservation of momentum
The total momentum before a collision = The total momentum after a collisionStep 3: Calculate the momentum before the collision
Before the collision, only the 1 kg object has any momentum
pbefore = mv = 1 × 3 = 3 kg m/sStep 3: Determine the momentum after the collision
The combined mass is now 1 + 2 = 3 kg
pafter = mv = 3 × vStep 4: Substitute values into conservation equation
pbefore = pafter
3 = 3 × vStep 5: Rearrange for the combined velocity v
v = 3 ÷ 3 = 1 m/s
Exam Tip: Always double-check the signs (positive or negative) for the velocity in your answers, as this is the most common type of calculation error!
|
124 videos|149 docs|37 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Grade 10 exam
|

|