Computer Generations in Various Years | Computer Science for Class 7 PDF Download
Computer Generations
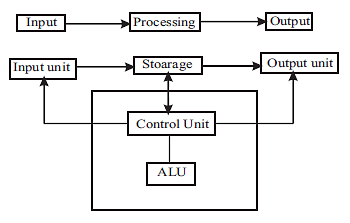
Generation in the computer industry is determined by development in technology. Earlier it used to be between different hardware technologies but later extended to both hardware and software which together make up a computer system.
There are five computer generation till today.
The First Generation ( 1942-1955 )
- They are characterized by vacuum tube.
- These computers were made using thousands of Vacuum tubes. Vacuum tube is a fragile glass device that can control and amplify electronic signal.
- These computer used to perform computation is milli – seconds (slow computer ).
- They were bulky in size and require large room for installation.
- Vacuum tubes dissipates large amount of heat and consumed lot of power(electricity). Hence continuous air conditioning was required.
- These computer were unreliable, as they used thousands of vacuum tubes which have filament with short life. Hence prone to frequent hardware failure and also require constant maintenance.
- Commercial production was difficult and was costly as thousands of components were assembled manually.
- Memory used were electronic relay and magnetic drum. Data and instruction were fed using punch card, which were used as secondary memory .
- Programs were written with low level programming language (Machine language and Assembly language).
- Used only for scientific computations.
Example: ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC I, IBM 701 , IBM 605, EDSAC, Mark I
The Second Generation of Computer (1955-1964 )
- They are characterised by transistor. Transistor was invented by John Bardeen , William Shockley and Walter Braltain at Bell Laboratories in 1947.
- It is solid state semiconductor device.
- The use of transistor made these computer more reliable , faster, less expensive, smaller and cooler to operate than the first generation computer.
- They were 10 times faster than first generation computer.
- Power consumption and heat dissipation were reduced but still required air conditioning.
- They used magnetic core for main/ primary memory and magnetic disk and tape as secondary storage media.
- Program were written with high-level programming language. ( FORTRAN, COBOL, ALGOL, SNOBOL).
- Use of batch operating system.
- Commercial use were started in business and industries for data processing applications like Payroll , Inventory control, Employ management.
- But commercial production was still difficult as transistor were assembled manually into electronic circuit.
- CDC 1604 was one of the first computer to replace vacuum tube with transistor.
Example: IBM1401, IBM 1620, UNIVAC 1108 , HONEYWELL 200, CDC 1604.
Third Generation of Computer (1964-75)
- They are characterised by integrated circuit. First IC was invented by Jock St. Clair Kilby and Robert Noyce in 1958.
- An IC is small silicon chip made up of extremely purified silicon crystal.
- It has numerous electronic components like transistor, resistor and capacitors.
- Small scale integration ( SSI ) chip have about 10 electronic component on a singal chip and medium scale integration ( MSI )which have about 100 electronic component on single chip.
- Concept of time sharing operative system was introduced which allowed interactive usage and simultaneous use of system by multiple users. It also made online system feasible , resulting in online airline reservation system.
- Operating system with multiprogramming and multitasking were introduced.
- Use of Integrated Circuit ( IC ) further increased the speed, made computer more reliable, reduced power consumption, reduced heat dissipation and size also reduced.
- Size of memories increased.
- Mainframe and minicomputer were developed in this generation.
- High level programing language like PASCAL and BASIC were introduces.
- Their manufacturing did not require manual assembly of components hence, commercial production was easier and cheaper.
- Used in area of education, small business and offices.
- User started to interact using keyboard and monitor. Computer where available for the first time to the mass use. User could use software according to their need as hardware and software were available separately.
The Fourth Generation of Computer: ( 1975 onwards )
- They are characterised by microprocessor. Large scale integration ( LSI ) which allow to tens of thousands ( 30000 ) of electronic component in single chip and Very Large Scale Integrating ( VLSI ) which allow about one million electronic component on single chip.
- Microprocessor contain all the circuit to perform arithmetic logic and control function.
- Semiconductor memories were used which replaced magnetic core memories.
- Hard disk with large capacity are used.
- Magnetic tapes and floppy disks are used for portable storage.
- Computer networking ( LAN & WAN ) and data communication become popular.
- Power consumption and heat dissipation is further reduced in third generation.
- Very reliable, powerful and small in size.
- Software like MS-DOS, MS Windows, applies propriety – OS individual who are not computer professionals can also use.
- Computer of this generation used graphical user interface (GUI ) to make computer more user friendly.
- Personal computer based application were also developed like word processing packages.
- Production cost is very less.
- Multiple Window on a single terminal screen could be opened.
- UNIX operating system and C programming languages were introduced.
Example: IBM PC , PDP 11 , Apples Macintosh
The Fifth Generation of Computer(Present and Onward)
- This generation is still under the development.
- It is based on the concept of artificial intelligence.
- ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration ) is used. In ULSI a microprocessor chip have ten million electronic components.
- The principle of parallel processing ( many processor grouped together ) and superconductivity are being used.
- Some applications used are voice recognition, visual recognition.
As we go from First generation to fifth generation the size, power consumption and hardware failure heat dissipation reduces, and speed, reliability, main memory storage capacity secondary memory storage capacity increase.
Classification of Computer
Classification of computer based of technology
(i) Analogue Computer: These are the computer which measure changes in continuous physical quantities. These computer are well suited to simulating system which work in real time environment. These computer are slow.
Example: Simulation in aircraft, ECG.
(ii) Digital Computer: These computer process there information in discrete from. In this the data is represented in binary form. That is 0 and 1.
These computer can process large volume of data with high speed and has large storage capacity hence are used in industrial, business and scientific application.
(iii) Hybrid Computer: As the name suggest, hybrid computer have the technology of both analogue as well as digital computer. In this computer converters (analogue to digital converter and digital to analogue converter) are used for conversion of signal.
Classification of Digital Computer
(i) Micro Computer
- These computer uses microprocessor in there CPU.
- These are general purpose computer i.e. can do different type of work by just changing program like we can listen music, watch movie and even play games.
- These computer generally support of single user.
- This includes our PCs ( personal Computer ), smartphone and laptop, handheld devices like PDA ( Personal Digital Assistant ) and tablets.
(ii) Mini Computer
- These can support multiple users, ( up to hundred user ) that means more than one user can work on this computer at the same time.
- These computer are used for scientific purposes and for small business establishment.
(iii) Mainframe Computer
- These computer are faster than minicomputer but slower that super computer.
- These can also support multiple user( up to thousand user ).
- These can process huge database hence used in big organisations like Banks and insurance companies, Research institutions.
- These are input-output bounded, that means the amount of work that can be performed is limited primarily by number and speed of it’s I/O devices.
(iv) Super Computer
- These are the fastest computer present now.
- These are special purpose machine i.e. Designed to handle defined problem.
Example: Metrological department uses for weather forecasting. - They use multiprocessing and parallel processing technologies that means multiple processors are used and parallel processing means a large problem is divided into smaller problem and is assigned to different processor and processed in parallel. Hence these are also known as parallel computer or parallel processor.
- The super computer execute few problem at a time as fast as possible.
- 1976 Cray I was developed by Cray research company and was the first super computer of the world.
- 1991 Param was developed by C-DAC Pune and is first Indian super computer In India.
- Anupam series of supercomputer is developed by Bhabha Atomic Research Centre ( BARC ).
- PACE series of supercomputer is developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation ( DRDO ).

Micro Computer
Personal Computer:
- These are non-portable i.e. are difficult to carry.
- These are general purpose computer.
- These support multitasking and are single user computers.
- There are two model of PC.
Desktop Model: The system unit is flat on the desk or in other words monitor is kept on the top of system unit.
- These are temporary memory in the CPU.
- All data and instruction is represented in the register before it is processed.
- These are the fastest memory.

Different Types of Register Accumulator
- It contains the data on which the operation has to be performed and then stores the result.
Instruction Register
- It holds the current instruction which is being executed.
Input/Output Register
- They are used communicate with the input and output devices.
Program Control(PC)
- It holds the address of net instruction to be executed.
Memory Address Register
- It holds the address of active memory location.
Memory Buffer Register
- It holds the information on its way to and from memory.
Output Unit
- The processed data of the computer is provided to the user by output unit.
- Processed data is in binary form , so output unit convert it to human understandable form.
Example: Monitor, Speaker etc.
|
26 docs|14 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|