Grade 11 Exam > Grade 11 Notes > Computer Science for Grade 11 > Computer Science Syllabus
Computer Science Syllabus | Computer Science for Grade 11 PDF Download
Learning Outcomes
Student should be able to
- develop basic computational thinking
- explain and use data types
- appreciate the notion of algorithm
- develop a basic understanding of computer systems - architecture, operating system and cloud computing
- explain cyber ethics, cyber safety and cybercrime
- Understand the value of technology in societies along with consideration of gender and disability issues
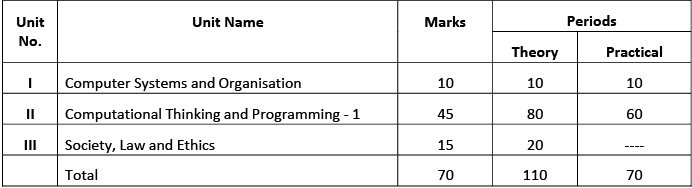
Distribution of Marks
Unit wise Syllabus
Unit I: Computer Systems and Organisation
- Basic Computer Organisation: Introduction to computer system, hardware, software, input device, output device, CPU, memory (primary, cache and secondary), units of memory (Bit, Byte, KB, MB, GB, TB, PB)
- Types of software: system software (operating systems, system utilities, device drivers), programming tools and language translators (assembler, compiler & interpreter), application software
- Operating system (OS): functions of operating system, OS user interface
- Boolean logic: NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, truth table, De Morgan’s laws and logic circuits
- Number system: Binary, Octal, Decimal and Hexadecimal number system; conversion between number systems.
- Encoding schemes: ASCII, ISCII and UNICODE (UTF8, UTF32)
Unit II: Computational Thinking and Programming– 1
- Introduction to problem solving: Steps for problem solving (analysing the problem, developing an algorithm, coding, testing and debugging). representation of algorithms using flow chart and pseudo code, decomposition
- Familiarization with the basics of Python programming: Introduction to Python, features of Python, executing a simple "hello world" program, execution modes: interactive mode and script mode, Python character set, Python tokens (keyword, identifier, literal, operator, punctuator), variables, concept of l-value and r-value, use of comments
- Knowledge of data types: number (integer, floating point, complex), boolean, sequence (string, list, tuple), none, mapping (dictionary), mutable and immutable data types
- Operators: arithmetic operators, relational operators, logical operators, assignment operator, augmented assignment operators, identity operators (is, is not), membership operators (in, not in)
- Expressions, statement, type conversion & input/output: precedence of operators, expression, evaluation of expression, python statement, type conversion (explicit & implicit conversion), accepting data as input from the console and displaying output
- Errors: syntax errors, logical errors, runtime errors
- Flow of control: introduction, use of indentation, sequential flow, conditional and iterative flow control
- Conditional statements: if, if-else, if-elif-else, flowcharts, simple programs: e.g.: absolute value, sort 3 numbers and divisibility of a number
- Iterative statements: for loop, range function, while loop, flowcharts, break and continue statements, nested loops, suggested programs: generating pattern, summation of series, finding the factorial of a positive number etc.
- Strings: introduction, indexing, string operations (concatenation, repetition, membership & slicing), traversing a string using loops, built-in functions: len(), capitalize(), title(), lower(), upper(), count(), find(), index(), endswith(), startswith(), isalnum(), isalpha(), isdigit(), islower(), isupper(), isspace(), lstrip(), rstrip(), strip(), replace(), join(), partition(), split()
- Lists: introduction, indexing, list operations (concatenation, repetition, membership & slicing), traversing a list using loops, built-in functions: len(), list(), append(), extend(), insert(), count(), index(), remove(), pop(), reverse(), sort(), sorted(), min(), max(), sum(); nested lists, suggested programs: finding the maximum, minimum, mean of numeric values stored in a list; linear search on list of numbers and counting the frequency of elements in a list
- Tuples: introduction, indexing, tuple operations (concatenation, repetition, membership & slicing), built-in functions: len(), tuple(), count(), index(), sorted(), min(), max(), sum(); tuple assignment, nested tuple, suggested programs: finding the minimum, maximum, mean of values stored in a tuple; linear search on a tuple of numbers, counting the frequency of elements in a tuple
- Dictionary: introduction, accessing items in a dictionary using keys, mutability of dictionary (adding a new item, modifying an existing item), traversing a dictionary, built-in functions: len(), dict(), keys(), values(), items(), get(), update(), del, clear(), fromkeys(), copy(), pop(), popitem(), setdefault(), max(), min(), count(), sorted(), copy(); suggested programs : count the number of times a character appears in a given string using a dictionary, create a dictionary with names of employees, their salary and access them
- Introduction to Python modules: Importing module using 'import <module>' and using from statement, Importing math module (pi, e, sqrt, ceil, floor, pow, fabs, sin, cos, tan); random module (random, randint, randrange), statistics module (mean, median, mode)
Unit III: Society, Law and Ethics
- Digital Footprints
- Digital society and Netizen: net etiquettes, communication etiquettes, social media etiquettes
- Data protection: Intellectual Property Right (copyright, patent, trademark), violation of IPR (plagiarism, copyright infringement, trademark infringement), open source softwares and licensing (Creative Commons, GPL and Apache)
- Cyber-crime: definition, hacking, eavesdropping, phishing and fraud emails, ransomware, preventing cyber crime
- Cyber safety: safely browsing the web, identity protection, confidentiality, cyber trolls and bullying.
- Safely accessing web sites: malware, viruses, trojans, adware
- E-waste management: proper disposal of used electronic gadgets
- Indian Information Technology Act (IT Act)
- Technology & Society: Gender and disability issues while teaching and using computers
Practical

Suggested Practical List
Python Programming
- Input a welcome message and display it.
- Input two numbers and display the larger / smaller number.
- Input three numbers and display the largest / smallest number.
- Generate the following patterns using nested loop.

- Write a program to input the value of x and n and print the sum of the following series:
- 1+x+x2+x3+x4+. .......... xn
- 1-x+x2-x3+x4 ................................. xn


- Determine whether a number is a perfect number, an armstrong number or a palindrome.
- Input a number and check if the number is a prime or composite number.
- Display the terms of a Fibonacci series.
- Compute the greatest common divisor and least common multiple of two integers.
- Count and display the number of vowels, consonants, uppercase, lowercase characters in string.
- Input a string and determine whether it is a palindrome or not; convert the case of characters in a string.
- Find the largest/smallest number in a list/tuple
- Input a list of numbers and swap elements at the even location with the elements at the odd location.
- Input a list/tuple of elements, search for a given element in the list/tuple.
- Input a list of numbers and find the smallest and largest number from the list.
- Create a dictionary with the roll number, name and marks of n students in a class and display the names of students who have scored marks above 75.
Suggested Reading Material
- NCERT Textbook for COMPUTER SCIENCE (Class XI)
- Support Materials on the CBSE website.
The document Computer Science Syllabus | Computer Science for Grade 11 is a part of the Grade 11 Course Computer Science for Grade 11.
All you need of Grade 11 at this link: Grade 11
|
84 videos|19 docs|5 tests
|
|
Explore Courses for Grade 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















