Grade 11 Exam > Grade 11 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) > Concentration
Concentration | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) PDF Download
Units of Concentration
- A solid substance that can dissolve in a liquid is termed a solute, while the liquid itself is known as a solvent. Together, they create a solution.
- Many chemical reactions occur within solutions, where solutes are dissolved in solvents, which could be water or organic solvents.
- Concentration denotes the quantity of solute present within a specific volume of the solvent.
- Higher concentrations are achieved when there's a greater amount of solute within the given volume.
- Solute quantity can be measured in grams or moles.
- Typically, concentration is represented as the amount of substance per cubic decimeter (dm3), leading to concentration units such as grams per cubic decimeter (g/dm3) or moles per cubic decimeter (mol/dm3).
Calculating Concentration
Understanding Concentration
- Concentration refers to the quantity of solute present in a specific volume of the solvent.
- In the context of concentration, a common formula used to determine concentration in grams per cubic decimeter (g/dm3) is:

Measuring Concentration
- Concentration can be expressed in grams per cubic decimeter.
- One cubic decimeter (dm3) is equivalent to 1000 cubic centimeters (cm3), which is also equal to one liter.
- When converting data between cm3 and dm3:
- To convert from cm3 to dm3, divide by 1000.
- To convert from dm3 to cm3, multiply by 1000.
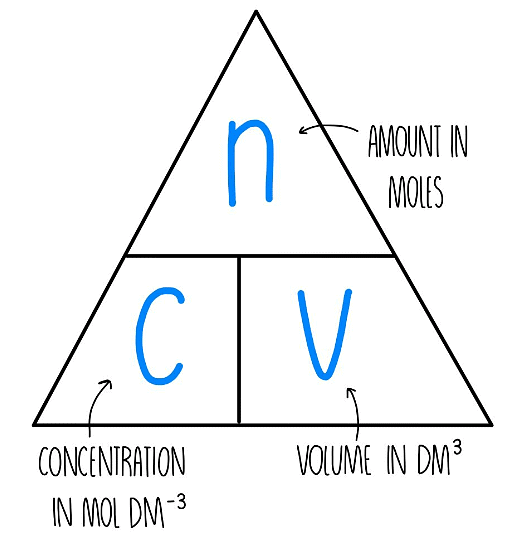
Calculating Concentration using Moles
- Expressing concentration in moles per unit volume is more beneficial for chemists compared to expressing it in mass per unit volume.
- Concentration can be quantified in moles per cubic decimeter (mol/dm3) using the formula:

- This formula can be adapted to include moles as a unit of concentration.
- The resulting units are typically written as mol/dm3, which can also be denoted as mol dm-3.
- Conversion between grams per cubic decimeter (g/dm3) and mol/dm3 may be necessary depending on the question:
- To convert from g/dm3 to mol/dm3, divide by the molar mass in grams.
- To convert from mol/dm3 to g/dm3, multiply by the molar mass in grams.
- Some students find formula triangles helpful in understanding this relationship.

Question for ConcentrationTry yourself: Which formula is used to determine concentration in grams per cubic decimeter (g/dm3)?View Solution
The document Concentration | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) is a part of the Grade 11 Course Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE).
All you need of Grade 11 at this link: Grade 11
|
103 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Concentration - Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE)
| 1. What are the units commonly used to express concentration? |  |
Ans. The units commonly used to express concentration include molarity (mol/L), mass/volume percent (%), volume/volume percent (%), and parts per million (ppm).
| 2. How is concentration calculated? |  |
Ans. Concentration can be calculated by dividing the amount of solute by the volume of solution. The formula is: Concentration = amount of solute / volume of solution.
| 3. How can concentration be calculated using moles? |  |
Ans. Concentration can be calculated using moles by dividing the number of moles of solute by the volume of solution in liters. The formula is: Concentration (mol/L) = moles of solute / volume of solution (L).
| 4. What is the significance of calculating concentration in chemistry? |  |
Ans. Calculating concentration in chemistry is important as it helps determine the amount of solute present in a solution, allows for accurate dilution of solutions, and is essential for conducting experiments with precise measurements.
| 5. Can concentration be expressed in different units for the same solution? |  |
Ans. Yes, concentration can be expressed in different units for the same solution. For example, the concentration of a solution can be given in molarity (mol/L) as well as in mass/volume percent (%), depending on the context and the information needed.

|
Explore Courses for Grade 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches