Cost Audit | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Cost Audit- Meaning |

|
| Importance of Cost Audit |

|
| Features of Cost Audit |

|
| Objectives of Cost Audit |

|
| Scope of Cost Audit |

|
| Who Is Required To Do A Cost Audit? |

|
| Types of Cost Audit |

|
Cost Audit- Meaning
Cost audit involves examining a company's spending and income to ensure that the costs incurred are justified and fair. It is a method used to identify areas where businesses can improve their expense management. A cost audit is typically conducted by a skilled professional who can pinpoint inefficiencies and recommend cost-saving strategies.
It is a financial audit that specifically looks at a company's cost structure. The audit checklist includes a thorough evaluation of various expenses such as the cost of goods sold, overhead expenses, and other costs incurred during regular business operations. The main goal of a cost audit is to discover inefficiencies and find ways to reduce costs without compromising product or service quality.
Importance of Cost Audit
Cost audit is crucial for any organization to evaluate and manage its cost structure effectively. Let's delve into the significance of cost audits.
- Cost audit provides valuable information for management decisions concerning cost reduction and optimization.
- It aids in determining the appropriate selling price for a product or service.
- Ensures that the company adheres to legal and regulatory requirements related to cost accounting.
- Helps enhance efficiency and productivity.
Features of Cost Audit
Cost audit has several distinct characteristics that set it apart from regular financial audits. Let's delve into these key aspects:
- Verification of Cost Accounting Records: Cost audits are conducted to ensure the accuracy of an organization's cost accounting records and to pinpoint any discrepancies that may exist.
- Evaluation of Management Efficiency: They help in assessing how effectively management controls costs, thus aiding in the improvement of operational efficiency.
- Detailed Examination of Cost Accounting System: Cost audits involve a thorough review of an organization's cost accounting system, procedures, and practices to identify areas for enhancement.
- Compliance with Laws and Regulations: Ensuring that the cost accounting system adheres to relevant laws and regulations is a crucial aspect of cost audits.
- Identification of Cost-Reduction Opportunities: By pinpointing areas where costs can be reduced, cost audits offer insights that can lead to more efficient operations.
- Data for Decision Making: They provide valuable data to management, aiding in informed decision-making processes.
- Conducted by Independent Professionals: Cost audits are carried out by independent professionals known as cost auditors, ensuring objectivity.
- Reporting and Advice: The cost auditor prepares a detailed report highlighting audit findings and offers recommendations for improvement.
- Submission to Management and Authorities: The audit report is submitted to the management and filed with government authorities as required by law.
Objectives of Cost Audit
To Verify the Accuracy of Cost Accounting Records
- One primary goal of cost audit is to confirm the correctness of a company's financial records related to costs. This involves a thorough examination of the cost accounting methods and processes to ensure they adhere to widely accepted accounting principles. Cost audit helps in identifying any errors or irregularities in the cost accounting records and takes necessary steps to correct them.
To Ensure Compliance With Legal Requirements
- Another significant objective of cost auditing is to guarantee that companies meet legal obligations. Many countries mandate cost audits as a legal requirement for businesses. Cost audit ensures that companies follow these regulations, thereby preventing legal consequences or fines.
Areas for Cost Reduction
- Cost Audit Importance: Cost audits are crucial for pinpointing where costs can be reduced without compromising quality.
- Thorough Analysis: Cost auditors carefully examine cost accounting records to identify areas where costs are higher than necessary.
- Suggestions for Cost Reduction: After pinpointing high-cost areas, cost auditors offer suggestions to lower costs in those specific areas.
Efficiency and Productivity Enhancement
- Improving Operations: Cost audits can enhance efficiency and productivity by suggesting changes to minimize expenses.
- Profitability Boost: Implementing cost-reduction measures can lead to improved profitability and competitiveness in the market.
Reliable Cost Information
- Decision-Making Support: Cost auditing is essential for providing accurate cost information to aid in corporate decision-making.
- Informed Resolutions: Precise cost data helps in making informed decisions regarding pricing, product composition, and production volumes.
- Dependable Data: Cost audits ensure that the cost-related information provided by the company is reliable and precise.
Scope of Cost Audit
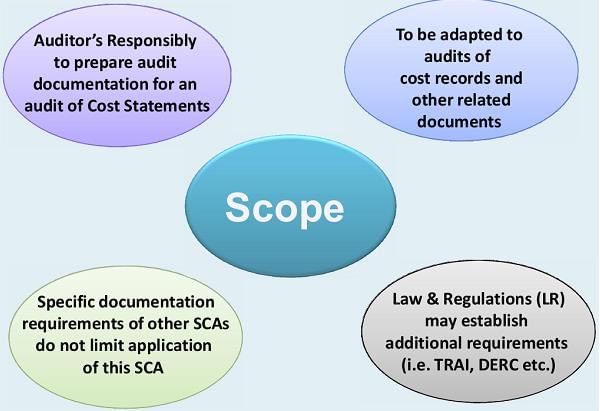 Key Points of Cost Audit Scope
Key Points of Cost Audit Scope
- Examination and verification of an organization's cost accounting records.
- Influence of industry or regulatory requirements on the audit's scope.
- Variation in audit scope based on organization size, nature, and complexity.
- Provision of valuable information for management decision-making.
- Assessment of the adequacy of the cost accounting system, procedures, and practices.
- Ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations related to cost accounting.
Advantages of Cost Audit
Identifying Areas For Cost Reduction:
- Cost audits help in pinpointing areas within a company where expenses are higher than necessary.
- By scrutinizing cost accounting documents, auditors can propose strategies to minimize costs.
- This leads to significant cost savings and increased profitability for the company.
Improving Efficiency And Productivity:
- Cost audits play a crucial role in enhancing a company's effectiveness and productivity.
- Companies can boost productivity by identifying areas that need cost reductions and implementing necessary changes.
- Optimizing operations leads to higher output and better resource allocation, fostering the company's growth.
Ensuring Compliance With Legal Regulations:
- Cost auditing is essential for ensuring that companies comply with legal regulations related to cost accounting.
- Many countries mandate cost audits to meet legal requirements.
- By conducting cost audits, firms ensure adherence to these regulations, avoiding potential legal consequences and penalties.
Disadvantages of Cost Audit
- Costly and Time-Consuming: Conducting cost audits can be expensive and time-consuming for companies. These audits require specialized knowledge and expertise that may not be readily available in-house, leading to the need to hire external auditors. This not only incurs additional costs but also prolongs the audit process, impacting the company's operational efficiency.
- May Disrupt Operations: Cost audits can disrupt a company's day-to-day operations. Auditors need access to the company's financial and operational records, which can interfere with normal business activities. This disruption can result in decreased productivity, causing delays and affecting the company's overall profitability.
- It can Lead to Resistance from Employees: Employees may resist cost audits because they may feel that their work is under scrutiny, which can be seen as intrusive. This resistance can create a negative perception of the audit process among employees, potentially compromising its accuracy and effectiveness.
- It May Not Always Provide Accurate Results: Cost audits may not always offer the most precise reflection of a company's financial standing. Evaluators may need to make educated guesses and approximations based on available data, which may not always be comprehensive or exact. Moreover, certain expenses of the company might be overlooked during the assessment, leading to incomplete and inadequate outcomes.
Limited Scope: Cost audit focuses on specific areas of a company's operations, which may result in an incomplete view of its overall cost structure. This method of evaluating expenses might not always provide the most accurate reflection of a company's financial standing.
Applicability of Cost Records
Cost records, also known as cost accounting records or cost audit, have varying applicability depending on the country and are governed by specific regulations from relevant government authorities. The main goal of maintaining these records is to ensure transparency, accuracy, and compliance in financial reporting, especially in cases involving cost-based pricing or government oversight. Here are common scenarios where cost records are relevant:
- Mandatory Under Tax Laws: Some countries require businesses to keep detailed cost records to ensure accurate calculation of taxable income, especially concerning transfer pricing and cost allocation issues.
- Government Contracts and Regulations: Companies involved in government contracts or operating in regulated industries like utilities, healthcare, and transportation must maintain cost records to comply with pricing regulations and contractual obligations.
- Customs and Trade Compliance: Businesses engaged in international trade use cost records to determine the value of imported or exported goods for customs purposes, aiding in the assessment of customs duties and taxes.
- Transfer Pricing: Multinational corporations maintain detailed cost records to support their transfer pricing policies, demonstrating that transactions between related entities are conducted at arm's length to minimize tax avoidance risks.
- Government Grants and Subsidies: Entities receiving government grants or subsidies often need to maintain cost records to show compliance with grant terms and conditions.
- Price Control and Regulation: In nations with price controls or regulations on specific goods or services, businesses must keep cost records to justify pricing and ensure adherence to government guidelines.
- Investor and Stakeholder Transparency: Some businesses voluntarily maintain detailed cost records to offer transparency to investors, stakeholders, and creditors, promoting trust and accountability.
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Industries like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and defense have specific regulations mandating cost record maintenance to guarantee safety, quality, and compliance.
- Statutory Audit and Reporting: Entities surpassing financial thresholds in certain jurisdictions undergo statutory cost audits, where independent auditors verify the accuracy and compliance of cost records with legal requirements.
- Environmental Compliance: Certain environmental regulations necessitate businesses to keep cost records related to environmental protection measures, pollution control, and sustainability initiatives.
It is crucial for businesses and individuals to seek guidance from tax authorities, industry regulators, and legal or financial advisors to ascertain their obligations regarding cost recordkeeping. Non-compliance can result in penalties, fines, and legal repercussions.
Who Is Required To Do A Cost Audit?
In certain countries, specific companies must undergo a cost audit. The necessity for a cost assessment typically hinges on the scale and nature of a firm's operations. Businesses operating in sectors like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and textiles often need to conduct a cost audit. Moreover, companies surpassing particular revenue thresholds are mandated to undertake cost assessments. The specific criteria for a cost audit can vary based on the nation and industry.
Process of Cost Audit

The process of a cost audit comprises various steps that can differ based on the specific requirements and extent of the audit. Here is a general outline of the cost audit process.
Planning and Scoping:
- During the initial phase of the cost audit process, the auditor devises a plan and defines the scope. This involves outlining the boundaries of the audit, pinpointing the specific areas to be audited, and establishing the audit objectives. Additionally, the auditor examines the company's internal control system to confirm its suitability for meeting the audit needs.
Data Collection:
- The subsequent step entails gathering data. This includes obtaining information from various sources such as financial reports, invoices, and other documents related to the company's activities. Furthermore, the auditor engages in conversations with relevant staff to gain a better understanding of the company's operations and cost structure.
Analysis and Evaluation:
- After gathering the necessary information, the auditor reviews and assesses it.
- This step involves comparing actual costs with budgeted costs, pinpointing areas with excessive costs, and thoroughly evaluating how well the organization's operational activities are performing.
Reporting:
- Reporting is the final phase in the expense scrutiny process.
- During this stage, the auditor creates a comprehensive summary of the examination's findings.
- Accompanying the summary are suggestions for enhancing the company's operations and reducing overall expenses.
- This report is then presented to the management of the organization and other relevant stakeholders.
Types of Cost Audit
Efficiency Audit:
- Focuses on evaluating how well a company operates to find areas where costs can be reduced while enhancing efficiency.
- Includes examining production processes, inventory management, and supply chain management.
- Goal is to enhance overall operational effectiveness and efficiency.
Propriety Audit:
- Ensures that a company's expenses align with its policies and regulations.
- Prevents misuse and ensures resources are utilized appropriately.
- Examines financial records and contracts to guarantee fairness and compliance.
Statutory Audit:
Definition of Statutory Audit:
- Statutory audit is a type of expense audit required by law.
Purpose of Statutory Audit:
- It ensures that certain companies follow laws that mandate expense audits.
Process of Statutory Audit:
- An auditor reviews a company's financial records to ensure accuracy and legal compliance.
- The internal control system of the company is also evaluated to determine its adequacy for the audit.
Importance of Statutory Audit:
- It guarantees that a company is in accordance with relevant laws and regulations.
Explain the Cost Audit Report
General Information In Cost Audit Report
- The general information section in a cost audit report includes basic details about the company, like its name, location, and industry.
- It may also cover information about the company's background, management structure, and ownership.
- This part sets the stage for the report and helps the reader understand the company's operations and context.
Cost Accounting System In Cost Audit Report
- This section of the cost audit report focuses on how the company handles its expenses and tracks costs.
- It explains the methods and systems used by the company to manage expenses, including cost allocation, inventory valuation, and expenditure monitoring.
- The goal here is to clarify how the company controls and supervises its spending.
- The auditor's role is to assess the efficiency of the cost accounting system and suggest improvements if needed.
- Additionally, the auditor reviews the internal controls related to expense accounting to identify any weaknesses in the system.
Financial Position In Cost Audit Report
- The part in a financial status section of a cost review does a deep evaluation of how well a company is doing money-wise. It can have details about how much money the company made, its financial statement, and cash flow statement.
- An examiner looks really closely at the company's money records to find any trends or worrying areas.
- Additionally, the examiner might compare how well the company is doing financially with other companies in the same field to see if it's doing better or worse.
- This part tries to fairly judge the company's financial growth and find areas that could be better.
Contents of Cost Audit Report
A cost audit report comprises the following key components:
- Introduction: This section offers a concise overview of the audit's scope and objectives.
- Methodology: Here, the audit approach and data gathering methods are detailed.
- Cost Structure Analysis: This part involves scrutinizing the company's cost structure to pinpoint areas for enhancement.
- Cost Control Recommendations: Recommendations are provided here for implementing cost control measures to refine the company's cost structure.
- Compliance Assessment: This segment evaluates the company's adherence to pertinent regulations and standards.
- Financial Analysis: It furnishes a financial evaluation of the company's performance and profitability.
- Conclusion and Recommendations: This section summarizes the audit findings and offers suggestions for future enhancements.
- Annexure: This part includes supporting data and documentation, such as financial statements and cost accounting records.
Conclusion
Cost audit has gained significant importance in a company's financial management due to current auditing trends. In today's fast-paced business environment and with advancing technology, analyzing expenses is crucial for ensuring an objective and precise evaluation of a company's financial performance. Auditors meticulously examine a company's financial records, comparing them with industry benchmarks to identify areas for improvement and assist companies in making well-informed decisions about their financial future.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Cost Audit - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is the meaning of Cost Audit? |  |
| 2. Why is Cost Audit important? |  |
| 3. What are the features of Cost Audit? |  |
| 4. What are the objectives of Cost Audit? |  |
| 5. Who is required to do a Cost Audit? |  |















