Coulomb's Law, Superposition Principle & Gauss's Law | Electricity & Magnetism - Physics PDF Download
Coulomb’s Law and Superposition Principle
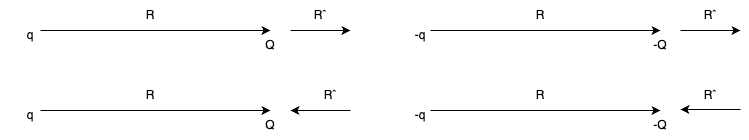
The electric force on a test charge Q due to a single point charge q , which is at rest and a distance R apart is given by Coulomb’s law:
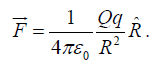
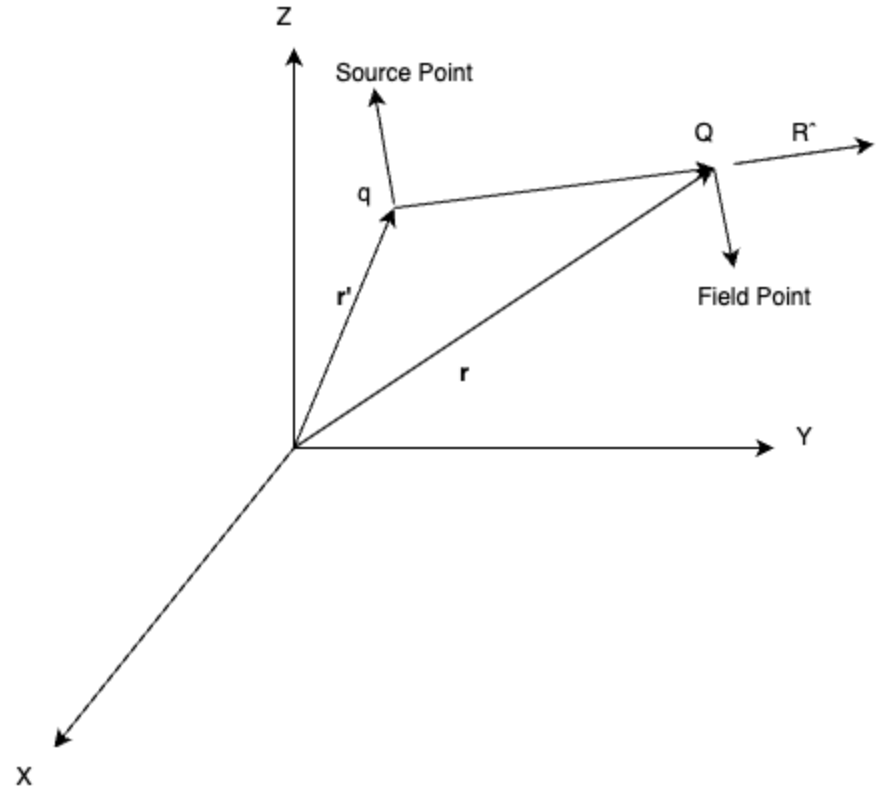 Coulomb's Law in Vector Form
Coulomb's Law in Vector Form
The constant ε0 is called the permittivity of free space.
In mks units,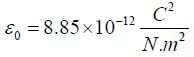
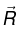 is the separation vector from
is the separation vector from 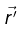 (the location of q ) to
(the location of q ) to 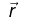 (the location of Q):
(the location of Q):
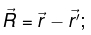
R is its magnitude, and 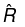 is its direction. The force points along the line from q to Q; it is repulsive if q and Q have the same sign, and attractive if their signs are opposite.
is its direction. The force points along the line from q to Q; it is repulsive if q and Q have the same sign, and attractive if their signs are opposite.
Electric Field
If we have many point charges q1,q2,...... at distances R1, R2, R3 ...... from test charge Q, then according to the principle of superposition the total force on Q is
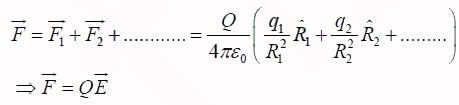
where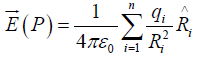
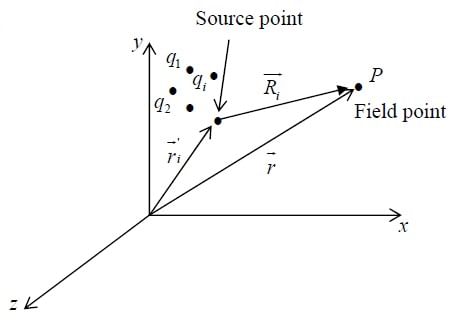
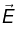 is called the electric field of the source charges. Physically
is called the electric field of the source charges. Physically 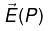 is the force per unit charge that would be exerted on a test charge placed at P .
is the force per unit charge that would be exerted on a test charge placed at P .
If charge is distributed continuously over some region, then
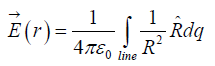
The electric field of a line charge is(dq = λ dl′)
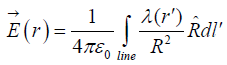 where λ is charge per unit length.
where λ is charge per unit length.
For surface charge (dq =σ da′)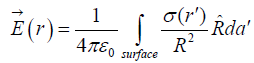
where σ is charge per unit area.
For a volume charge (dq = ρdτ′)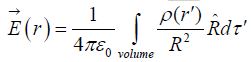
where ρ is charge per unit volume.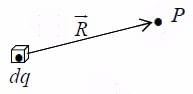 (a) Continuous distribution
(a) Continuous distribution
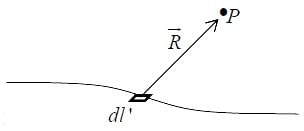 (b)Line charge, λ
(b)Line charge, λ
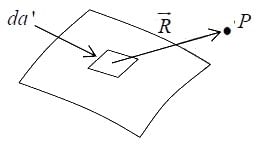 (c)Surface charge, σ
(c)Surface charge, σ
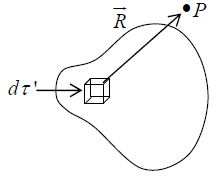 (d)Volume charge, ρ
(d)Volume charge, ρ
Example 1: (a) Find the Electric a distance z above the mid point between two equal charges, q , a distance d apart.
(b) Repeat part (a) after replacing right hand charge to −q .
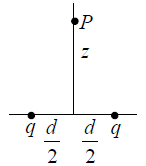
(a)
Horizontal components cancels andEz = E1 cosθ + E2 cosθ = 2E1 cos θ
Since
When,(looks like a single charge 2q ).
(b)
Component along z-direction cancel out.
Thus,
When,
Example 2: Find the electric field a distance z above the midpoint of a straight line segment of length 2L , which carries a uniform line charge λ.
Horizontal components of two field cancels and the field of the two segment is
Net field is
Here
Thus
for
and when
Example 3: Find the electric field a distance z above the center of a circular loop of radius r , which carries a uniform line charge λ .
“Horizontal” components cancel, leaving:
Here, r2 = R2 + z2, cos θ =z/r (both constants)
Gauss’s Law
Field Lines and Electric Flux
Consider that a point charge q is situated at the origin: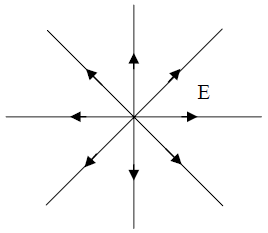
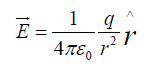
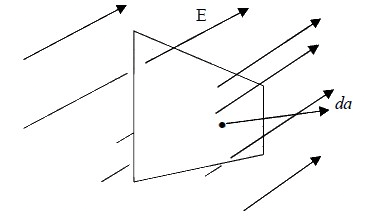
This field is depicted by the field line displayed in the figure below. The strength of the field is denoted by the density of the field lines: it is more intense near the center where the lines are closely packed, and less intense farther out where they are more spaced apart. The field strength (E) is directly proportional to the number of field lines per unit area (area perpendicular to the lines). The flux of E through a surface S, 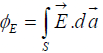 is a measure of the “number of field lines” passing through S.
is a measure of the “number of field lines” passing through S.
For the case of point charge at the origin, the flux of 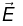 through a sphere of radius r is
through a sphere of radius r is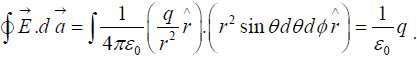
Note that, any surface whatever its shape, would trap the same number of field lines. So the flux through any surface enclosing the charge is q/ε0.
Now suppose that instead of a single charge at the origin, we have a bunch of charges scattered about. According to the principle of superposition, the total field is simply the (vector) sum of all the individual fields: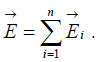
The flux through any surface that encloses them all, then, is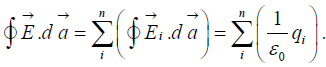
A charge outside the surface would contribute nothing to the total flux, since its field lines
go in one side and out the other. It follows, then, that for any closed surface,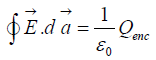
where Qenc is the total charge enclosed within the surface. This is Gauss’s law in integral form. We can convert Gauss’s law in integral form to differential form, for continuous charge
distributions, by applying the divergence theorem: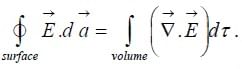
We can write Qenc in terms of the charge density ρ, we have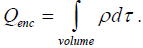
So Gauss’s law becomes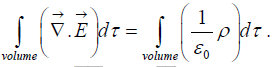
Since this holds for any volume, the integrands must be equal: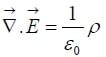
Applications of Gauss’s Law
Gauss's law is universally valid, but its utility is limited to specific symmetrical scenarios:1. Spherical Symmetry: Utilize a concentric sphere as your Gaussian surface.
2. Cylindrical Symmetry: Employ a coaxial cylinder as your Gaussian surface.
3. Plane Symmetry: Opt for a "pillbox" shape for your Gaussian surface, extending equally above and below the surface.
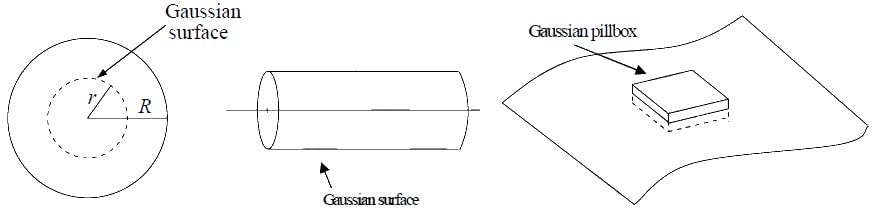
Example 4: Find the field inside and outside a uniformly charged solid sphere of radius R and total charge q.
Draw a spherical surface of radius r < R , which is called as “Gaussian surface”. According Gauss’s Law
For outside point, draw a spherical surface of radius r > R,
Example 5: A long cylinder carries a charge density that is proportional to the distance from the axis; ρ = kr , for some constant k . Find the electric field inside this cylinder.
Draw a Gaussian cylinder of length l and radius r .
For this surface, Gauss’s Law states:
Now,Symmetry dictates that
must point radially outward and the two ends contribute nothing to electric flux as
For curved portion
Example 6: Find the electric field a distance r from an infinitely long straight wire, which carries a uniform line charge λ .
Draw a Gaussian cylinder of length l and radius r .
For this surface, Gauss’s Law state:
Example 7: An infinite plane carries a uniform surface charge σ . Find its electric field.
Draw a “Gaussian pill box”, extending equal distances above and below the plane.
Apply Gauss’s Law to this surface:
In this case, Qenc = Aσ, where A is the area of the pill box. By symmetry,points away from the plane (upward for the points above, downward for points below).
Thuswhereas sides contribute nothing. Thus

whereis the unit vector pointing away from the surface
Example 8: Suppose the electric field in some region is found to be 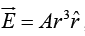 in spherical coordinates ( A is some constant).
in spherical coordinates ( A is some constant).
(a) Find the charge density ρ .
(b) Find the total charge contained in a sphere of radius R , centered at the origin.
(a)
(b) By Gauss's Law,

Also,
Example 9: A charge q sits at the back corner of a cube as shown in figure. What is the flux of 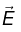 through the shaded side?
through the shaded side?
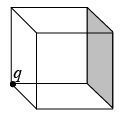
Think of this cube as one of 8 surrounding the charge. Each of the 24 squares which make up the surface of this larger cube gets the same flux as every other one.
|
82 videos|32 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Coulomb's Law, Superposition Principle & Gauss's Law - Electricity & Magnetism - Physics
| 1. What is Coulomb's Law and how is it related to the electric field? |  |
| 2. What is the Superposition Principle in the context of electric charges and forces? |  |
| 3. How does Gauss's Law relate to electric fields and charges? |  |
| 4. Can Coulomb's Law be used to calculate the electric field in all situations? |  |
| 5. How is the Superposition Principle applied in the context of Gauss's Law? |  |





 (looks like a single charge 2q ).
(looks like a single charge 2q ).






















 must point radially outward and the two ends contribute nothing to electric flux as
must point radially outward and the two ends contribute nothing to electric flux as 







 points away from the plane (upward for the points above, downward for points below).
points away from the plane (upward for the points above, downward for points below). whereas sides contribute nothing. Thus
whereas sides contribute nothing. Thus

 is the unit vector pointing away from the surface
is the unit vector pointing away from the surface 























