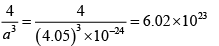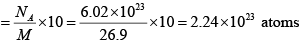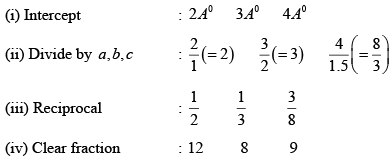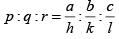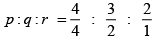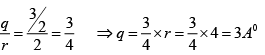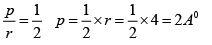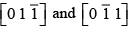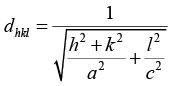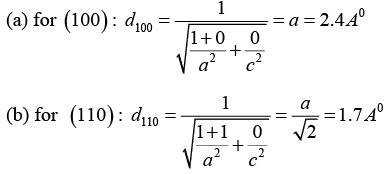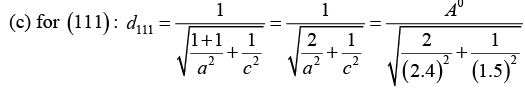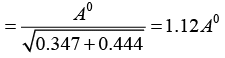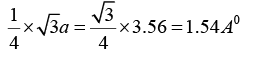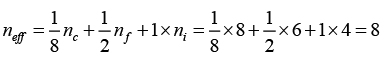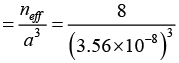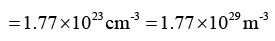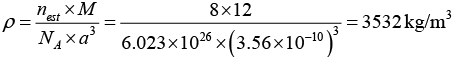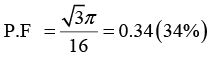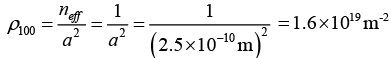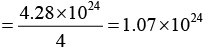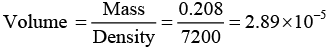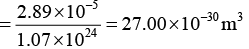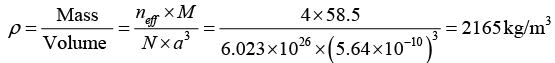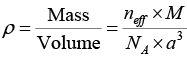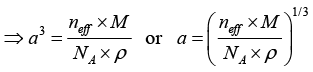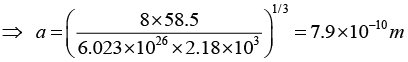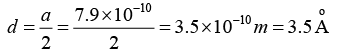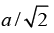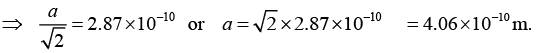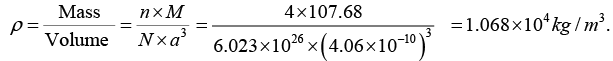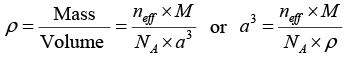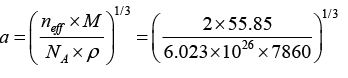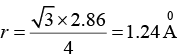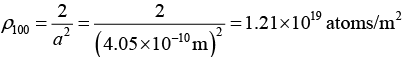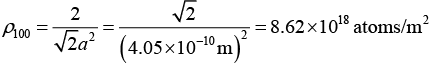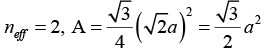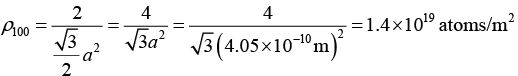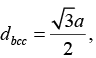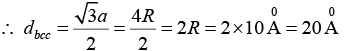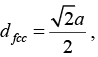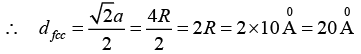Crystal Structure: Assignment | Solid State Physics, Devices & Electronics PDF Download
Q.1. The lattice constant of an Al is 04.05 Å and atomic mass is 26.9 a.m.u. The unit cell structure of Al is face centered cubic (fcc).
(a) How many unit cells are there in an Al foil of 0.1 mm thick and side 20 cm2 ?
(b) If the foil weighs 10 g , than how many atoms are present?
(a) Volume of the foil = 20 x 20 x 0.01 = 4 cm3
Volume of the unit cell = a3
∴ Number of unit cell =
(b) Number of atoms
Q.2. Find the Miller indices of a plane that makes intercept of 4Å,5Å,2Å on the crystallographic axes of an orthorhombic crystal with a : b : c = 2 : 3 : 4.
The lattice parameters are a = 2 Å, b= 3 Å, and c = 4Å
Following the standard procedure of finding the miller indices we have
(i) intercepts are : 4Å,5Å, 2Å
(ii) Divide by lattice constant : 4/2(=2) (5/3) 2/4(=1/2)
(iii) Reciprocal : (1/2) (3/5) 2
(iv) Clear fraction : 5 6 20
Therefore, the required miller indices of the plane is (5 6 20)
Q.3. A plane makes intercept of 2Å, 3Å, 4Å on the co-ordinate axes of a tetragonal crystal with b : c = 1 : 1.5 . Find the Miller indices.
For tetragonal lattice, a = b¹ c
Therefore, lattice parameters are a =b= 1 and c = 3/2
Q.4. Miller indices of a plane is (4 2 1) . If the plane makes intercept of 4Å along the z -axis of an orthorhombic crystal with a : b : c = 4 : 3 : 2 , find the intercept along the x and y-axis.
Given a = 4 Å, b = 3Å, c = 2 Å and (h k l) = (4 2 1)
∴
Now,
And
Therefore, intercept along x - and y- axes are 2 Å and 3 Å
Q.5. Draw the planes 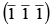 and
and 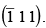 Find the indices of lines common to these two planes.
Find the indices of lines common to these two planes.
The planes
are drawn together as shown in the figure.
The line common to this plane have indices
Q.6. In a tetragonal crystal, the lattice parameters are a = b = 2.4Å and c = 1.5Å. Calculate the interplanar spacing between (a) (1 0 0) planes (ii) (1 1 0) planes and (iii) (1 1 1) planes
Q.7. Diamond crystal structure has the cube edge of 3.56Å, calculate
(a) the distance between the nearest neighbours and
(b) the number of atoms per unit volume
(c) density of the diamond (where atomic mass of carbon is 12 a.m.u.)
(d) packing fraction of the crystal
(a) The nearest neighbour distance = 1/4 x ( diagonal length)
(b) Effective number of atoms in diamond crystal is
Therefore, number of atoms / unit volume
(c)
(d)
Q.8. Calculate the planar density of the plane (1 0 0) in a simple cubic lattice having lattice constant of 2.5Å.
Planer density of the (100 ) plane is
Q.9. An element crystallizes into an fcc structure where, 208 gms of the substance contain 4.28 x 1024 atoms. Calculate the length of the unit cell if its density is 7200 kg /m3.
Given Crystal structure is fcc, so that neff = 4,
Mass of the one mole of the substance = 208 gm= 0.208 kg,
The number of atoms = 4.28 x 1024, ρ = 7200kg /m3, a = ?
We know that the number of atoms in 2.208 kg of materials are (= number of atoms/unit cell ) x number of unit cells
or 4.28 x 1024 = 4 x number of unit cell
or Number of unit cells
Further, Volume of 0.208 kg of materials is
Therefore, volume of the unit cell (a3) = Volume of 0.208 of materials/Number of unit cells in 0.208kg
a = (27 x 10-30)1/3 = 3 x 10-10m = 3Å
Q.10. A unit cell of a NaCl has four formula units. Calculate its density if the side of the unit cell is 5.64 Å.
Given neff = 4, a = 5.64Å = 5.64 x 10-10m,
Molecular Weight of NaCl = 23 + 35.5 = 58.5 amu, ρ = ?
We know that the density of the crystal material is given by
Q.11. Sodium chloride has a fcc structure. Its density is 2.18 x 103 k /m3. The atomic weights of sodium and chlorine are 23amu and 35.5 amu, respectively. Calculate the interatomic separation.
Given, Molecular Weight of is NaCl = 23 + 35.5 = 58.5 amu, and density ρ = 2.18x103 kg/m, neff = 8
Since;
Where, a is the side of the unit cell
Therefore, the interatomic distance
Q.12. The nearest neighbour distance in a silver crystal is 2.87Å. Silver crystallizes in fcc form, determine its density.
Given; Crystal structure is fcc , so that neff = 4,
Nearest neighbour distance = 2.87Å = 2.87 x 10.-10m,
Atomic Weight. of silver = 107.68 amu, ρ= ?
We know that the nearest neighbour distance in fcc crystal is
Now the density of crystal material is given by
Q.13. Calculate the radius of an atom in a -iron belonging to a bcc structure. The density of the α -iron is 7860 kg/m3 and the atomic weight is 55.85 amu.
Given ρ = 7860kg/m3, atomic weight= 55.85 amu,
Structure bcc, so that 2, neff n = r = ?
We know that the density of crystal material is given by
or
a = 2.86 x 10-10m = 2.86Å
Further, in a bcc structure, we have 4r = √3a
Where, r is the radius of the atom
Therefore,
Q.14. Calculate the density of atoms in the (1 0 0) , (1 1 0) and (1 1 1) planes of an fcc aluminum whose lattice parameter is 4.05Å.
Given; Planes are (100) , (110) and (111) , crystal structure is fcc, and lattice constant is a = 4.05Å = 4.05x10-10m
We know that the number density of atoms in a crystal plane is given by
(a) In fcc structure, for plane (100) : neff = 2, A = a2
Therefore,
(b) In fcc structure, for plane (110) : neff = 2, A = √2a2
Therefore,
(c) In fcc structure, for plane (100):
Therefore,
Q.15. Determine the nearest neighbour distance in a bcc and fcc structures when the atomic radius is given as 10Å.
Given Radius of the atom, R = 10Å nearest neighbour distance, say dbcc = ?, dfcc = ?
The nearest neighbour distance in a bcc structure is
Where, a is the side of the cube and √3a = 4R
Similarly, the nearest neighbour distance in an fcc structure is
where a is the side of the cube and √2a = 4R
Q.16. Calculate the packing factor of a sodium chloride structure. The ionic radii of Na+ and Cl- are 0.98Å and 1.81Å, respectively.
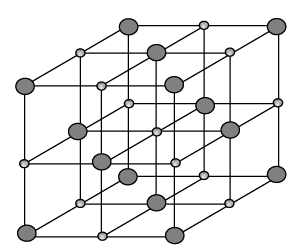
Given the ionic radius of Na+ = 0.98Å, Cl- = 1.81Å, (PF)Nacl = ?
The structure of NaCl is shown in the figure.
The Na+ and Cl- ions touch each other, so that a = 2 (radius of Na+ + radius of Cl-)
= 2 (0.98+ 1.81) = 5.58ÅTherefore, the unit cell volume is V = a3 = (5.58)3(Å)3
Further in the figure, we observe that there are 4 NaCl molecules in the unit cell.
Therefore, according to the definition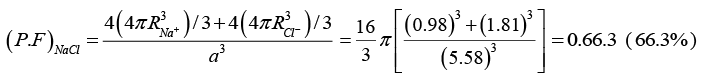
|
91 videos|21 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Crystal Structure: Assignment - Solid State Physics, Devices & Electronics
| 1. What is crystal structure? |  |
| 2. How is crystal structure determined? |  |
| 3. What are unit cells in crystal structures? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of crystal structures? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of studying crystal structures? |  |