DBMS Architecture | Database Management System (DBMS) - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Two Tier Architecture
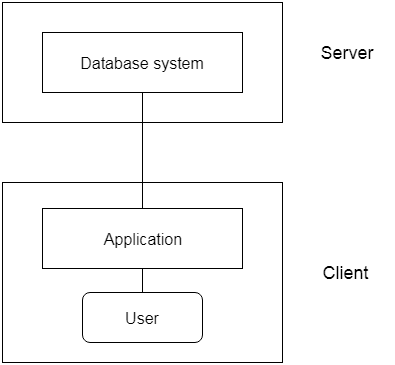
Two tier architecture is similar to a basic client-server model. The application at the client end directly communicates with the database at the server side. API’s like ODBC,JDBC are used for this interaction. The server side is responsible for providing query processing and transaction management functionalities. On the client side, the user interfaces and application programs are run. The application on the client side establishes a connection with the server side in order to communicate with the DBMS.
An advantage of this type is that maintenance and understanding is easier, compatible with existing systems. However this model gives poor performance when there are a large number of users.

Three Tier Architecture
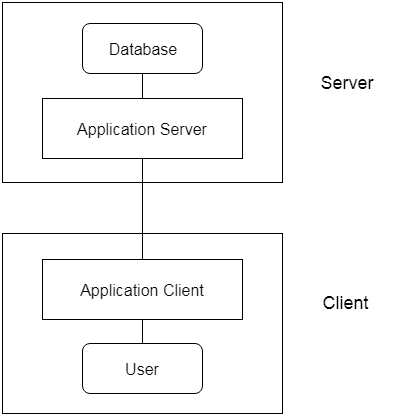
In this type, there is another layer between the client and the server. The client does not directly communicate with the server. Instead, it interacts with an application server which further communicates with the database system and then the query processing and transaction management takes place. This intermediate layer acts as a medium for exchange of partially processed data between server and client. This type of architecture is used in case of large web applications.
1. Advantages- Enhanced scalability due to distributed deployment of application servers. Now, individual connections need not be made between client and server.
- Data Integrity is maintained. Since there is a middle layer between client and server, data corruption can be avoided/removed.
- Security is improved. This type of model prevents direct interaction of the client with the server thereby reducing access to unauthorized data.
Increased complexity of implementation and communication. It becomes difficult for this sort of interaction to take place due to presence of middle layers.
Three-Tier Architecture
DBMS Architecture
- The DBMS design depends upon its architecture. The basic client/server architecture is used to deal with a large number of PCs, web servers, database servers and other components that are connected with networks.
- The client/server architecture consists of many PCs and a workstation which are connected via the network.
- DBMS architecture depends upon how users are connected to the database to get their request done.
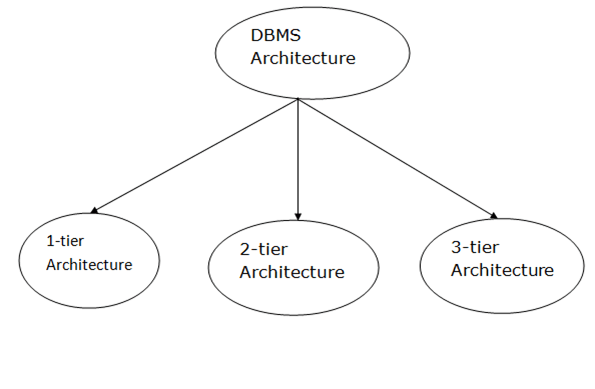
Database architecture can be seen as a single tier or multi-tier. But logically, database architecture is of two types like: 2-tier architecture and 3-tier architecture.
1. 1-Tier Architecture
- In this architecture, the database is directly available to the user. It means the user can directly sit on the DBMS and uses it.
- Any changes done here will directly be done on the database itself. It doesn't provide a handy tool for end users.
- The 1-Tier architecture is used for development of the local application, where programmers can directly communicate with the database for the quick response.
2. 2-Tier Architecture
- The 2-Tier architecture is same as basic client-server. In the two-tier architecture, applications on the client end can directly communicate with the database at the server side. For this interaction, API's like: ODBC, JDBC are used.
- The user interfaces and application programs are run on the client-side.
- The server side is responsible to provide the functionalities like: query processing and transaction management.
- To communicate with the DBMS, client-side application establishes a connection with the server side.
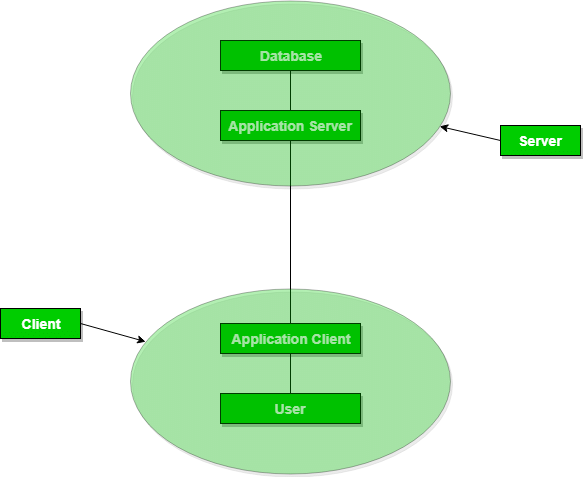
3. 3-Tier Architecture
- The 3-Tier architecture contains another layer between the client and server. In this architecture, client can't directly communicate with the server.
- The application on the client-end interacts with an application server which further communicates with the database system.
- End user has no idea about the existence of the database beyond the application server. The database also has no idea about any other user beyond the application.
- The 3-Tier architecture is used in case of large web application.
|
62 videos|66 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on DBMS Architecture - Database Management System (DBMS) - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is DBMS architecture? |  |
| 2. What are the main components of DBMS architecture? |  |
| 3. What is the role of data models in DBMS architecture? |  |
| 4. How does transaction management work in DBMS architecture? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of user interfaces in DBMS architecture? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|

















