DK Goel Solutions: Provisions and Reserves | DK Goel Solutions - Class 11 Accountancy - Commerce PDF Download
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Define Provisions. Mention three main importance of creating a provision?
Ans: The term ‘Provisions’ refers to the amount retained or written off by way of providing for depreciation, renewals and diminution in the value of assets.
The three main importance of provision are.
- To establish the authentic net profit of a firm
- To determine the true financial status of a company
- To predict future losses in the future
Q2: Mention the differences between the Provisions and Reserves.
Ans: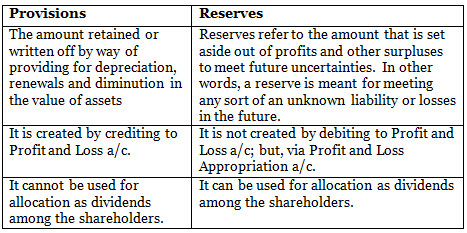
Q3: Distinguish between provision and reserve on the following basis.
(i) Basic Nature
(ii) Purpose
(iii) Effect on taxable profits
(iv) Presentation in Balance Sheet
(v) Elements of Compulsion
(vi) Use of payment of dividend
Ans: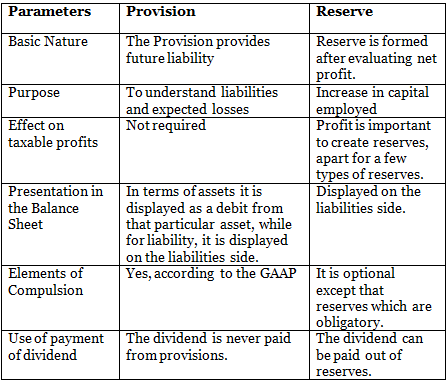
Q4: Differentiate between provision and reserve on the following basis.
(i) Appropriate or charge
(ii) Financial position
(iii) Distribution
Ans: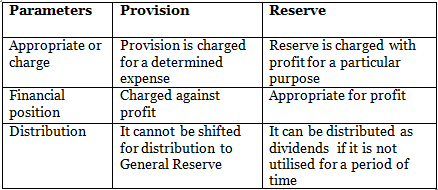
Q5: Give five examples of capital reserves
Ans: The five example of capital reserves are.
- Profit on the redemption of debentures
- Profit on the purchase of an operating business
- Profit on fixed assets sale
- Profit from the reissue of forfeited share
Q6: Distinguish between revenue and capital reserve
Ans: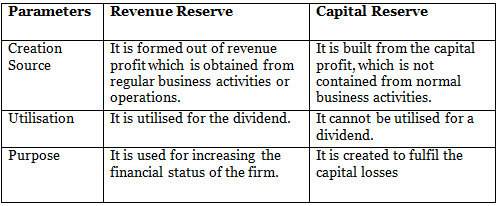
Q7: Define capital reserve.
Ans: A reserve created from the firm’s profit generated from its non-operating activities for a particular period of time is defined as capital reserves.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Give a few examples of provision.
Ans: Few examples of provision are
- Provision for Taxation
- Provision for bad and doubtful debts
- Provision for depreciation of assets
- Provision for discount on debtors
Q2: Define Reserves.
Ans: Reserves refer to the amount that is set aside out of profits and other surpluses to meet future uncertainties. In other words, a reserve is meant for meeting any sort of an unknown liability or losses in the future.
Q3: Give two examples of reserves.
Ans:The two examples of reserves are.
- Dividend Equalization Reserve
- Debenture Redemption Reserves
- Contingency Reserves
- Capital Redemption Reserves
Q4: What is dividend equalisation reserve?
Ans: A reserve generated to support a stable rate of dividend is known as dividend equalisation reserve.
Q5: What is the workmen compensation fund?
Ans: The workmen compensation fund is generated to dispense compensation payable to workers if any accident or unknow event occurs.
Q6: Mention two example of the specific reserve.
Ans: The two example of specific reserves are dividend equalisation reserve and workmen compensation fund.
Q7: Give one difference between general and specific reserve.
Ans:The one difference between general and specific reserve is.
- Any reserve which is not generated for any particular purpose is defined as a general reserve. Whereas, a reserve generated for a specific purpose is defined as a specific reserve.
Q8: Name the reserve that can be used in the distribution of divided.
Ans:The reserve that can be used in the distribution of divided is revenue reserve
Q9: Where will you transfer profit on the sale of a fixed asset?
Ans:The profit on the sale of a fixed asset is defined as capital profit. So, it will be transferred to capital reserve.
FAQs on DK Goel Solutions: Provisions and Reserves - DK Goel Solutions - Class 11 Accountancy - Commerce
| 1. What are the main differences between provisions and reserves in accounting? |  |
| 2. How are provisions treated in financial statements? |  |
| 3. Can reserves be used for any purpose within a company? |  |
| 4. Why is it important for companies to maintain both provisions and reserves? |  |
| 5. How do accounting standards impact the recognition of provisions and reserves? |  |




















