Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Data Collection
Data Collection | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Health and safety in the field |

|
| Data Collection in Fieldwork |

|
| Data Collection Methods |

|
| Environmental Quality Surveys |

|
Health and safety in the field
- Dress appropriately for the weather conditions to stay warm and dry
- Bring sunscreen and a hat if sunny weather is expected
- Always have contact/meeting points, emergency contact numbers, and your school's telephone number readily available
- Check the weather forecast for the area beforehand
- Ensure all mobile phones are fully charged with emergency numbers saved
- Establish designated rendezvous points and emergency contacts
River Safety
- Avoid pushing or engaging in water-related activities
- Exercise caution near river banks, especially on steep or wet terrain
- Wear appropriate footwear and refrain from swimming in the water
Coastal Fieldwork Guidelines
- Check high and low tide times for safety
- Use designated footpaths to access the beach area
- Avoid climbing on groynes or sea defense structures
- Do not handle beach litter without gloves
- Stay at least one meter away from the tide line and pay attention to waves
- Avoid entering the sea under any circumstances
- Maintain visual contact with staff members and stay in pairs or small groups
Town Center Guidelines
- Keep contact numbers for staff and ensure they have your mobile phone number
- Charge your mobile phone and keep it in credit
- Use the map provided to familiarize yourself with the area
- Stay with your group at all times and avoid being alone
- Conceal valuables, especially digital cameras, at your own risk
- Exercise caution when asking for help and avoid duplicating questions within the same area
- Utilize pedestrian crossings where available
Equipment Preparation
- Ensure all equipment is functional and prepare enough for each student/group with spares
- Familiarize yourself with specific equipment and recording sheets
- Practice using equipment in a safe environment before fieldwork
- Check for internet access if using laptops or smartphones and download necessary apps
Data Collection in Fieldwork
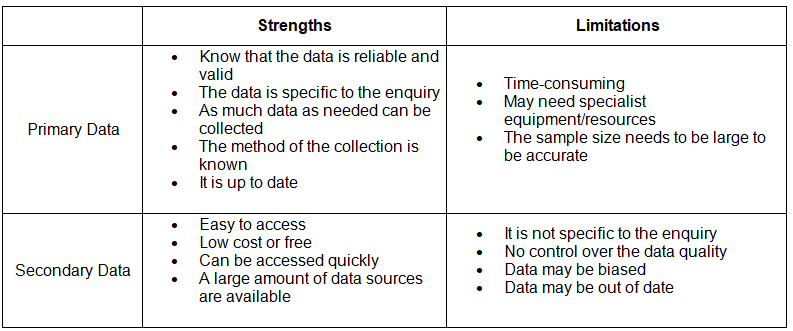
- Data gathered by students during fieldwork constitutes primary data.
- Primary data examples:
- Questionnaire data
- River data (e.g., width, depth)
- Video/audio recordings
- Photographs
- Interview information
- Data collected by others but utilized by students in their investigation is termed secondary data.
- Secondary data examples:
- Census results
- Weather data
- Old photographs
- Maps
- Newspaper articles
- Websites
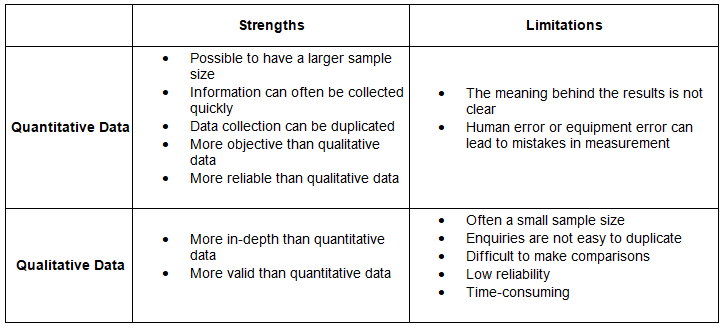
- Quantitative Data:
- Quantitative data pertains to recorded quantities.
- Examples include numerical information gathered from questionnaires, traffic counts, environmental quality surveys, river data (such as velocity and discharge), and weather data.
- Qualitative Data:
- Qualitative data involves descriptive information.
- Examples encompass field sketches, photographs, non-numeric questionnaire responses, and interview answers.
Question for Data CollectionTry yourself: What should you do to ensure your safety during coastal fieldwork?View Solution
Data Collection Methods
- Closed Questions: These types of questions limit respondents to providing specific answers, such as single words, numbers, or a list of options. For instance, "Are you satisfied with the product? (Yes/No)"
- Statements: Statements utilize a scale to measure people's opinions or views on a particular topic. For example, "On a scale of 1 to 5, how satisfied are you with the service provided?"
- Open Questions: In contrast, open questions allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted answers. An example would be "What improvements would you suggest for our services?"
Types of Questioning
- Questionnaires: Questionnaires are effective for gathering a large volume of data from a broad audience. They are structured and can be distributed widely to collect diverse responses.
- Interviews: Interviews involve more in-depth conversations and are typically used to collect detailed information from a smaller sample of participants. Interviewers can probe for elaboration and clarification during the discussion.
Environmental Quality Surveys
- Environmental quality surveys are utilized to evaluate the environmental conditions of various sites.
- These surveys rely on the judgement of the surveyor to assess environmental quality based on a set of indicators.
- Typically, a sliding scale ranging from 1 to 5 or a bipolar scale from -3 to 3 is employed.
- A lower score generally indicates a more negative evaluation of the environmental quality.
- These assessments are subjective as they are based on the surveyor's personal opinion.
- To reduce subjectivity, surveys can be conducted in small groups to establish a consensus on scoring.
- Alternatively, utilizing the mode of Environmental Quality Scores (EQS) from multiple students can enhance objectivity.
- Environmental quality surveys yield quantitative data, offering measurable insights.
The document Data Collection | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
57 videos|70 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Data Collection - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
1. What are some common health and safety risks that fieldworkers may encounter while conducting environmental quality surveys? $#
Ans. Fieldworkers conducting environmental quality surveys may face risks such as exposure to hazardous chemicals, extreme weather conditions, physical injuries from rough terrain, and encounters with wild animals.
2. How can fieldworkers ensure their safety while collecting data in the field? $#
Ans. Fieldworkers can ensure their safety by wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, staying hydrated, following safety protocols, working in pairs or groups, and being aware of their surroundings at all times.
3. What are some data collection methods commonly used in environmental quality surveys? $#
Ans. Common data collection methods in environmental quality surveys include visual inspections, water and soil sampling, air quality monitoring, using sensors and instruments, and conducting interviews with local communities.
4. How important is data accuracy in fieldwork, especially in environmental quality surveys? $#
Ans. Data accuracy is crucial in fieldwork, particularly in environmental quality surveys, as it forms the basis for making informed decisions and policies regarding environmental conservation and protection.
5. What measures can fieldworkers take to ensure the reliability of the data collected during environmental quality surveys? $#
Ans. Fieldworkers can ensure data reliability by calibrating their instruments regularly, following standardized protocols for data collection, cross-checking data with other sources, and maintaining detailed records of the survey methodology.
Ans. Fieldworkers conducting environmental quality surveys may face risks such as exposure to hazardous chemicals, extreme weather conditions, physical injuries from rough terrain, and encounters with wild animals.
2. How can fieldworkers ensure their safety while collecting data in the field? $#
Ans. Fieldworkers can ensure their safety by wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, staying hydrated, following safety protocols, working in pairs or groups, and being aware of their surroundings at all times.
3. What are some data collection methods commonly used in environmental quality surveys? $#
Ans. Common data collection methods in environmental quality surveys include visual inspections, water and soil sampling, air quality monitoring, using sensors and instruments, and conducting interviews with local communities.
4. How important is data accuracy in fieldwork, especially in environmental quality surveys? $#
Ans. Data accuracy is crucial in fieldwork, particularly in environmental quality surveys, as it forms the basis for making informed decisions and policies regarding environmental conservation and protection.
5. What measures can fieldworkers take to ensure the reliability of the data collected during environmental quality surveys? $#
Ans. Fieldworkers can ensure data reliability by calibrating their instruments regularly, following standardized protocols for data collection, cross-checking data with other sources, and maintaining detailed records of the survey methodology.
Related Searches