Data Communication in Computers | Computer Science for Class 7 PDF Download
Introduction
Data Communication is the transmission of coded data between remore terminals and a centralized computer installation or between two or more computer centers over established communication links.Advantages of data communication system:
- Saving of time in data preparation and psical transportation of prepared data.
- Full utilizations of processing power and storage capacity of modern computer.
- Quick retrials of information from files.
- Reducing the cost of data transmissions.
Types of Transmission channel
There are mainly two types of transmission channel.
(i) simplex channel
In this channel transmission of data is always in one direction i.e. after receiving the radio signal from radio-station the receiver cant send back the signal to radio-station. Transmission always flow from A to B.
(ii) Half Duplex
In this channel transmission of data is in both directions, but at any one instant of time it is only in one direction. It means there is flow of transmission from either A to B from B to A one time. Such as telephone line.
(iii) Full Duplex Channel
In this channel transmission of data is in both directions simultaneously. It means there is flow of transmission from A to B and from B to A at aby one instant of time.
Information transfer Speed
Information transfer speed is measured by bit and bud rates. Bit rates indicates the speed of bits transmitted within one second and Buad rate counts the number of times of a transmission change state.
Data communication channel
Data is transmitted from a terminal to a computer system or from a computer system to a terminal over communication channels which are also called communication lines or data links they are of the following:
(i) Standard telephone line
It is widely used as communication channels. It is very efficient useful to the user of data communication because of it is easy to join and the complex network of telephone line has been already established all over the world. It consists of two wire of copper covered with insulator.
(ii) Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable is the kind of copper cable used by cable TV companies between the community antenna and user homes and businesses. Coaxial cable is called “coaxial” because it includes one physical channel that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical channel, both running along the same axis. The outer channel serves as a ground. Many of these cables or pairs of coaxial tubes can be placed in a single outer sheathing and, with repeaters, can carry information for a great distance.
(iii) Microwave transmission
It transmits signals through open space like radio signal. It provides a much faster transmission rate than telephone line or coaxial cable. In this system data transmits on a line of sight path and needs antenna, microwave antennas are usally placed on top of building, towers, hills, and usually placed on top of buildings. Microwave transmission is the transmissionof information or energy by electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths are measured in small numbers of centimetre; these are calledmicrowaves. This part of the radio spectrum ranges across frequencies of roughly 1.0 gigahertz (GHz) to 300 Ghz.

(iv)Satellite communications
In satellite communication, signal transferring between the sender and receiver is done with the help of satellite. In this process, the signal which is basically a beam of modulated microwaves is sent towards the satellite. Then the satellite amplifies the signal and sent it back to the receiver’s antenna present on the earth’s surface. So, all the signal transferring is happening in space. Thus this type of communication is known as space communication Two satellites which are commonly used in satellite communication are Active and passive satellites.

(v) Fiber Optic
Fiber Optic works on the properties of light. When light ray hits at critical angle, it tends to refracts at 90 degree. This property has been used in fiber optic. The core of fiber optic cable is made of high quality glass or plastic. From one end of it light is emitted, it travels through it and at the other end light detector detects light stream and converts it to electric data. Fiber Optic provides the highest mode of speed. It comes in two modes, one is single mode fiber and second is multimode fiber. Single mode fiber can carry a single ray of light whereas multimode is capable of carrying multiple beams of light.
Network
When you have two or more computers connected to each other, you have a network. The purpose of a network is to enable the sharing of files and information between multiple systems. The Internet could be described as a global network of networks. Computer networks can be connected through cables, such as Ethernet cables or phone lines, or wirelessly, using wireless networking cards that send and receive data through the air. It is a combination of hardware and software which provide facility of sending and receiving of information between computers sharing of information between computing devices.Computer network used for several purpose:
- cost reduction by sharing hard- and software resourced.
- high reliability by having multiple sources of supply
- cost reduction by downsizing to microcomputer-based networks instead of using mainframe
- greater flexibility because of possibility to connect devices from various vendors
Some network related terms
Protocol
When computers communicate with each other, there needs to be a common set of rules and instructions that each computer follows. A specific set of communication rules is called a protocol. Because of the many ways computers can communicate with each other, there are many different protocols — too many for the average person to remember. Some examples of these different protocols include PPP, TCP/IP, SLIP, HTTP, and FTP. Can you guess what the last “P” in each acronym stands for? If you guessed “protocol,” send yourself a congratulations e-mail.
Server
As the name implies, a server serves information to computers that connect to it. When users connect to a server, they can access programs, files, and other information from the server. Common servers are Web servers, mail servers, and LAN servers. A single computer can have several different server programs running on it.
Terminals
The word “terminal” comes from early computer systems that were used to send commands to other computers. Terminals often consist of just a keyboard and monitor, with a connection to another computer. The purpose of a terminal is not to process information (like a typical computer), but to send commands to another system. For example, a network administrator may use a terminal to log in to a network and manage devices connected to the network.
Dumb Terminal
Dumb terminal are display and imput devices which don’t process data and input locally instead transmitting input to computer to which it is connected and displaying the resulting output.
Network devices
There are devices to establish a network:-
- Repeaters
- Hub
- Switches
- Rou ters
- Gateway
Types Of Networks
Personal Area Network: A Personal Area Network (PAN) is smallest network which is very personal to a user. This may include Bluetooth enabled devices or infra-red enabled devices. PAN has connectivity range up to 10 meters. PAN may include wireless computer keyboard and mouse, Bluetooth enabled headphones, wireless printers, and TV remotes.
Local Area Network: A computer network spanned inside a building and operated under single administrative system is generally termed as Local Area Network (LAN). Usually, LAN covers an organization offices, schools, colleges or universities. Number of systems connected in LAN may vary from as least as two to as much as 16 million. LAN provides a useful way of sharing the resources between end users. The resources such as printers, file servers, scanners, and internet are easily sharable among computers.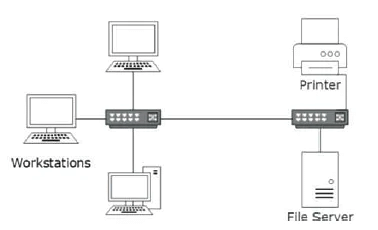
Metropolitan Area Network: The Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) generally expands throughout a city such as cable TV network. It can be in the form of Ethernet, Token-ring, ATM, or Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI). Metro Ethernet is a service which is provided by ISPs. This service enables its users to expand their Local Area Networks. For example, MAN can help an organization to connect all of its offices in a city.
Wide Area Network: As the name suggests, the Wide Area Network (WAN) covers a wide area which may span across provinces and even a whole country. Generally, telecommunication networks are Wide Area Network. These networks provide connectivity to MANs and LANs. Since they are equipped with very high speed backbone, WANs use very expensive network equipment.
Network Topology
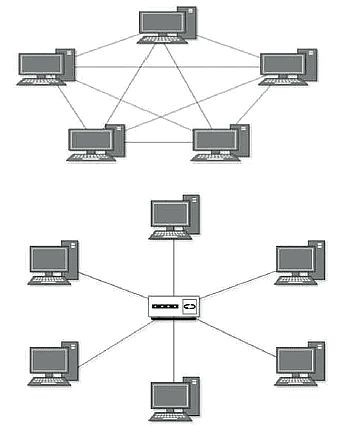
Mesh Topology
In this type of topology, a host is connected to one or multiple hosts . This topology has hosts in point-to-point connection with every other host or may also have hosts which are in point-to-point connection with few hosts only.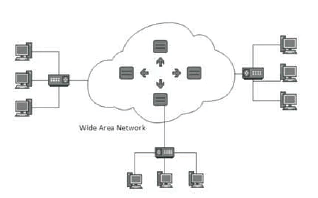
Star Topology
All hosts in Star topology are connected to a central device, known as hub device, using a point-to-point connection. That is, there exists a point to point connection between hosts and hub. The hub device can be any of the following:
- Layer-1 device such as hub or repeater
- Layer-2 device such as switch or bridge
- Layer-3 device such as router or gateway
Ring Topology
In ring topology, each host machine connects to exactly two other machines, creating a circular network structure. When one host tries to communicate or send message to a host which is not adjacent to it, the data travels through all intermediate hosts. To connect one more host in the existing structure, the administrator may need only one more extra cable.

Bus Topology
In case of Bus topology, all devices share single communication line or cable. Bus topology may have problem while multiple hosts sending data at the same time. Therefore, Bus topology either uses CSMA/CD technology or recognizes one host as Bus Master to solve the issue. It is one of the simple forms of networking where a failure of a device does not affect the other devices. But failure of the shared communication line can make all other devices stop functioning.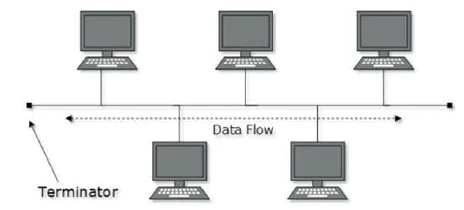
There are three types of modulations
(i) Amplitude modulation
It is a process to change the amplitude of carrier signal according to digital signal having informations.
(ii) frequency modulation
It is a process to change the frequency of carrier signal according to digital signal having ingormations.
(iii) Phase modulation
It is a process to change the phase of carrier signal according to digital signal having informations.
Data Transmissions services
In telecommunication, a public data transmission service is a data transmission service that is established and operated by a telecommunication administration, or a recognized private operating agency, and uses a public data network.
- VSNL (Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited.)
- BSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited.)
- MTNL ( Mahanagar Telecom Nigam Limited)
Various data transmission services
Dial up lines
A dial-up connection uses a modem to connect to an ISP or another computer. It uses standard analog phone lines to transfer data up to 56 Kbps. Before the year 2000, dial-up was the standard way to connect to Internet. However, most users now connect to the Internet is via a DSL or cable modem connection. Both cable and DSL services provide a constant connection and support data transfer speeds over 100 times faster than dial-up modems.
Digital Subscriber line
An asymmetric DSL (ADSL) connection allows download speeds of up to about 1.5 megabits (not megabytes) per second, and upload speeds of 128 kilobits per second. That is why it is called ADSL and not just DSL (because of the asymmetric speeds). There is also a “Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line” (SDSL) which is similar to ADSL, but allows data transfer speeds of 384 Kilobits per second in both directions.
ISDN
Stands for “Integrated Services Digital Network.” No, it’s not the same thing as the ISBN you see in books. ISDN is a data transfer technology, created in 1984, that can transfer data significantly faster than a dial-up modem. ISDN enables wide-bandwidth digital transmission over the public telephone network, which means more data can be sent at one time. A typical ISDN connection can support transfer rates of 64K or 128K of data per second. While these speeds are faster than what you can get with a dial-up modem, the newer DSL technology can support even faster transfer rates and is less costly to set up and maintain.
Internet Security Threats
Virus: It is a program written to attack the normal operation of a Computer, normally which affects the programs associated with the Operating System or Device Driver. Usually it is transmitted through the executable files. Viruses can run only if the affected program is running. These are the most well-known internet security threat.Worms: Similar to viruses but much more dangerous. They spread rapidly by accessing your email address book and automatically forwarding themselves to every address it has.
Trojan: It is a program written to make your Computer unprotected so that hackers can reach the data in your computer. Trojans are self-sufficient programs. These programs give unrestricted access of computers to attackers.
Spyware: It is a software that secretly collects user information while on the internet. Spyware can capture information like web browsing habits, email messages, usernames and passwords, and credit card information.
Adware: This program launches the advertisements in the form of pop ups. Usually the add words are based on the internet behavior of the user.
Spam: These are unwanted emails. In other words we can call them as unsolicited promotional mail.
Phishing: This is acquiring the personal and sensitive information of a person through official looking emails. Users of online banking and e-commerce websites are more prone to this attack.
Pharming: More advance method of Phishing in which the attackers create duplicate or similar looking website of other companies, to attract the customers and steal the data.
Cookies: These are program or information secretly stored in a computer especially the internet browser, which allows other users to monitor the internet activities of a person. These programs usually monitor the browsing nature of person so that the companies can create better marketing strategies.
Mail Bomb: An excessively large email (typically many thousands of messages) or one large message sent to a user’s email account. This is done to crash the system and prevent genuine messages from being received.
Scareware: A common trick cyber criminals use to make users think that their computer has become infected with malware to get them to purchase a fake application. Often the fake application that the user is tricked into purchasing is actually a malicious program which can disable real antivirus software and wreak havoc on a user’s machine.
Sniffers: A software program used to monitor the traffic in a network. The hackers may use the sniffed data to access important confidential data.
Root kit: A program designed to hide objects such as processes, files or Windows registry entries (often including its own). This type of software is not malicious in itself, but is used by hackers to cover their tracks in previously compromised systems. There are types of malware that use root kits to hide their presence on the system.
|
26 docs|14 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
















