Depreciation - (Part - 6) | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Page No 14.53:
Question 26: Astha Engineering Works purchased a machine on 1st July, 2015 for ₹ 1,80,000 and spent ₹ 20,000 on its installation.
On 1st April, 2016, if purchased another machine for ₹ 2,40,000. On 1st October, 2017, the machine purchased on 1st July, 2015 was sold for ₹ 1,45,000 plus CGST and SGST @ 6% each. On 1st January, 2018, another machine was purchased for ₹ 4,00,000 plus IGST @ 12%.
Prepare the Machinery Account for the years ended 31st March, 2016 to 2018 after charging Depreciation @ 10% p.a. by Diminishing Balance Method. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year.
ANSWER: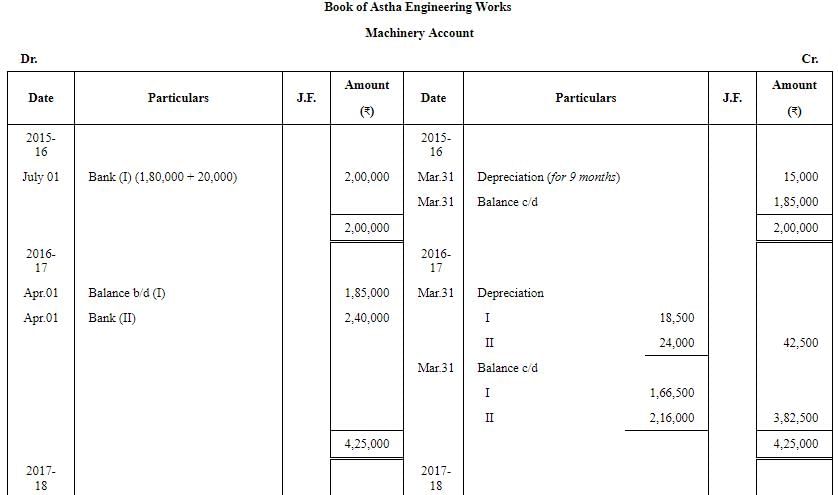
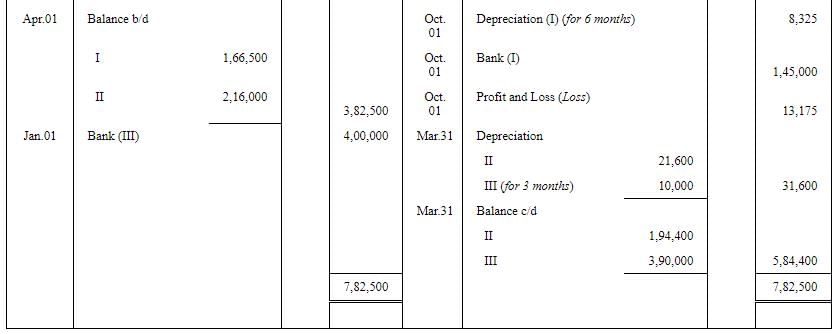 Working Note:
Working Note:
(1) Calculation of profit or loss on sale of Machine I: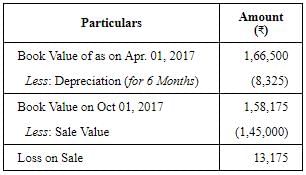
(2) Journal entry for purchase with GST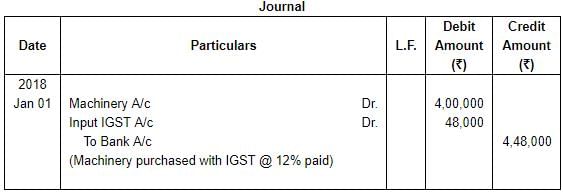
Page No 14.53:
Question 27: Following balances appear in the books of M/s. Amrit as on 1st April, 2018:
On 1st April, 2018, they decided to dispose off a machinery for ₹ 8,400 which was purchased on 1st April, 2014 for ₹ 16,000.
You are required to prepare the Machinery Account, Provision for Depreciation Account and Machinery Disposal Account for the year ended 31st March, 2019. Depreciation was charged at 10% p.a on Cost following Straight Line Method.
ANSWER: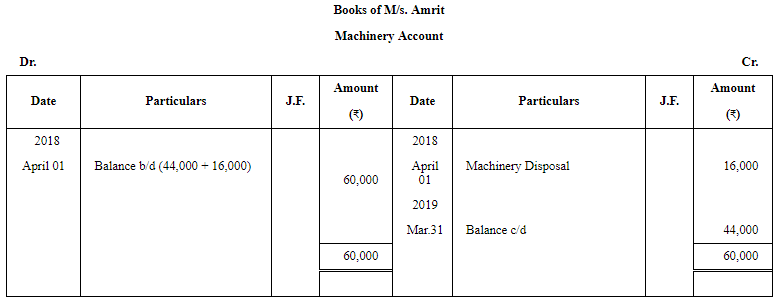
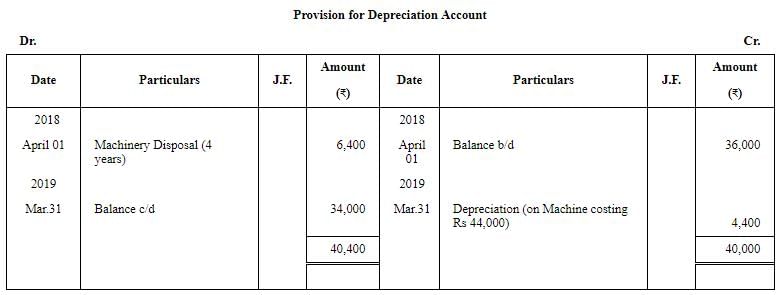
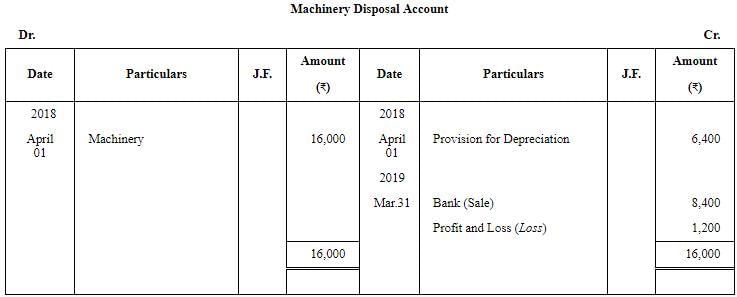
Working Note
1. Calculation of profit or loss on Machine Sold: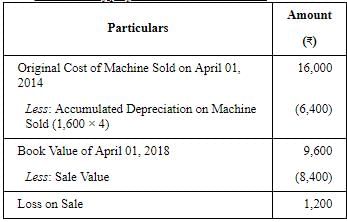
Page No 14.54:
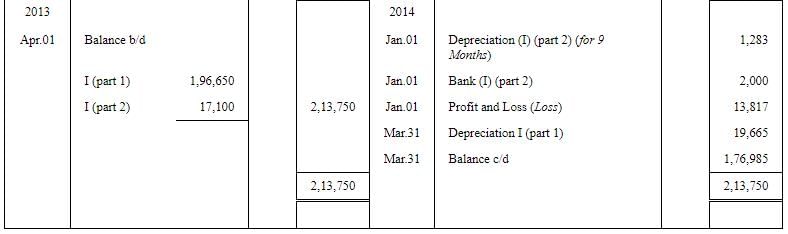
Question 28: On 1st October, 2011, X Ltd. purchased a machinery for ₹ 2,50,000. A part of machinery which was purchased for ₹ 20,000 on 1st October, 2011 became obsolete and was disposed off on 1st January, 2014 (having a book value ₹ 17,100 on 1st April, 2013) for ₹ 2,000. Depreciation is charged @ 10% annually on written down value. Prepare Machinery Disposal Account and also show your workings. The books being closed on 31st March of every year.
ANSWER: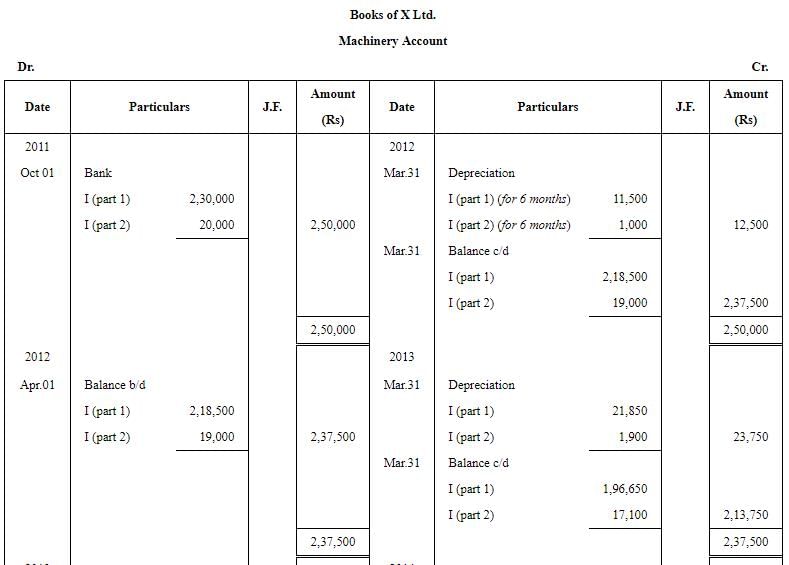
Page No 14.54:
Question 29: Sharma & Co. whose books are closed on 31st March, purchased a machinery for ₹ 1,50,000 on 1st April, 2016, Additional machinery was acquired for ₹ 50,000 on 1st October, 2016. Certain machinery which was purchased for ₹ 50,000 on 1st October, 2016 was sold for ₹ 40,000 on 30th September, 2018.
Prepare the Machinery Account and Accumulated Depreciation Account for all the years up to the year ended 31st March, 2019. Depreciation is charged @ 10% p.a. on Straight Line Method. Also, show the Machinery Disposal Account.
ANSWER: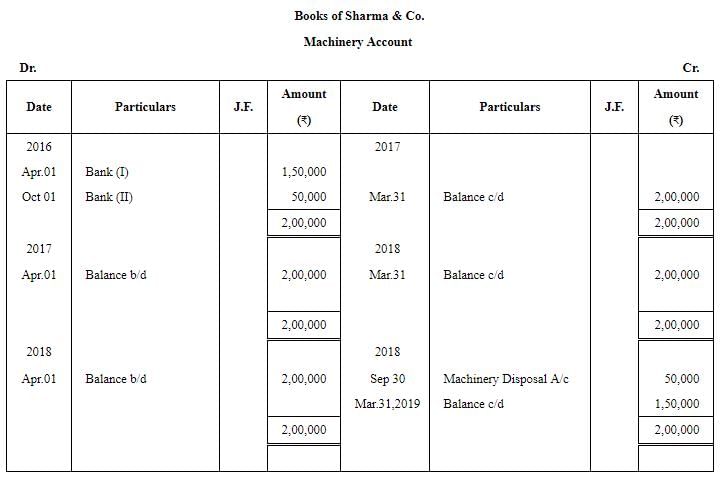
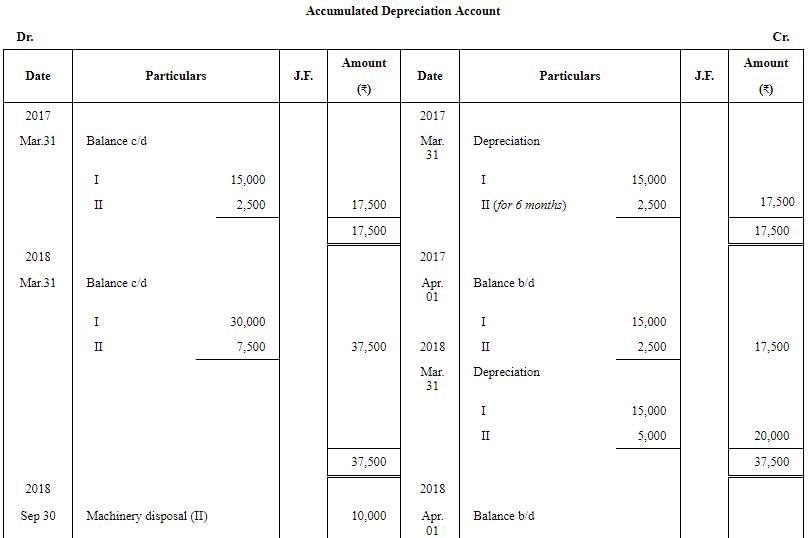
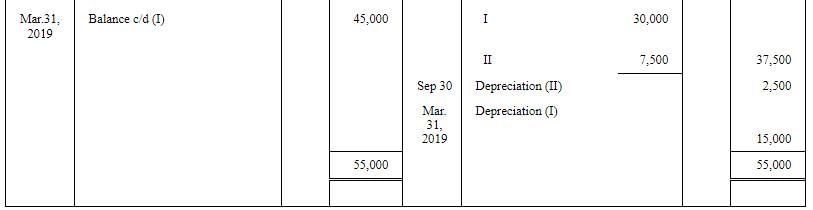
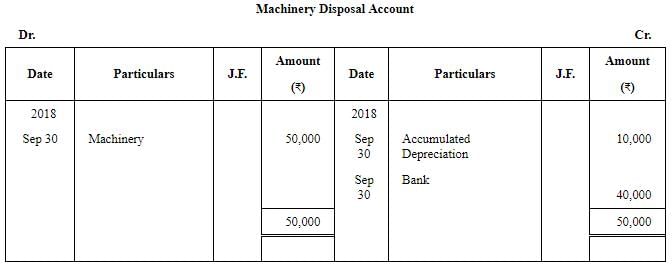
Working note
1. Calculation of Profit or Loss on sale of Machine II: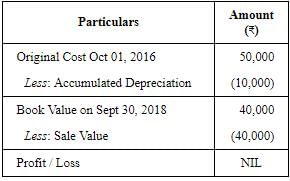
|
64 videos|152 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Depreciation - (Part - 6) - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is depreciation in commerce? |  |
| 2. How is depreciation calculated? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of depreciation in accounting? |  |
| 4. How does depreciation affect financial statements? |  |
| 5. Can depreciation be reversed or reversed? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|

















