Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Mathematics for NDA PDF Download
Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions: The class of inverse functions is very general and as the name suggests, is responsible for doing the opposite of what a function does. For eg- The multiplication function is inverse to the division function. Due to their wide applicability, it is crucial to understand their continuous and differentiable nature over a particular domain.
As a result, the derivatives of inverse functions can be defined. It is also noteworthy that the derivative of the inverse function is algebraically related to the derivative of the original function by the formula: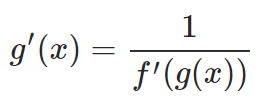
where f(x) and g(x) are inverse to each other.
In this section, we will discuss how to find the derivative of inverse trigonometric functions by the technique of Implicit Differentiation. The same technique can then be easily employed to compute the derivatives of other inverse functions as well.
Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
You must have encountered inverse trigonometric functions when studying trigonometry. Hence, you must know that to avoid ambiguity, their range is restricted to the set of principal values of the specific trigonometric function.
Corresponding to this range, one can then choose a particular domain, which would make the two sets (the domain and the range) one-to-one. It is in this chosen region that we can define the derivative of the function.
Derivative of sin-1x
Let us denote the function as y = sin-1x. We will use Implicit Differentiation to calculate the derivative of this function. Proceed in the following way:
– Remove the inverse from the function:
y = sin−1x ⇔ siny = x
– Write it in the form of the new function:
x = siny,
where the domain of y is restricted to the range of the principal values that the sin-1 function can choose.
– Differentiate the equation on both sides with respect to y:
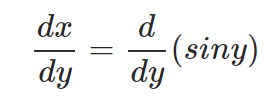
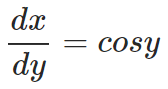
– Using the trigonometric identity, sin2x + cos2x = 1; we get: 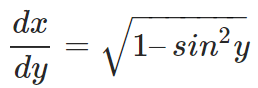
– Use the inverse function to write the equation as:
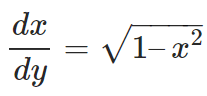
– Now, if you recall; by the reciprocal rule of derivatives we have:
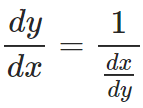
Thus,
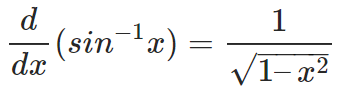
which is the required derivative.
Derivatives of Other Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Similar to the method described for sin-1x, one can calculate all the derivative of inverse trigonometric functions. They are listed out together below. 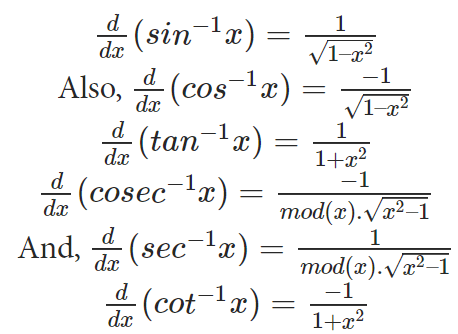
Note:
From the identities on trigonometric functions, you would remember that if only the principal values are being considered, then we have – 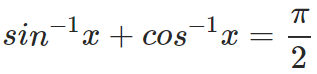
If you differentiate the above equation with respect to x on both sides, you get –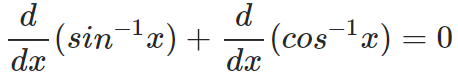
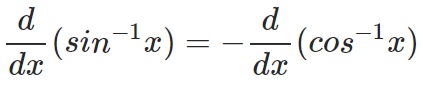
Can you confirm this from the formulae mentioned above? This is thus, a convenient relation to be kept in mind, which also helps you in remembering the formulae better. Similarly, from the other two identities: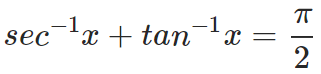
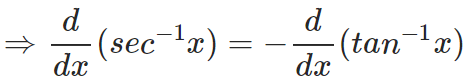 and,
and,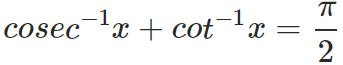
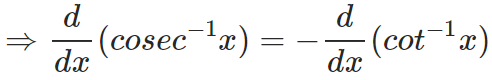 Now let us solve a simple question that invloves the derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions.
Now let us solve a simple question that invloves the derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions.
Solved Examples for You
Question 1: Find the derivative of tan-1(sin-12x).
Answer: We just need to apply the chain rule of differentiation and use the formulae for the derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions directly to solve this problem. Then one can get: 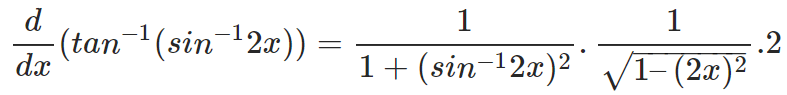
Question 2: What is the inverse of sin?
Answer: The inverse of sin is the arcsin function. However, sine itself will not be invertible since it’s not injective, so it is not bijective (invertible). To attain arcsine function you will have to restrict the domain of sine to [−π2,π2]
Question 3: How do you find the inverse?
Answer: If there is the function f(x) and you want to find the inverse function, f−1(x) f − 1 (x). We will start by replacing f(x) with y. We do this in order to simplify the rest of the procedure. Thus, we will be replacing every x with a y and replacing every y with an x.
Question 4: Why is Secant called Secant?
Answer: Secant is a mathematical term that has been derived from the Latin word ‘secare’. It means to cut. It is the trigonometric function of the cosine. Further, the secant method is a root-finding algorithm in numerical analysis which is on the basis of secant lines to graphs of functions.
Question 5: How do you integrate?
Answer: We make use of an “S” shaped symbol to mean the integral of. Further, we write dx at the end of the terms that are meant to integrate. This means “with respect to x”. Thus, it is the same “dx” that appears in dy/dx. In other words, in order to integrate a term, you need to increase its power by 1 and divide by this figure.
|
276 videos|265 docs|221 tests
|
FAQs on Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions - Mathematics for NDA
| 1. What are the inverse trigonometric functions? |  |
| 2. How do you differentiate the inverse trigonometric functions? |  |
| 3. Can you provide an example of finding the derivative of an inverse trigonometric function? |  |
| 4. What is the range of the inverse trigonometric functions? |  |
| 5. How are the derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions used in real-life applications? |  |
















