Class 9 Geography Chapter 6 Notes - Population
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Population Size and Distribution |

|
| Population Growth and Processes of Population Change |

|
| Conclusion |

|
| Difficult Words |

|
Introduction
The people are crucial for the development of the economy and society. They make and use resources and are themselves resources with varying qualities.
- For example, coal was merely a piece of rock until people invented technology to obtain and make it a valuable resource.
- Hence, the population is the pivotal element in social studies, serving as the point of reference from which all other elements are observed and derive significance and meaning.
- The numbers, distribution, growth, and characteristics of the population provide the basic background for understanding and appreciating all aspects of the environment.
- Human beings are both producers and consumers of the earth’s resources.
- Therefore, it is important to know how many people are in a country, where they live, how and why their numbers are increasing, and their characteristics.

Three major aspects of the population are of primary concern:
- Population size and distribution: How many people are there and where are they located?
- Population growth and processes of population change: How has the population grown and changed through time?
- Characteristics or qualities of the population: What are their age, sex-composition literacy levels, occupational structure and health conditions?
Census: A census is an official enumeration of the population done periodically. In India, the first census was held in 1872. The first complete census however was taken in the year 1881. Since then, censuses have been held regularly every tenth year. The Indian census is the most comprehensive source of demographic, social and economic data.
Population Size and Distribution
India’s Population Size and Distribution by Numbers
- India’s Population Size: As of March 2011, India's population was 1,210.6 million, accounting for over 17% of the world's population.
- Geographical Distribution: India covers an area of 3.28 million square km, which is 2.4% of the world's total area.
- Most Populous States:
- Uttar Pradesh is the most populous state with a population of 199 million, making up about 16% of India's population.
- Almost half of India's population lives in just five states: Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal, and Andhra Pradesh. - Least Populous States
- Sikkim has a population of approximately 0.6 million.
- Lakshadweep has a population of 64,429.
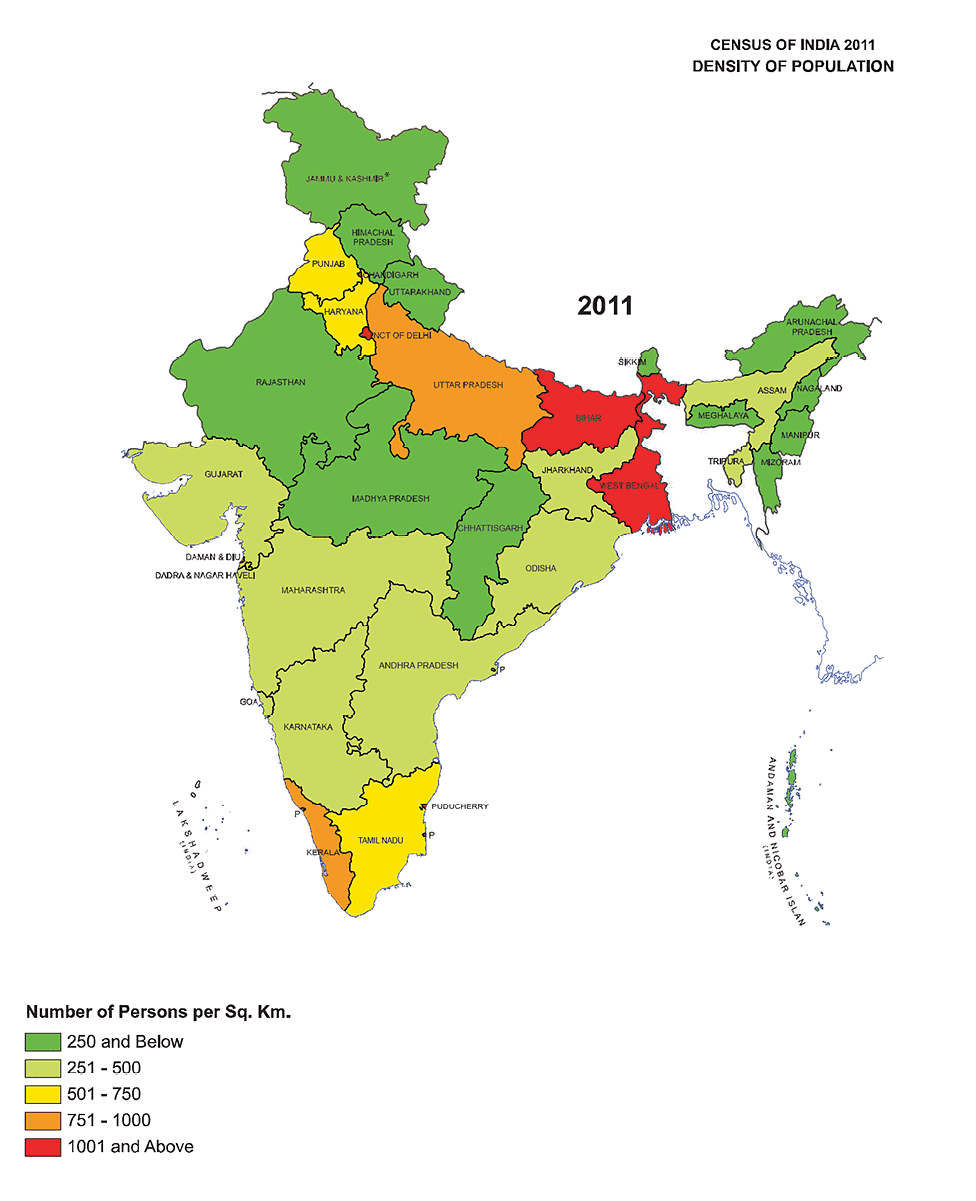
Indian’s Population Distribution by Density
Population density is calculated as the number of persons per unit area. India is one of the most densely populated countries in the world. The population density of India in the year 2011 was 328 persons per sq. km. densities vary from 1,102 persons per sq. km in West Bengal to only 17 persons per sq km in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Low Density: The states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttaranchal, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Tripura, Meghalaya, Rajasthan And Madhya Pradesh Have Very Low Population Density. Rugged terrain and unfavorable climatic conditions are mainly responsible for the sparse population in these areas.
- Moderate Density: The bulk of the peninsula blocks and Assam have a moderate density of population. The distribution of population is influenced here by the rocky nature of the terrain, low to moderate rain, and shallow and less fertile soil.
- High density: The Northern Plains, Tamil Nadu and Kerala have a high to very high density of population because of the plain terrain, rice and fertile soil, abundant rainfall and moderate climate.
Population Growth and Processes of Population Change
The population is a dynamic phenomenon. The numbers, distribution and composition of the population are constantly changing. This is the influence of the three processes, namely – births, deaths and migrations.
Population Growth
Population growth refers to the change in the number of inhabitants over a specific period, such as a decade.
- It can be expressed in absolute numbers (magnitude of increase) or as a percentage change per year (annual growth rate).
- Absolute Increase: Absolute increase is calculated by subtracting the earlier population figure from the later figure (e.g., population in 2001 from 2011).
Example: India's population increased from 361 million in 1951 to 1210 million in 2011. - Annual Growth Rate: The annual growth rate is expressed as a percentage and represents the rate of increase per year (e.g., a 2% growth rate means an addition of two people for every 100 in the base population).
- Historical Trends:
- From 1951 to 1981, India experienced a steady increase in the annual rate of population growth, with the population rising from 361 million to 683 million.
- Since 1981, the growth rate has been gradually declining, largely due to a decrease in birth rates.
- Despite this decline, the 1990s saw an addition of 182 million people, reflecting a high absolute increase. - Current Situation:
- India's large population means that even a low annual growth rate results in a substantial absolute increase.
- As of 2023, India has overtaken China to become the most populous country in the world.
- The large annual increase continues to challenge efforts to conserve resources and protect the environment.

Processes of Population Change / Growth
There are three main processes of population change. They are:
(i) Birth rates
(ii) Death rates and
(iii) Migration
The natural increase in population is the difference between birth rates and death rates.
1. Birth rate: Birth rate indicates the number of births in a country during a year per 1,000 population.
2. Death rate:
- Death rate indicates the number of deaths in a country during a year per 1,000 population.
- The main cause of the rapid rate of growth of the Indian population is the fast decline in death rates.
- Since 1980, birth rates have started declining gradually, resulting in a gradual decline in the rate of population growth.
The reasons for this trend are:
(i) Most people, especially in urban areas, have adopted the two-child norm.
(ii) The birth rate has also declined at a faster rate.
(iii) Standard of living has increased considerably.
(iv) Women folk are more conscious of their health.
(v) Family Welfare Schemes are being adopted in a big way.
(vi) The Muslim population is also trying to keep their family small.
3. Migration
Migration means the movement of people across regions and territories.

- Migration can be internal or international.
- In India, most migrations have been from rural to urban areas because of the ‘push’ factor in rural areas.
- These are adverse conditions of poverty and unemployment in the rural areas and the ‘pull’ of the city in terms of increased employment opportunities and better living conditions.
- Migration is an important determinant of population change.
- It changes not only the population size but also the population composition of urban and rural populations in terms of age and sex composition.
- In India, the rural-urban migration has resulted in a steady increase in the percentage of the population in cities and towns.
- The urban population increased from 17.29 percent of the total population in 1951 to 31.80 percent in 2011.
- There has been a significant increase in the number of ‘million-plus cities’ from 35 to 53 in just one decade, i.e. 2001 to 2011.
Adolescent Population
- The most significant feature of the Indian population is the size of its adolescent population.
- It constitutes one-fifth of the total population of India.
- Adolescents are generally grouped in the age group of 10 to 19 years.
- They are the most important resource for the future.
- The nutrition requirements of adolescents are higher than those of a normal child or adult.
- Poor nutrition can lead to deficiency and stunted growth.
- The diet available to adolescents is inadequate in all nutrients.
- A large number of adolescent girls suffer from anemia.
- Their problems have so far not received adequate attention in the process of development.
National Population Policy
Recognizing that the planning of families would improve health and welfare, the Government of India initiated the comprehensive Family Planning Programme in 1952. The Family Welfare Programme has sought to promote responsible and planned parenthood on a voluntary basis.
 Major features of NPP 2000:
Major features of NPP 2000:
- The NPP 200 provides a policy framework for imparting free and compulsory school education to children up to 14 years of age.
- It aims to reduce infant mortality to below 30 per 1000 live births. Another aim is to achieve universal immunization of children against all vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Promotion of delayed marriage for girls.
- It also aims at making family welfare a people-centred programme.
Conclusion
This chapter underscores the significance of understanding population dynamics to comprehend the broader socio-economic and environmental context. Population growth, distribution, and density are key indicators of a nation's development and influence resource utilization and policy-making. The chapter highlights the interdependence between population characteristics and various factors such as health, education, and employment. Recognizing these aspects enables us to appreciate the challenges and opportunities that come with managing a growing population. Ultimately, informed population management is crucial for sustainable development and improving the quality of life for all.
Difficult Words
- Population Dynamics - The study of how and why populations change in size and structure over time.
- Socio-economic - Relating to or concerned with the interaction of social and economic factors.
- Environmental Context - The conditions or surroundings in which an organism, system, or process operates.
- Population Growth - The increase in the number of individuals in a population.
- Distribution - How something is shared among a group or spread over an area.
- Density - The number of people living per unit of an area (e.g., per square kilometre).
- Resource Utilization - The way resources are used or consumed.
- Policy-making - The process of creating laws, regulations, and guidelines.
- Population Characteristics - The attributes or features of a population, such as age, gender, and health status.
- Interdependence - Mutual dependence between things.
- Sustainable Development - Economic development that is conducted without depletion of natural resources.
|
53 videos|437 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 6 Notes - Population
| 1. What factors contribute to population growth? |  |
| 2. How does population size and distribution impact a country's economy? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of processes of population change? |  |
| 4. How does urbanization affect population growth and distribution? |  |
| 5. What are some challenges associated with a rapidly growing population? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















