Class 9 Civics Chapter 1 Notes - What is Democracy? Why Democracy?
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Democracy? |

|
| Features of Democracy |

|
| Why Democracy? |

|
| Broader Meaning of Democracy |

|
| Role of Citizens Played in a Democracy |

|
| Conclusion |

|
| Key Terms |

|
What is Democracy?
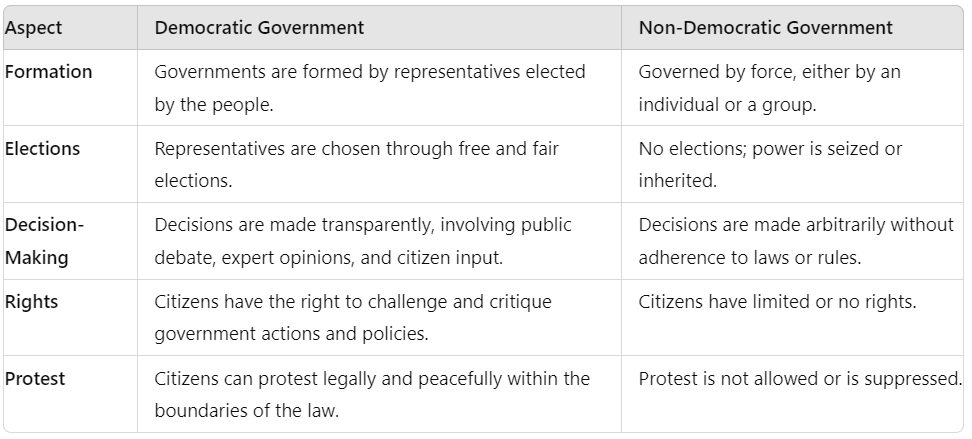
The word ‘Democracy’ has been derived from the Greek word ‘Democratic’. ‘Demos’ means people and ‘Kratia’ means the rule. So, democracy is the rule by the people. Democracy is a form of government where rulers are elected by the people. A key characteristic of all democracies is that the government is chosen through popular elections.

Why define Democracy?
Understanding Differences: Defining democracy helps distinguish it from non-democratic systems. This distinction is crucial for understanding how different governments operate.
- Examples of Non-Democratic Systems:
Myanmar: Rulers were not elected by the people; the military took control, leaving citizens without a say.
Dictatorships: Leaders like Pinochet in Chile were not elected by the public.
Monarchies: Power is typically inherited or seized, rather than elected. The Kings of Saudi Arabia rule not because the people have chosen them to do so but
Here's a table comparing Democratic and Non-Democratic Governments:
A Simple Definition
A simple definition of democracy is : "Democracy is a form of government in which the rulers are elected by the people"
- This basic definition of democracy—"rule by the people"—is insufficient on its own.
- While it highlights the concept of people’s rule, applying this definition without careful consideration could mistakenly classify nearly every government with elections as a democracy. Such an interpretation would be misleading and inaccurate.
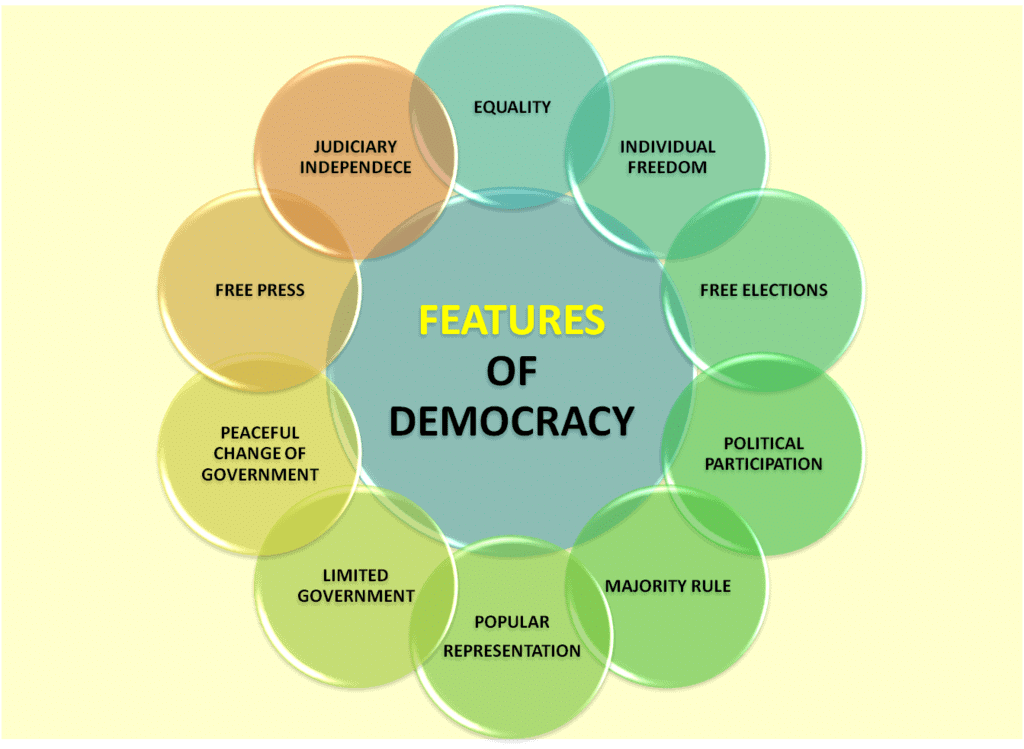
Features of Democracy
The simple definition of democracy gives rise to various questions, which are given below:
Key Questions:
Who are the Rulers?
In a democracy, rulers are those elected by the people.What Constitutes a Democratic Election?
A democratic election is free, fair, and allows all eligible citizens to vote and stand for office.Who Can Elect or Be Elected?
All eligible citizens have the right to vote in elections and can run for office.What Form of Government is Democracy?
Democracy is a form of government where power rests with the people and is exercised through elected representatives.
 To address these questions fully, we need to examine the features of democracy.
To address these questions fully, we need to examine the features of democracy.Major Decisions by Elected Leaders
A democratic government is one in which the people’s representatives participate in the decision-making process. They own collective responsibility for all the decisions taken by the government.
- Dictatorships and Monarchies: Representatives may be elected but lack real decision-making power.
- Case Study: Pakistan: Under General Pervez Musharraf, who came to power through a military coup in October 1999, the real power was held by non-elected leaders, despite the presence of an elected parliament and government.
- This gives us the first feature of democracy. In a democracy, the final decision-making power must rest with those elected by the people.
Free and Fair Electoral Competition
A Democracy must be based on a Free and Fair Election
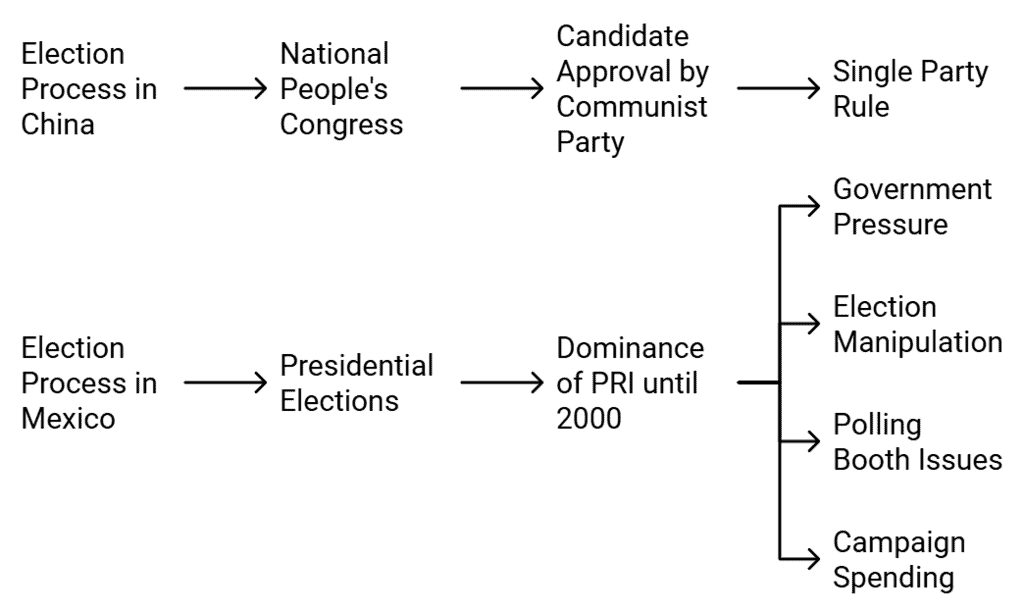
Elections in China:
- Election Process: China holds elections every five years for its parliament, the National People's Congress.
- Power and Membership: The National People's Congress appoints the President and includes nearly 3000 members, some elected by the army.
- Candidate Approval: Candidates must have the approval of the Chinese Communist Party. In the 2002-03 elections, only members of the Communist Party or allied parties were allowed to run.
- Single Party Rule: The Communist Party always forms the government.
- Historical Impact: The lack of multi-party elections and an independent press in China may have contributed to issues like the 1958-1961 famine.
Elections in Mexico:
- Election History: Since 1930, Mexico has held presidential elections every six years without military or dictatorial rule.
- Democratic Shortcomings: Despite regular elections, Mexico was not truly democratic until 2000.
- Dominance of PRI:Until 2000, the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) won every election. PRI employed various tactics to ensure victory:
- Government Pressure: Government employees were required to attend PRI meetings.
- Election Manipulation: Teachers pressured parents to vote for PRI, and media largely ignored or criticized opposition parties.
- Polling Booth Issues: Polling booths were sometimes moved last minute, complicating voting for many citizens.
- Campaign Spending: PRI spent significant amounts on campaign efforts.
 Elections in China vs Elections in Mexico
Elections in China vs Elections in Mexico
Here, we have the second feature of Democracy. Democracy must be based on a free and fair election where those currently in power have a fair chance of losing.
One Person, One Vote, One Value

- A true democracy grants its citizens what is called the ‘universal adult franchise’. it means all adults have a right to vote without any discrimination based on sex, colour, race, caste or class.
- Each person can cast one vote, all votes are counted, and the person who gets the maximum number of votes gets elected in many countries, this is not how the system works.
- There are many instances of denial of equal right to vote
(i) In Saudi Arabia, women do not have the right to vote.
(ii) Estonia has made its citizenship rules in such a way that people belonging to the Russian minority find it difficult to get the right to vote.
(iii) In Fiji, the electoral system is such that the vote of an indigenous Fiji has more value than that of an Indian Fijian. - That gives us the third feature of democracy. In a democracy, each adult citizen must have one vote, and each vote must have one value.
Rule of Law and Respect for Rights
- In Zimbabwe, elections are held regularly but are won by only one party, i.e. Zanu-PF. the party uses unfair practices in elections that are against the principles of democracy.
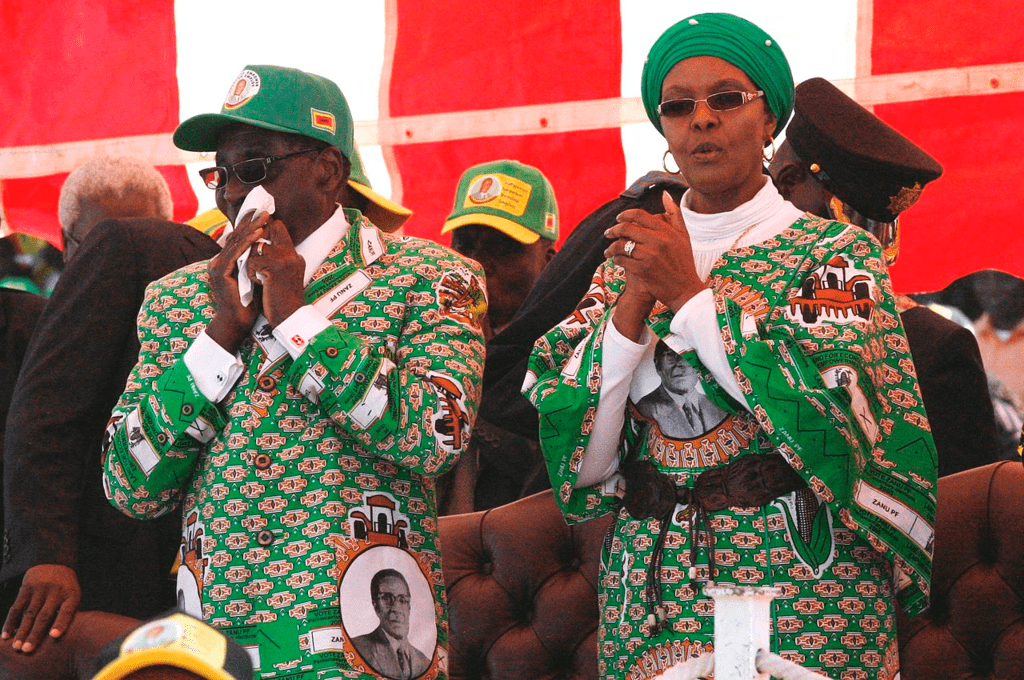

- Robert Mugabe has been ruling Zimbabwe since independence.
- Over the years, President Mugabe has changed the constitution several times to increase the power of the president and make him less accountable.
- In a democracy, people and opposition can criticize the government, but this is not allowed in Zimbabwe.
- The government has ignored some court judgments, which are also against the principles of democracy.
- Television, radio, and press are controlled by the government.
- The example of Zimbabwe shows that popular approval of the rulers is necessary in a democracy, but it is not sufficient. Popular government can be undemocratic. Popular leaders can be autocratic. In a democracy, the state should respect some basic rights of the citizen. They should be free to think, have opinions, express these in public, form associations, protest, and take other political actions.
- Everyone should be equal in the eyes of the law. These rights must be protected by an independent judiciary whose orders are obeyed by everyone. A democratic government cannot do whatever it likes simply because it has won an election. It has to respect some basic rules. In particular, it has to respect some guarantees to minorities. Every major decision has to go through a series of consultations.
- The fourth and final feature of democracy. A democratic government rules within limits set by constitutional law and citizen's rights.
Summary Definition
Democracy is a form of government in which:
- Rulers elected by the people make all the major decisions.
- Elections offer a choice and fair opportunity to the people to change the current rulers.
- This choice and opportunity are available to all people on an equal basis.
- The exercise of this choice leads to a government limited by basic rules of the constitution and citizens' rights.
Why Democracy?
Debating Merits of Democracy
- A democratic government is a better government because it is a more accountable form of government.
- Democracy improves the quality of decision-making.
- Democracy provides a method to deal with differences and conflicts.
- Democracy enhances the dignity of citizens.
- Democracy allows us to correct our own mistakes.
Arguments Against Democracy
- Leaders keep changing in a democracy. This leads to instability.
- Democracy is all about political competition and power play. There is no scope for morality.
- So many people have to be consulted in a democracy, and this leads to delays.
- Elected leaders do not know the best interests of the people. It leads to bad decisions.
- Democracy leads to corruption, for it is based on electoral competition.
- Ordinary people do not know what is good for them; they should not decide anything.
Arguments for Democracy
- A democratic government is a better government because it is a more accountable form of government.
- Democracy provides a method for the quality of decision-making.
- Democracy provides a method to deal with differences and conflicts.
- Democracy enhances the dignity of citizens.
- Democracy is better than other forms of government because it allows us to correct our own mistakes.
- Democracy is considered the best form of government.
Broader Meaning of Democracy
Representative Democracy, its Importance
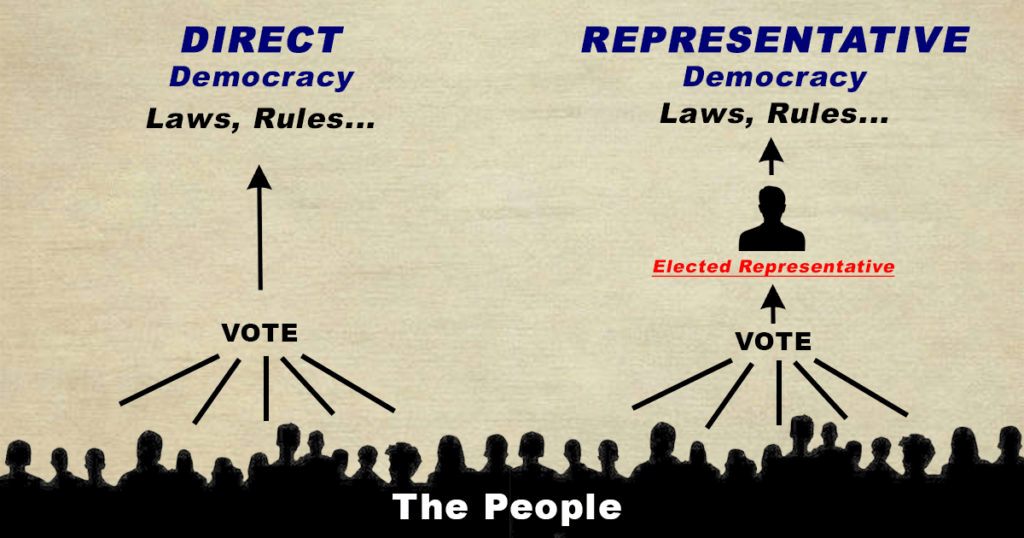
- Representative democracy is one in which people elect their representatives to legislatures. These representatives, in turn, form the government and govern. In this type of democracy, a majority is allowed to make decisions on behalf of all the people.
- Representative democracy becomes necessary because of the following reasons:
(i) Modern Democracies involve such a large number of people that it is physically impossible for them to sit together and make a collective decision.
(ii) Even if they could, the citizens do not have the time, the desire or the skills to take part in all the decisions.
Nominal Democracy and Ideal Democracy
- A nominal democracy, as we normally use the term, refers to a system of governance that is run by the people’s elected representatives.
- An ideal democracy is a broader concept. An ideal democracy is a system in which every citizen must be able to play an equal role in decision-making. For this, one does not need just an equal right to vote.
- Every citizen needs to have equal information, basic education, equal resources and a lot of commitment. There may not be any country in the world that passes this test of democracy. Yet, an understanding of democracy as an ideal reminds us of why we value democracy.
Role of Citizens Played in a Democracy
 Citizens Exercising the Right to Vote
Citizens Exercising the Right to Vote
- Citizens must learn to tolerate the differences and views of all others who disagree with them. That is, the citizens must accept the principle of mutual tolerance and dissent.
- Citizens must act with a sense of discipline and responsibility. They have a right to express their dissent. They must express their grievance through channels provided by the democratic system.
- Citizens must participate and seek to influence public opinion. This can happen only when they are well-informed on civic matters.
- Citizens must exercise their right to vote. This provides a direction to the whole democratic process.
Conclusion
Democracy a Government by Discussion and Persuasion
It is a government by discussion because of the following reasons:(ii) The majority view is respected and given due consideration during discussion.
(iii) The majority view is heard and not shut down by force.
It is a government by persuasion because:
(i) The opposition is encouraged to participate in debates about government policies and programs.
(ii) During the discussion, opponents are persuaded to accept the government's viewpoint.
(iii)At times, the government itself may see merit in what the opposition has to say and accept it.
Key Terms
Universal Adult Franchise: The right of all adult citizens to vote, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or any other restriction, subject to very few exceptions.
Free and Fair Elections: Elections that are conducted impartially, openly, and in accordance with established laws, where all voters are able to vote freely without coercion, and all votes are counted accurately.
Constitutional Law: A body of law that defines the role, powers, and structure of different entities within a state, namely, the executive, the parliament or legislature, and the judiciary, as well as the basic rights of citizens.
Rule of Law: The principle that all people and institutions are subject to and accountable to law that is fairly applied and enforced.
Electoral Competition: The contest between political parties or candidates for electoral power.
Multi-party System: A system of government in which multiple political parties across the political spectrum run for national election, and all have the capacity to gain control of government offices, separately or in coalition.
Nominal Democracy: A form of democracy where although elections take place and representatives are chosen, many characteristics essential to a functional democracy might be missing, like free media, civil liberties, or meaningful choice between candidates.
Ideal Democracy: A theoretical concept of democracy in which all citizens have equal access to power and education, allowing them to participate fully and effectively in the political process.
Representative Democracy: A type of democracy founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to direct democracy, where individuals vote on policy initiatives directly.
Popular Government: A government that is elected by and derives its power from the people, as opposed to being inherited or imposed through force.
Constitutional Limits: Legal limits on the powers of government officials or bodies established in a constitution to prevent abuse of power and to protect citizens' rights.
Opposition Party: A political party that does not form part of the government and is responsible for challenging and providing an alternative to the policies of the government.
Democratic Institutions: Structures, organizations, or mechanisms in a society that work according to democratic processes, like parliaments, local councils, or judicial systems.
Electoral Manipulation: Actions taken by a government or party in power to alter election results or influence the election process in their favour, which can undermine the fairness and free nature of elections.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Civics Chapter 1 Notes - What is Democracy? Why Democracy?
| 1. What are the main features of democracy? |  |
| 2. Why is democracy considered important? |  |
| 3. How can citizens participate in a democracy? |  |
| 4. What is the broader meaning of democracy beyond just elections? |  |
| 5. What role do citizens play in maintaining a democracy? |  |
















