Nervous System Class 5 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Nervous System? |

|
| Brain |

|
| Spinal Cord |

|
| Nerves |

|
| Reflex Actions |

|
| Sense Organs and Their Care |

|
What is Nervous System?
The nervous system manages and organizes the functions of all our body parts. It includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Nerves transmit messages from our senses to the brain, where they're understood and sent to the appropriate body parts. There are three types of nervous systems: the Central Nervous System, Peripheral Nervous System, and Autonomous Nervous System.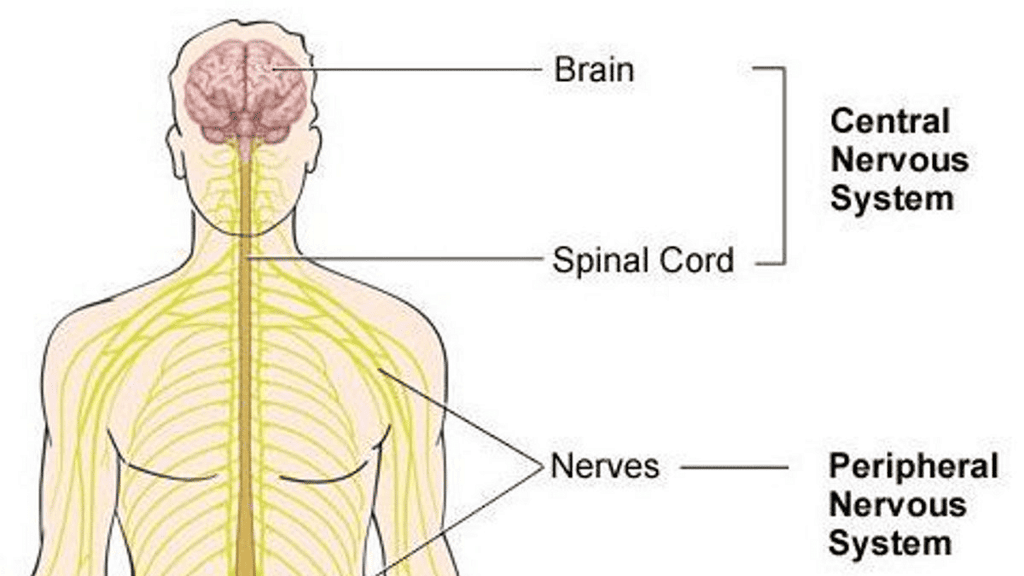 Nervous System
Nervous System
Brain
- The brain is the main organ of the nervous system.
- It is the control centre of our body.
- It sends and receives messages from different parts of the body through the spinal cord and nerves.
 Brain
Brain
- It is protected by a bony closed structure, the skull.
- The space between the brain and the skull is filled with a fluid that acts as a shock absorber.
- The brain's average weight is about 1.5 kg.
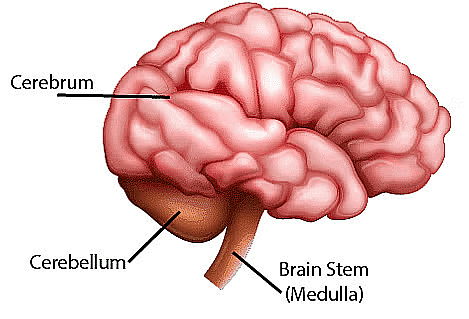
The Parts of Brain
 Parts of Brain
Parts of Brain
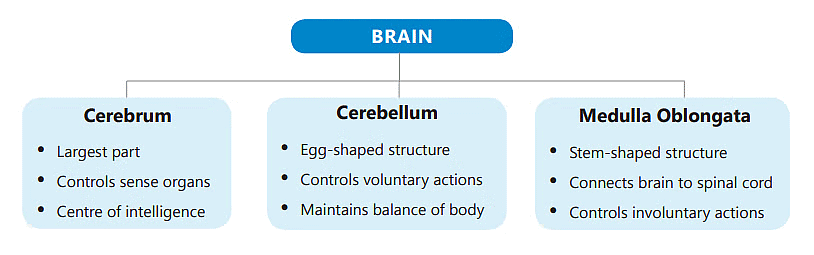
1. Cerebrum
- The cerebrum is the largest and the main part of the brain.
- It has many grooves and folds.
- It controls our sense organs and is the center of intelligence.
- It controls our voice and also helps us to think, learn, remember and recall memories. It also controls our emotions
2. Cerebellum
- The cerebellum is an egg-shaped structure situated below the cerebrum.
- It is the second largest part of the brain, also called the small brain.
- It controls and coordinates the actions of voluntary muscles involved in activities like running, walking, dancing, and standing.
- It also helps in maintaining the balance of our bodies.
3. Medulla Oblongata
- The medulla oblongata is also called the brain stem.
- It is a stem-shaped structure that lies below the cerebrum but in front of the cerebellum.
- It connects the brain to the spinal cord.
- It controls involuntary actions like the lungs' movement in breathing and the heart, etc.
Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord is a long, thick bundle of nerves that extends down from the medulla to the lower end of the backbone.
- It is enclosed in the hard, bony vertebral column.
- Nerves originate from the spinal cord and spread all over the body.
- The spinal cord is responsible for carrying messages between the brain and the rest of the body through nerves.
- It also controls the actions that do not involve the brain. These actions are called reflex actions.
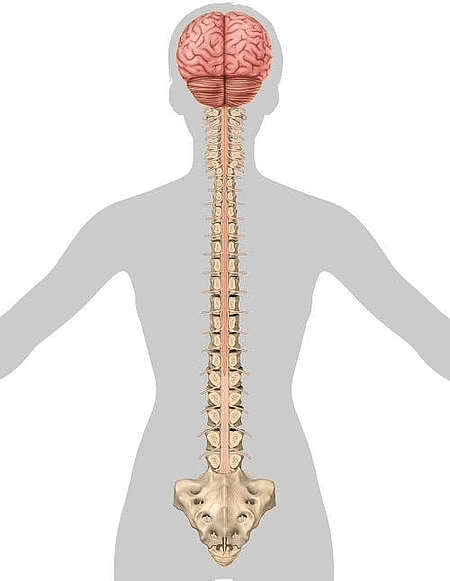 Spinal cord in the human body
Spinal cord in the human body
Nerves
- Nerves are thread-like structures extending from the brain and spinal cord to all body parts.
- Each nerve is composed of bundles of fibers (neurons) through which impulses pass between the brain or other parts.
- The network of nerve cells or neurons runs throughout the body.
- The nerves from the head and the neck join the brain directly, while the nerves from the other parts of the body are connected to the spinal cord.
 Nerves
Nerves
Types of Nerves
1. Sensory Nerves
- These nerves carry messages from the sense organs to the brain or the spinal cord.
- These messages are information about such things as temperature, smell, color or pressure.
2. Motor Nerves
- These nerves send messages from the brain or the spinal cord to the muscles of different organs.
- These are the messages that make the muscles move.
3. Mixed Nerves
- The mixed nerves connect the sensory and motor nerves.
- These nerves work both ways:
They carry messages from the brain or spinal cord to different organs.
They bring messages from the organs to the spinal cord or the brain.
Reflex Actions
- An automatic, quick action that our body makes, often without us even thinking about it, in response to a stimulus is called reflex action.
- Some of our actions are involuntary and cannot be under our control.
- These automatic actions are controlled by the spinal cord without any involvement of the brain.
- The reflex actions are very fast.
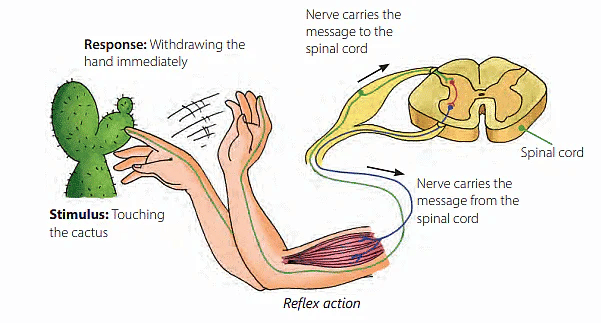 Reflex Actions
Reflex Actions
Example: When we touch a sharp object, the nerve endings in the finger feel the pain as the message reaches the spinal cord through the sensory nerve. The spinal cord sends the command back through the motor nerve to the muscles of the hand to move away.
Sense Organs and Their Care
Sense organs are our window to the outside world. The five sense organs of our body are eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin. They help us see, hear, smell, taste and feel.
 Sense Organs
Sense Organs
1. Eyes
- Our eyes are incredibly important sense organs, functioning like cameras to capture images of the world around us.
- They're safely situated in bony sockets, which protect them from harm. Additionally, our eyebrows, eyelids, and eyelashes act as barriers to prevent dirt and dust from entering our eyes.
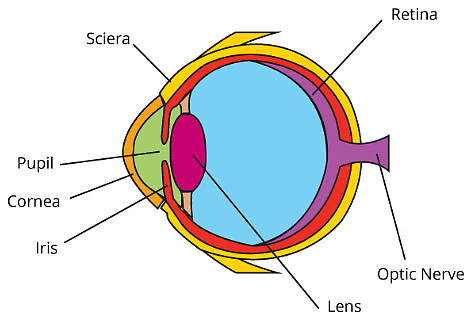 Eye
Eye
- The clear front part of the eye is called the cornea, and the coloured section is the iris. Within the iris is the black pupil, through which light enters.
- Behind the pupil lies the retina, which acts as a screen for forming images. The retina communicates with the brain via the optic nerves, which relay information for interpreting the images seen.
Care of Eyes
- We should wash our eyes regularly with clean and cold water.
- Never work and study in dim or very bright light.
- Try to avoid watching TV or working on the computer for long periods.
- Do not rub your eyes with dirty hands or a dirty towel.
- Never read in a moving vehicle.
2. Ears
- Our ears serve two main purposes: hearing and maintaining body balance. They consist of three parts: the external, middle, and internal ear.
- The external ear is the visible part that collects and transmits sound to the internal ear.
- The middle ear, situated between the external and internal ear, acts as a passage for sound and aids in balancing the body.
- The internal ear, the innermost part, sends sound signals to the brain via auditory nerves for processing.
 Ear
Ear
Care of Ears
- Ears can be damaged by very loud sounds. Therefore, it is necessary to protect our ears from such sounds.
- We should always clean our ears with a cotton swab.
- Never use a matchstick, pencil or hairpin to clean it.
- We should immediately go to a doctor if any small insect accidentally enters our ears.
3. Nose
- The nose assists in breathing and smelling.
- Sensory cells within the nose send messages to the brain. Various cells in the nose detect different odours.
- Additionally, the nose acts as a filter, blocking dust particles from entering our respiratory system.
 Nose
Nose
Care of Nose
- Keep your nose clean by blowing it gently and regularly.
- Avoid breathing through the mouth as it cannot filter the air that you inhale.
4. Tongue
- The tongue is responsible for detecting taste and aiding in speech. It contains small bumps called taste buds, which detect four main tastes: sweet, sour, salty, and bitter.
- Nerve endings in the taste buds transmit signals to the brain, where the taste is interpreted.
 Tongue
Tongue
Care of Tongue
- We should clean our tongue with fresh water.
5. Skin
- The skin is the outer layer of our body and shields our internal organs. It contains small sensory nerve endings linked to the brain and spinal cord.
- These nerve endings enable us to sense touch, temperature, pressure, pain, and tickling.
Care of Skin
- We should take bath every day.
- Wear clean and comfortable clothes.
- Apply an antiseptic on scratch, cut or burn on the skin.
- An antiseptic prevents the entry of germs on the affected area.
|
43 videos|198 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Nervous System Class 5 Notes Science
| 1. What is the role of the brain in the nervous system? |  |
| 2. How does the spinal cord contribute to the nervous system? |  |
| 3. What are nerves in the nervous system? |  |
| 4. What are reflex actions and how do they relate to the nervous system? |  |
| 5. How can we take care of our sense organs? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 5 exam
|

|


















