How does a Plant Grow from the Seed? | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| How does a Plant Grow from the Seed? |

|
| Dispersal of Seeds |

|
| Real-Life Examples |

|
| Some Amazing Facts |

|
| Some Myths about Plants |

|
Introduction
- Did you know that every big tree you see starts from a tiny seed?
- Have you ever wondered how seeds grow into the trees you see every day?
- Seeds are like nature's secret treasure. They hold everything needed for a plant to grow.
- Let’s unlock the treasure and find out how a seed turns into a plant that can give us food, flowers, and even shade!

How does a Plant Grow from the Seed?
- All plants have a life cycle, just like humans and other animals.
- The plant life cycle describes the stages the plant goes through from the beginning of its life until the end when the process starts all over again.
- Let us understand the life cycle of a plant, starting with a seed.
(a) Seeds
- The life cycle of a plant begins with a seed.
- A seed has a protective coating called the shell. The shell contains everything needed to start a new plant.
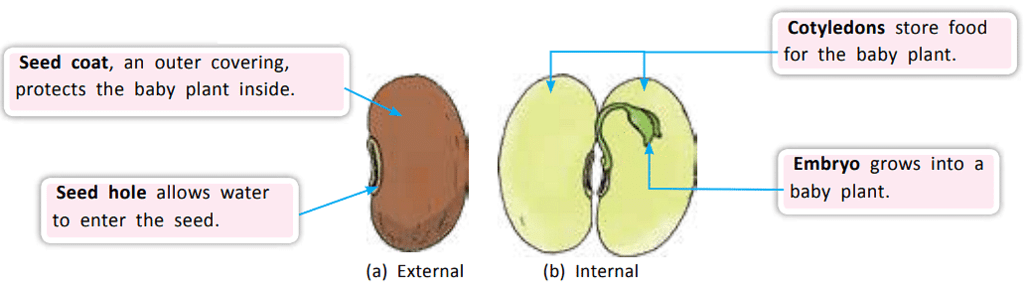 Structure of a Kidney Bean Seed
Structure of a Kidney Bean Seed
Structure of a Seed
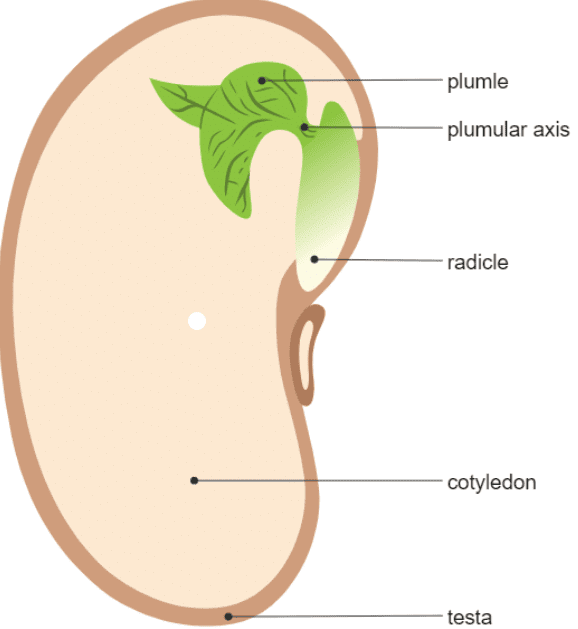
Seed coat: The outer layer of a seed that protects it from damage, drying out, or getting wet is called the seed coat.
Hilum: It is a small opening in the seed coat that absorbs water.
Cotyledons: It is the fleshy parts inside the seed that store food for the baby plant.
Embryo: The baby plant inside the seed. It uses the food from the cotyledons until it can grow its own roots and leaves. The radicle grows into the root, and the plumule becomes the shoot.
Radicle: The part of the baby plant that grows into the root.
Plumule: The part of the baby plant that grows into the shoot.
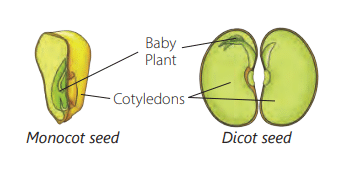
Types of Seeds
- Monocotyledonous Seeds: Some seeds have only one seed leaf, called monocotyledons. Examples include wheat, maize, bajra, and rice.
- Dicotyledonous Seeds: Some seeds have two seed leaves, called dicotyledons. Examples include mango, gram, and pea.
(b) Germination
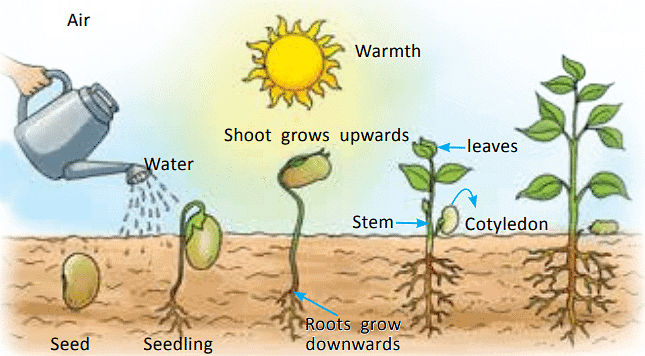
The process by which a plant grows from a seed is called germination.
- Seeds need water, appropriate temperature, and oxygen to germinate.
- When the proper conditions are met for the seed, it will begin to sprout.
- Until the new plant (seedling) grows its first leaves, it depends on the food stored inside the seed to grow.
- Seed dormancy: Sometimes, seeds don’t germinate even with enough water, air, and warmth. This is because some seeds need to rest first. This resting period is called seed dormancy, and the seeds germinate once it's over.
 Stages of Seed Germination
Stages of Seed Germination
(c) Seedlings
- When a seed gets enough water during germination, it swells and the seed coatbreaks open.
- This allows the baby plant, called a seedling, to start growing.
- Inside the seed, the embryo gets food from the cotyledons.
- The baby plant first grows its root from the radicle, which goes down into the soil.
- Then the plumule grows into a shoot that reaches up towards the sunlight.
However, not only can the seeds form new plants, but some other parts of plants such as roots, leaves, and stems are also used to grow new plants out of them.
Example:
(i) Sweet potatoes can be grown from an old plant's roots. However, it is to be checked first whether the roots are still alive or not.
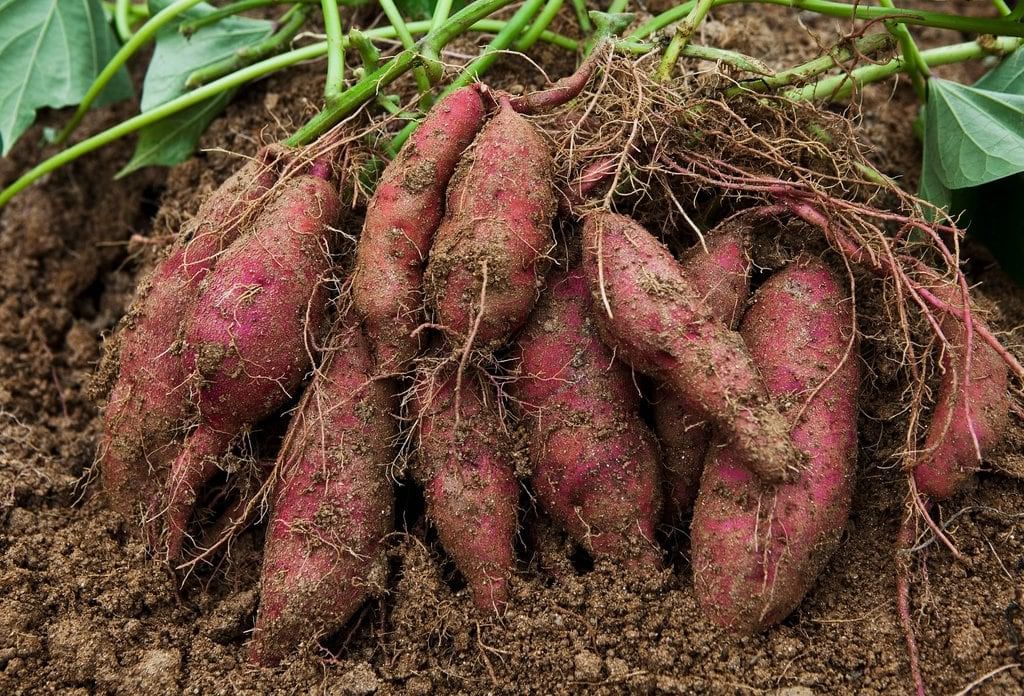 The roots of sweet potatoes used to grow new plants(ii) The stems of sugarcane and roses are used to grow new plants. The cutting of stem is planted into the soil, and after some time, a new plant grows out of it. This method is known as cutting.
The roots of sweet potatoes used to grow new plants(ii) The stems of sugarcane and roses are used to grow new plants. The cutting of stem is planted into the soil, and after some time, a new plant grows out of it. This method is known as cutting.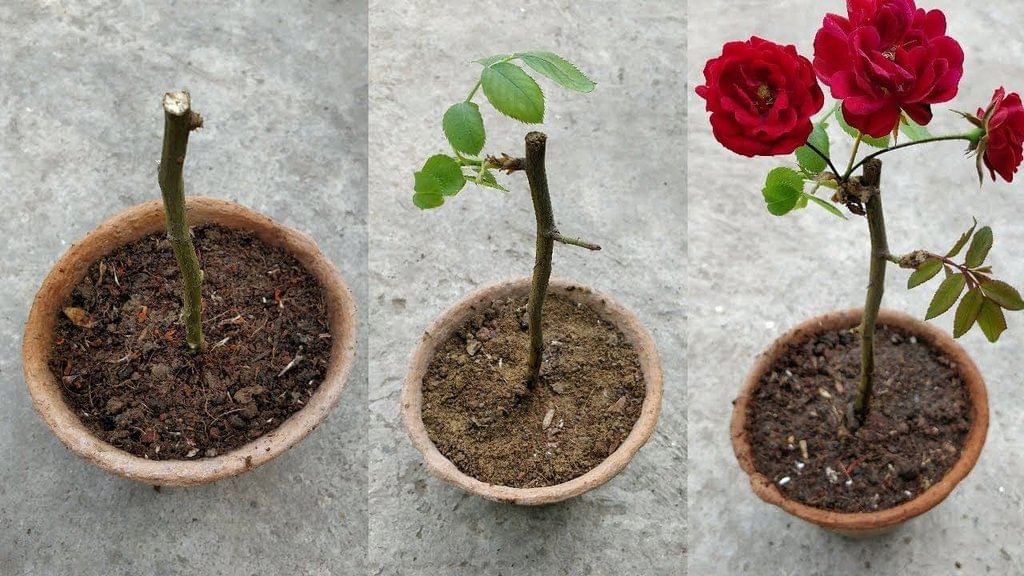  A stem of the rose is used to grow a new plant(iii) Sometimes the stem is not separated from the tree. A branch of the tree, while still attached to the tree, is buried in the earth, and a new plant starts to grow from it after some time. It starts developing roots. Then it is detached from the parent plant. This method of using the stem to produce new plants is called layering.
A stem of the rose is used to grow a new plant(iii) Sometimes the stem is not separated from the tree. A branch of the tree, while still attached to the tree, is buried in the earth, and a new plant starts to grow from it after some time. It starts developing roots. Then it is detached from the parent plant. This method of using the stem to produce new plants is called layering.
Example: Jasmine
 Process of Layering
Process of Layering
(iv) Sometimes, the leaves of plants are also used to produce new plants, such as in Bryophyllum.
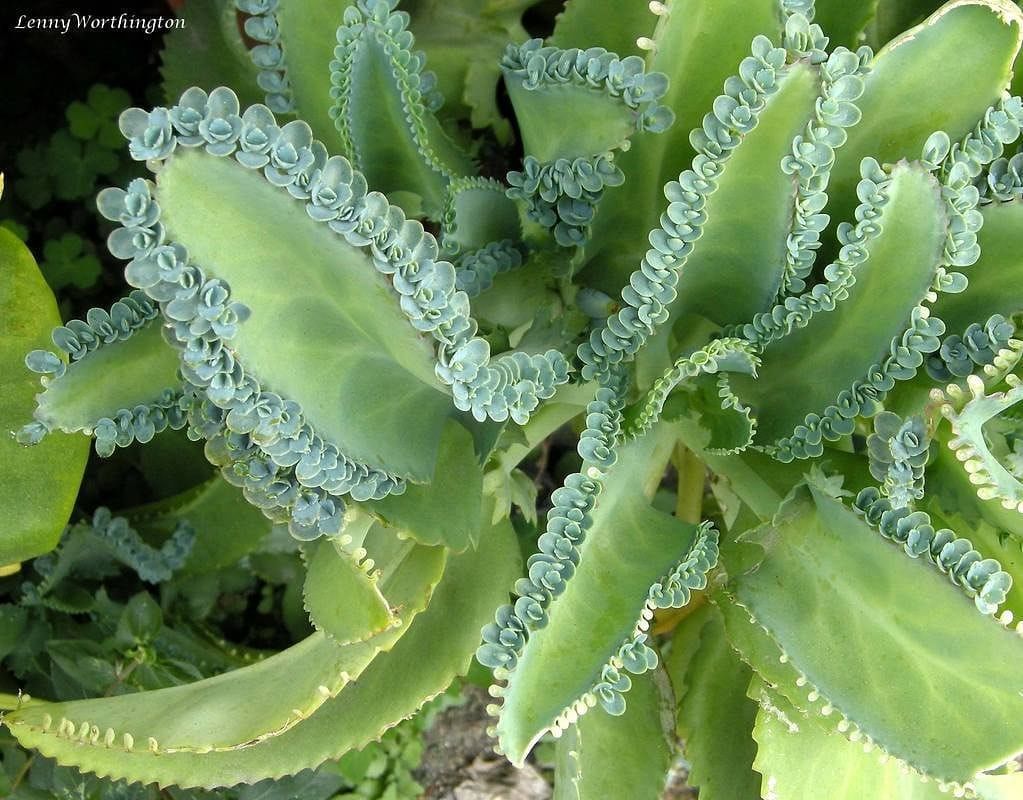 Bryophyllum has leaves on its leavesBut the most common method to grow plants remains through seeds.
Bryophyllum has leaves on its leavesBut the most common method to grow plants remains through seeds.
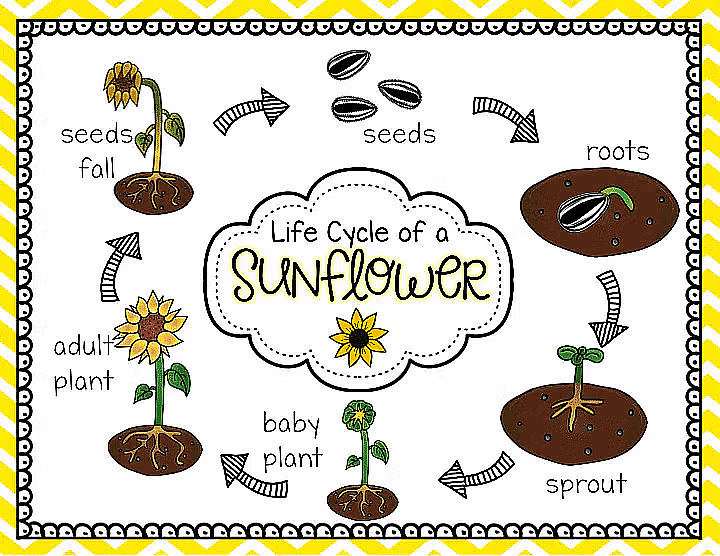
The life cycle of a plant can be summed up in the image below with an example of a Sunflower.
Dispersal of Seeds
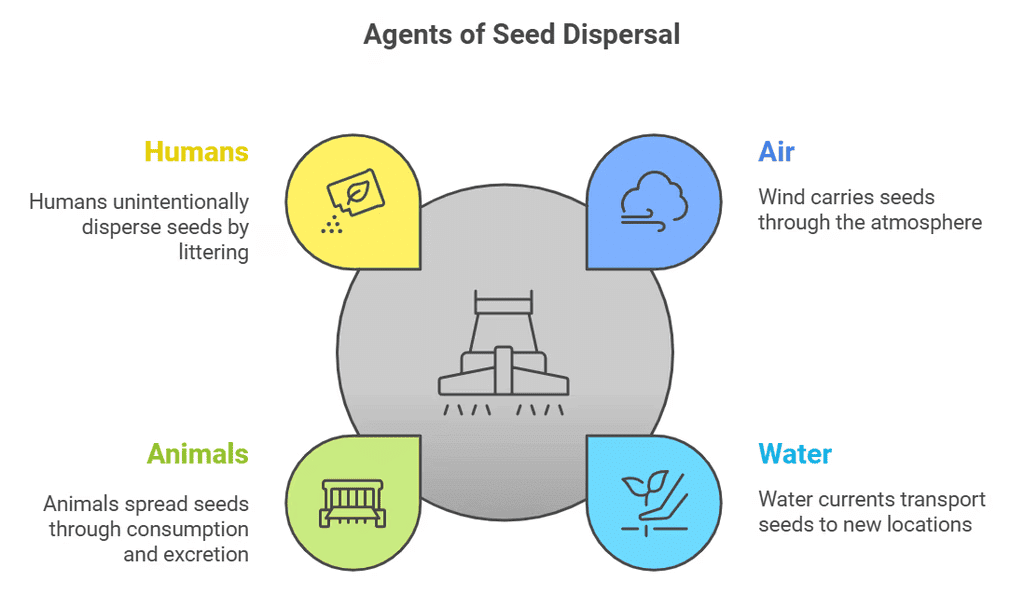
Dispersal of seeds means spreading the seeds so that they can grow. Air, water, small insects, and animals help to disperse the seeds.
- When the field is ploughed, the farmer disperses the seeds manually.
- When the animals eat something (a fruit) and go to other places, sometimes they leave the seeds of the fruit at some place which helps in dispersal.
- In the same manner, humans also disperse the seeds when we eat out at a place, say any fruit on a picnic, and we throw the leftover somewhere.
- Seeds are dispersed by wind, water, animals and the explosion of fruits. These are known as agents of dispersal.
1. Dispersal by Wind
- Some seeds, like orchid seeds, are very light and carried by the wind.
- Seeds like dandelions have hair-like structures that act like parachutes, helping them float away.
- Sycamore fruits have winged seeds that are also spread by the wind.
- These adaptations help the seeds to be carried by the wind.
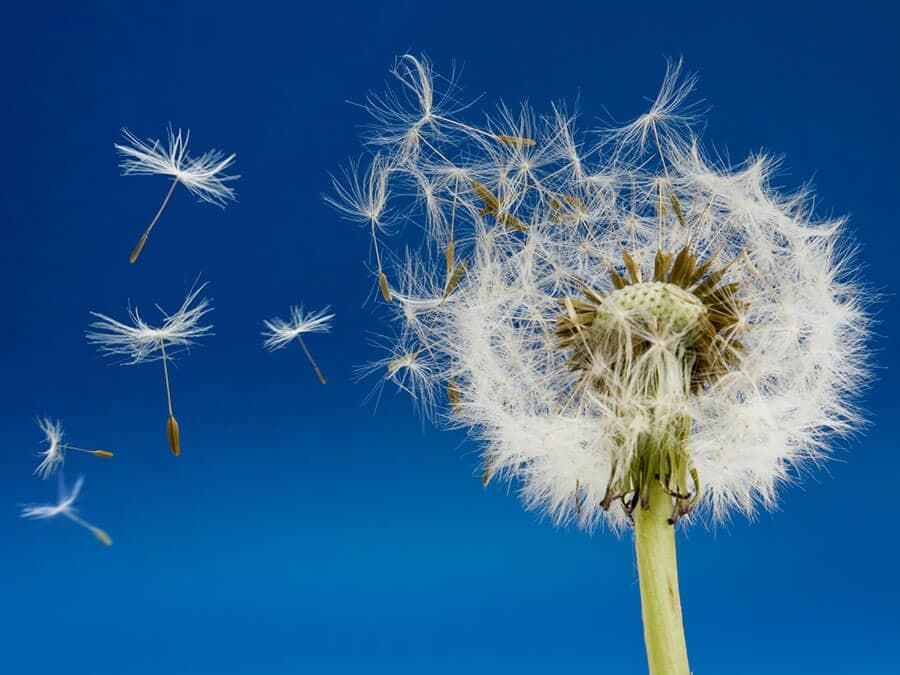 Dispersal of seeds by wind
Dispersal of seeds by wind
2. Dispersal by Water
- Seeds that can float are carried by water.
- Plants that grow in or near water, such as coconuts and lotus, use this method to spread their seeds.
- The thick, fibrous coat of coconut helps it to float and travel long distances across water.
- The fruit of the lotus has a spongy part that enables it to remain on the surface of the water.
 Seed dispersal by water
Seed dispersal by water
3. Dispersal by Animals
- Some plants have fruits that are juicy for humans and animals. Seeds from these fruits are often thrown away because they are not edible.
- Some animals eat the fruits along with their seeds.
- In these cases, only the fleshy part of the fruit is digested by the animals.
- The seeds, or stones and pips, are passed out undamaged and can grow into new plants.
- This process can happen far from the original plant because animals move around.
- Fruits such as blackberries, cherries, and apples spread their seeds this way.
- Birds also assist in spreading seeds through their droppings.
- Some fruits, like those from the burdock and datura plants, have seeds with hook-like structures. These seeds can attach to the fur of animals and get carried away.
- When these seeds find the right conditions, they can germinate and grow into new plants.
 Seed dispersal by Insects
Seed dispersal by Insects
4. Dispersal by Explosion
- Some plants have pods that burst open when they are ripe and dry.
- This way of spreading seeds is known as an explosion.
- Instead of just falling close to the parent plant, the seeds are thrown away.
- Examples of such plants include okra, bitter gourd, peas, beans, and balsam.
- Since plants cannot move to spread their seeds, nature has developed various methods for them to do so.
 Seed dispersal in Palm tree
Seed dispersal in Palm tree
Real-Life Examples
- In our daily cooking, we use many types of seeds.
- Packed with anti-inflammatory fats, proteins, and nutrients galore, nuts and seeds make a great addition to a healthy daily diet.
 Seeds used in a daily healthy diet
Seeds used in a daily healthy diet
Some Amazing Facts
- A sunflower looks like one large flower, but each head is composed of hundreds of tiny flowers called floret, which ripen to become the seeds.
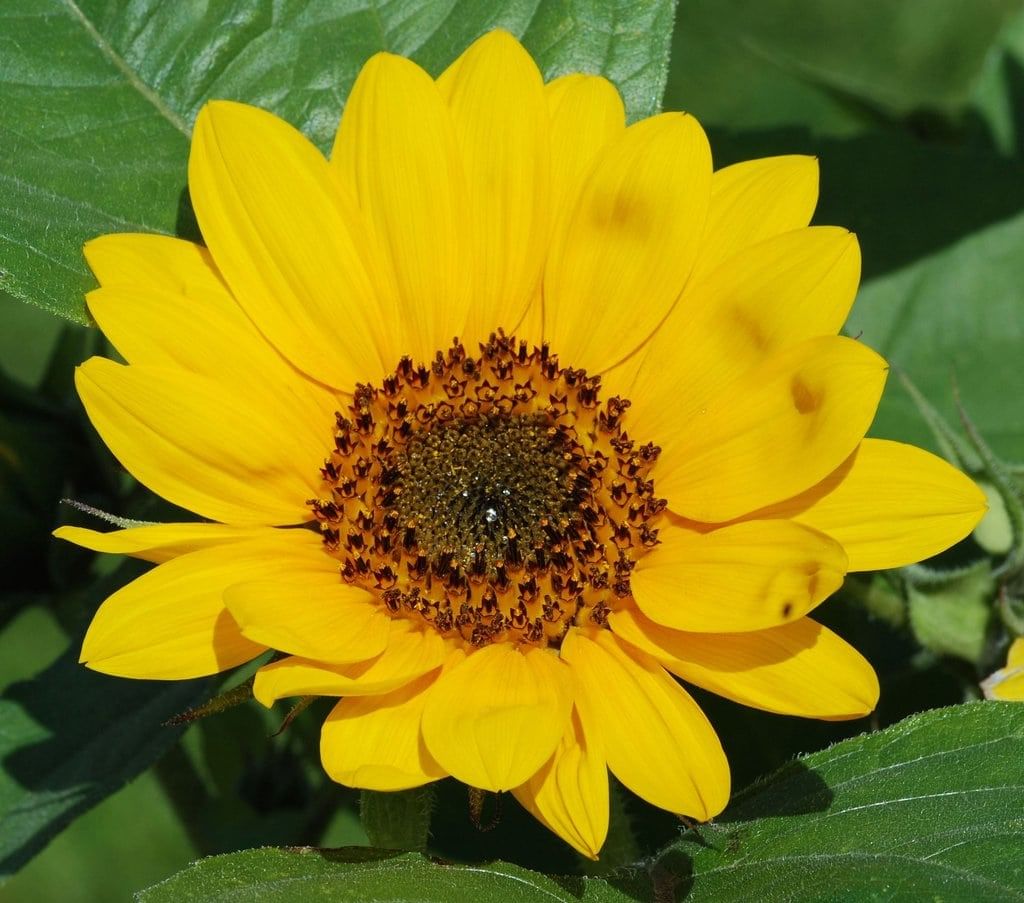 Florets on a Sunflower
Florets on a Sunflower
- The average strawberry has 200 seeds. It’s one of the only fruits that bear seeds on the outside.
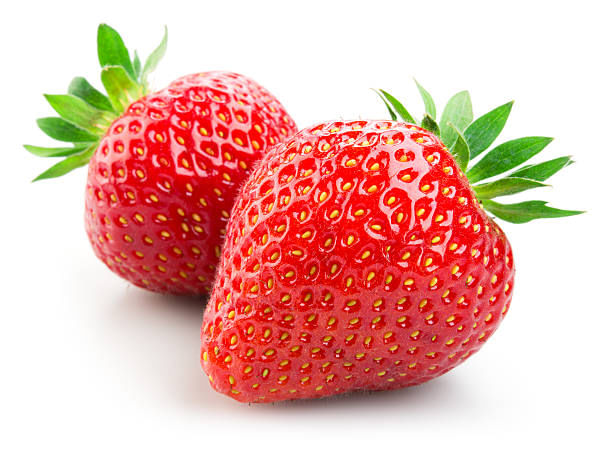 Seeds of Strawberry on the outer side
Seeds of Strawberry on the outer side
- The first potatoes were cultivated in Peru about 7,000 years ago.
- During the 1600s, tulips were so valuable in Holland that their bulbs were worth more than gold. The craze was called tulip mania, or tulipomania, and was caused by the Dutch economy. Tulips can continue to grow as much as an inch per day after being cut.
Some Myths about Plants
- Myth: Peanuts are nuts.
Fact: Peanuts are not nuts, but legumes related to beans and lentils. They have more protein, niacin, folate, and phytosterols than any nut, according to the National Peanut Board. - Myth: Garlic mustard is a type of garlic
Fact: Garlic mustard is a member of the mustard family, not garlic. This invasive herb out-competes native plants in the Eastern and Midwestern United States, posing a threat to other native plants and the species that depend on them.
|
11 videos|15 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on How does a Plant Grow from the Seed? - Advance Learner Course: Science Class 4
| 1. How do seeds germinate? |  |
| 2. What factors affect the growth of a plant from a seed? |  |
| 3. How do seeds disperse in nature? |  |
| 4. Can you give examples of plants that grow from seeds? |  |
| 5. What are some common myths about plants and their growth? |  |
















