Introduction: Cubes and Dice | CSAT Preparation - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Dice? |

|
| Important Rules: Dice |

|
| Solved Examples: Dice |

|
| Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them |

|
| Cubes |

|
| Types of Cube Problems |

|
| Solved Examples: Cubes |

|
Dice-based puzzles are a staple in the Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation (LRDI) section of CAT. They test your spatial visualisation, pattern recognition, and ability to manage multiple conditions under time pressure. This guide will introduce you to the core concepts, common question types, solution strategies, and practice tips.

What is a Dice?
A dice is a small cube-shaped object with six faces, each face showing a different number of dots (from 1 to 6).
It is used in games of chance and probability.
Key Terms
Face: One surface of the cube.
Edge: Line segment where two faces meet.
Vertex: Point where three edges join.
Net: 2D layout of the cube’s faces.
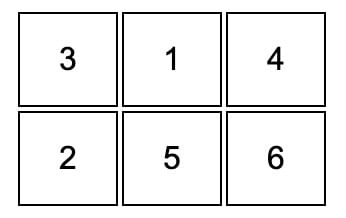 Net of a DiceTip: Opposite faces never share an edge in the net.
Net of a DiceTip: Opposite faces never share an edge in the net.
Some important points are given below:
- There are 6 faces in the cube - ABCG, GCDE, DEFH, BCDH, AGEF and ABHF.
- Always four faces are adjacent to one face.
- Opposite of ABCG is DEFH and so on.
- CDEG is the upper face of the cube.
- ABHF is the bottom of the cube.
Structure of a Standard Dice
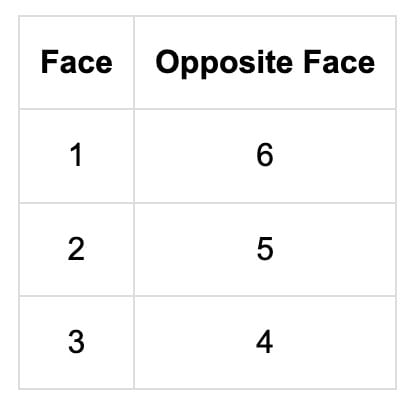
- Faces: 6 faces numbered 1 to 6.
- Opposite Faces Rule: Sum of opposite faces = 7.
Types of Dice Problems
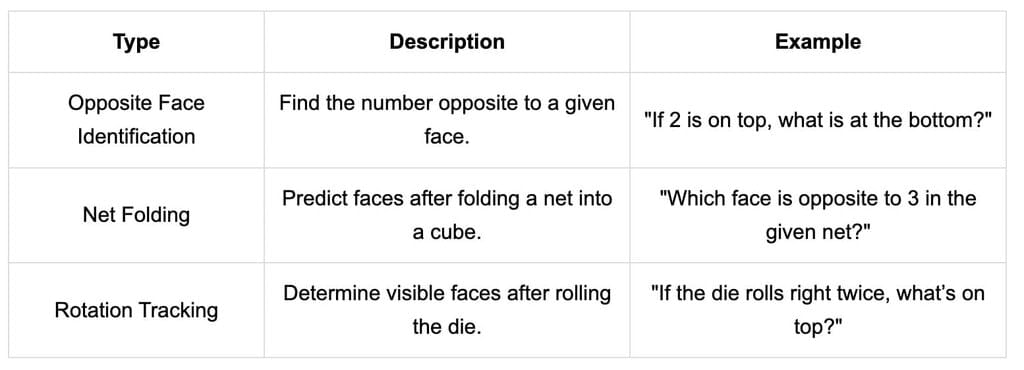
There are certain rules with the help of which questions on dice can be easily determined.
Important Rules: Dice
Rule No. 1:
Two opposite faces cannot be adjacent to one another.
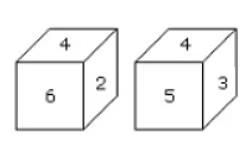
Example: Two different positions of a dice are shown below. Which number will appear on the face opposite to the face with number 4?
Sol:
Faces with four numbers 6, 2, 5 and 3 are adjacent of to the face with No. 4.
Hence, the faces with no. 6, 2, 5 and 3 cannot be opposite to the face with no. 4.
Therefore, the remaining face with no.1 will be the opposite of the face with no. 4.
Rule No. 2:
If two different positions of a dice are shown and one of the two common faces is in the same position, then the remaining faces will be opposite to each other.
Example: Two different positions of a dice are shown below.
Sol:
Here, in both shown positions two faces 5 and 3 are common.
The remaining faces are 2 and 4.
Hence, the number on the face opposite to the face with number 2 is 4.
Rule No. 3:
If in two different positions of dice, the position of a common face be the same, then each of the opposite faces of the remaining faces will be in the same position.
Example: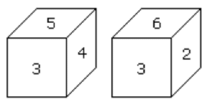
Sol:
Here in both positions of common (3) is the same.
Therefore, the opposite of 5 is 6, and the opposite of 4 is 2.
Rule No. 4:
If in two different positions of a dice, the position of the common face is not the same, then the opposite face of the common face will be that which is not shown on any face in these two positions. Besides, the opposite faces of the remaining faces will not be the same.
Example:
Sol:
Here in two positions of a dice, the face with the number 1 is not in the same position.
The face with number 6 is not shown.
Hence, the face opposite to the face with number 1 is 6.
Besides, the opposite face of 3 will be the face with number 2 and the opposite face to face 5 will be the face with number 1.
Solved Examples: Dice
Q.1. A dice with six faces is marked with six numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 respectively. This dice is rolled three times and three positions are shown as: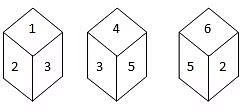
Find the number opposite to 1.
A. 2
B. 6
C. 5
D. 4
Ans: C
Explanation:
From figures (ii) and (iii), we can conclude that the numbers 2, 4, 3, and 6 appear adjacent to the letter 5. Therefore, the number 1 appears opposite to 5. In other words, 5 appears opposite to 1.
Q.2. You are given three positions of dice then which face is opposite to the face with alphabet B?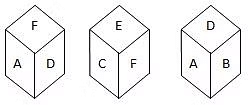
A. E
B. F
C. D
D. A
Ans: B
Explanation:
From figures (i) and (ii), we can conclude that the alphabets C, D, A and E lie adjacent to the alphabet F.
So, the alphabet B lies opposite F, and conversely, F lies opposite B.
Q.3. Which face is opposite to face with alphabet B, if four positions are given as below as?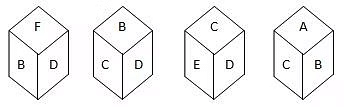
A. B
B. A
C. F
D. E
Ans: D
Explanation:
From figures (i), (ii) and (iv), we can conclude that F, D, C and A lie adjacent to B. Hence, E must lie opposite to B.
Q.4. Which of the following patterns can be formed from the piece of cardboard (X) as shown below?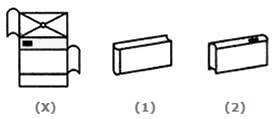
A. 4
B. 2
C. 1
D. 3
Ans: C
Explanation:
The pattern on the fig. (X) and the fact that the faces are rectangular and fig.(2) is eliminated as the dot on the upper face is on the left side instead of the right.
Fig. (3) and figure (4) also get eliminated as the smaller rectangular faces should be blank instead of having a dot on them.
So, figure (1) is the only possible figure as it has three blank faces adjacent to each other.
Directions for questions 5 to 9: Six different positions of dice are given below: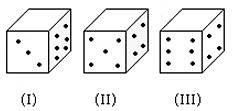
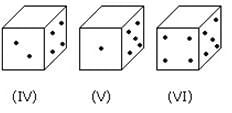
The sum of the numbers of dots on the opposite face is 7.
Q.5. If an even numbered dice have an odd number of dots on their top faces, then find the total number of dots on the top faces of their dice?
A. 22
B. 3
C. 10
D. 24
Ans: B
Explanation:
Even numbered dice are: (II), (IV) and (VI)
Number of dots on the top face of (II) dice = 1
Number of dots on the top face of (IV) dice = 1
Number of dots on the top face of (VI) dice = 1
Therefore, the required total = 1+1+1=3
Q.6. If an odd numbered dice have an odd number of dots on their top faces, then find the total number of dots on top faces of their dice is?
A. 11
B. 12
C. 13
D. 14
Ans: C
Explanation:
Odd numbered dice are : (II), (III) and (V)
Numbers of dots on the top faces of these dice are 5, 5 and 3 respectively.
Required total = 5+5+3=13
Q.7. If dice (I), (II) and (III) have an odd number of dots on their top faces, and the dice (IV), (V) and (VI) have an even number of dots on their top faces, then what is the difference in the total number of top faces between the two sets?
A. 0
B. 3
C. 1
D. -5
Ans: D
Explanation:
The number of faces on the top faces of the dice (I), (II) and (III) are 5, 1 and 5, respectively.
Therefore, the total of these numbers = 5 + 1 + 5 = 11
The number of dots on the top faces of the dice (IV), (V) and (VI) are 6, 4 and 6, respectively.Therefore, the total of these numbers = 6+4+6=16
Required difference = 11 -16=-5
Q8. If the odd numbers of dice have an even number of dots on their top faces and an even-numbered dice have an odd of dots on their bottom faces, then what is the total number of dots on their top faces?
A. 26
B. 12
C. 16
D. 18
Ans: A
Explanation:
The number of dots on the top faces of the dice (II), (IV) and (VI) are 2, 2 and 4, respectively.
The number of dots on the top faces of the dice (I), (III) and (V) are 6, 6 and 6, respectively.
Required total = 2 + 2 + 4 + 6 + 6 + 6 =26
Q9. If the dice (I), (II) and (III) have an odd number of dots on their top faces, then what is the total number of dots on their top faces?
A. 7
B. 14
C. 12
D. 11
Ans: D
Explanation:
No. of dots on the top faces of dice (I), (II) and (III) are 5, 1 and 5, respectively.
Required total = 5 + 1 + 5 = 11
Q10.Refer to the following four positions of the dice and find out the color which is opposite the face grey?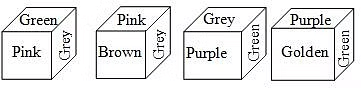
A. Golden
B. Purple
C. Brown
D. Green
Ans: A
Explanation
The colours adjacent to grey are green, pink, purple and brown. Hence, golden will be opposite to grey.
Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them

Cubes
Building on your mastery of dice, the following section introduces cube-based puzzles—another spatial-reasoning staple in CAT LRDI. Use these techniques alongside your dice strategies for acing this topic.
Types of Cube Problems
Key Formulas for Painted Cubes
When a large cube of size n by n by n is painted on all six faces and then cut into smaller cubes of size 1 x 1 x 1, these smaller cubes will have different numbers of painted faces depending on where they are located in the large cube.
The formulas below give the number of smaller cubes with a certain number of painted faces.

Solved Examples: Cubes
Example 1: A 5×5×5 cube is painted and cut into 1×1×1 cubes. How many have exactly 2 painted faces?
Ans:36 cubes.Sol:
- Formula: 12(n - 2) = 12(5 - 2) = 12 × 3 = 36.
Example 2: A cube is cut into 125 smaller cubes. How many cuts were made along each axis?
Ans: 12 cuts.Sol:
- 125 = 5×5×5 → n = 5.
- Cuts along each axis = (n - 1) = 4.
- Total cuts = 4×3 = 12 (3 axes).
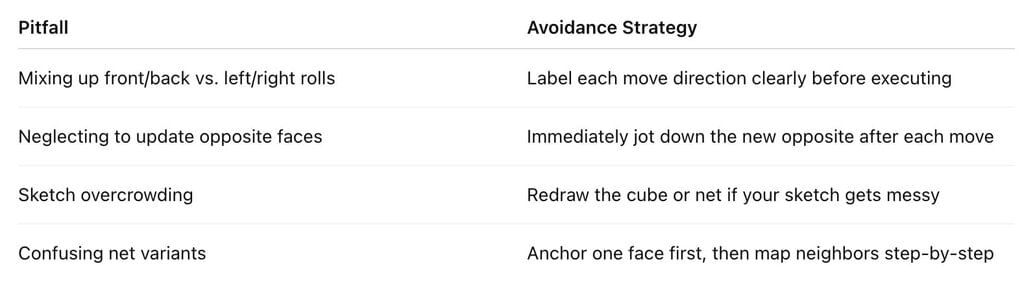
Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
|
205 videos|264 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction: Cubes and Dice - CSAT Preparation - UPSC
| 1. What are dice used for? |  |
| 2. How many sides does a standard dice have? |  |
| 3. What is the shape of a dice? |  |
| 4. How are dice typically made? |  |
| 5. Can dice be customized with different symbols or images? |  |