Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > Did the Second World War Change Life in Nazi Germany?
Did the Second World War Change Life in Nazi Germany? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
How Important was the Second World War for the Collapse of Nazi Germany
- Many Germans supported the Nazis’ actions when war broke out in September 1939. Even by 1941, Nazi Party support remained strong. Utilizing blitzkrieg tactics, the German Army defeated the French in six weeks and expelled the British Army from Europe. Numerous European nations fell under Nazi control.
- Operation Barbarossa marked a significant turning point in the war's success and public opinion. Poor German tactics and planning led to widespread disillusionment with the government. The defeat at the Battle of Stalingrad in 1942 indicated that the war would not be quick as the Germans had hoped. By this time, all sectors of society felt the war's impact. Rationing, resource shortages, high casualty rates, and aerial bombings angered the German public. Despite a 1943 Nazi propaganda campaign, more Germans began opposing the regime.
- By 1944, Germany was fighting a losing battle on two fronts. By April 1945, Hitler and Goebbels committed suicide, and Germany surrendered to the Allied forces. Historians debate whether Nazi Germany would have collapsed without World War II. Some argue that the economy was failing by 1939, causing public discontent, and that Hitler expedited plans to invade Poland to regain support. Others contend that the Nazi Party had strong pre-war support and that it was the impact of total war that weakened the regime and decreased support.
Changes to the Economy
- In 1936, Hitler dismissed Dr. Schacht and appointed Hermann Goering as Minister of the Economy. Hitler sought a more radical economic policy and had four main objectives:
- Achieve Autarky: Ensuring Germany's economy and food supply wouldn't be destroyed by a blockade, as experienced during the First World War.
- Increase Farming Output
- Increase Rearmament
- Implement More Government Control on Industry
- The Four Year Plan, initiated in 1936 and lasting until 1939, included the following measures by Goering:
- Reich Food Estate: Established to guarantee prices for farmers.
- Increased Ersatz Goods Production: Using coal to make rubber and acorns to make coffee.
- Government Production Targets: Set for various industries.
- Government Control: Over iron ore production, coal mining, steel, and armament factories.
- Hermann Goering Works: Created as industrial centers for heavy industry.
- Enslaved Labor Utilized: From people in concentration camps and newly-occupied territories.
- Criticism of the Four Year Plan:
- Many Nazis doubted Goering's suitability due to his lack of economic experience, unlike Schacht.
- Business leaders did not support the plan.
- Excessive rearmament led to a decreased standard of living, following a 'guns, not butter' economic approach.
The Nazi War Economy
Many historians argue that the Nazi economy was a significant weakness in the Second World War due to several factors:
- Failure to Achieve Autarky: Germany had not become self-sufficient.
- Dependency on Imports: By 1939, Germany still imported one-third of its raw materials.
- Economy Not War-Ready: The economy was not initially designed for wartime needs.
- Late Shift to War Economy: Only by 1943, under Albert Speer as the new Minister of Armaments and War Production, did Germany transition to a war economy.
- Inability to Support War Effort: The economy could not sustain the demands of the war.
- Resource Shortages: Germany faced shortages in fuel, coal, and food and lacked sufficient workers to produce necessary goods.
- Reliance on Plunder: Germany depended on resources looted from occupied countries to support its citizens.
- Insufficient Supplies for Operations: During Operation Barbarossa, Germany did not have enough supplies, hindering the effective use of blitzkrieg tactics against the USSR.
- Depletion of War Supplies: Battles consistently reduced their war supplies.
- Enslaved Labor: The government relied heavily on enslaved labor from ghettos and concentration camps.
- High Proportion of Enslaved Workforce: By 1944, one-quarter of Germany's workforce was comprised of enslaved individuals.
Question for Did the Second World War Change Life in Nazi Germany?Try yourself: What was one of the main objectives of Hitler's economic policy in Germany?View Solution
Support During the War
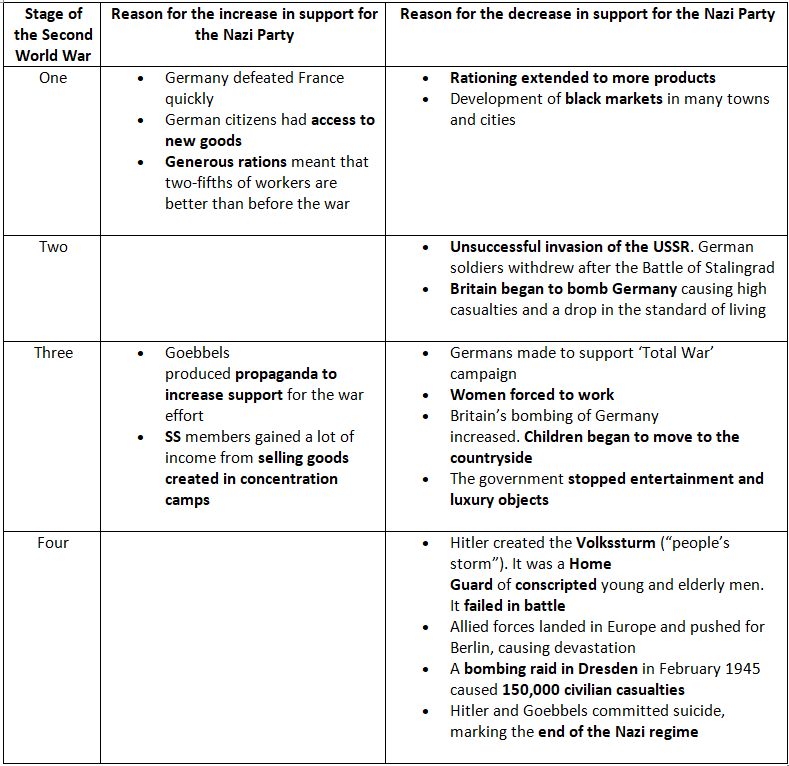
How Did the Second World War Impact Germans?
The German experience of war affected people differently depending on their gender, age and ethnicity:
The document Did the Second World War Change Life in Nazi Germany? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
81 videos|86 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Did the Second World War Change Life in Nazi Germany? - History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. How important was the Second World War for the collapse of Nazi Germany? |  |
Ans. The Second World War was crucial for the collapse of Nazi Germany as the country faced significant military defeats, economic strain, and loss of support from its allies, ultimately leading to its downfall.
| 2. How did the Second World War impact Germans? |  |
Ans. The Second World War had a profound impact on Germans as it resulted in widespread destruction, loss of life, displacement, and economic hardship, causing immense suffering and trauma for the population.
| 3. Did the Second World War change life in Nazi Germany? |  |
Ans. Yes, the Second World War drastically changed life in Nazi Germany as the country faced rationing, bombing raids, conscription of men for the military, and increased propaganda. The war disrupted daily life and brought about fear and uncertainty.
| 4. How did changes to the economy affect Nazi Germany during the war? |  |
Ans. Changes to the economy during the war, such as resource shortages, inflation, and increased production of military equipment, strained the Nazi war economy and contributed to the country's eventual collapse.
| 5. How did support for Nazi Germany shift during the Second World War? |  |
Ans. Support for Nazi Germany fluctuated during the war as military defeats and hardships increased dissent among the population, leading to a decline in loyalty towards the regime and contributing to its downfall.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















