Disorders of Circulatory System | Biology A-Level - A Level PDF Download
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by the flowing blood on the elastic walls of arteries. Blood flows in closed vessels so it exerts a pressure on the walls of these vessels. As soon as the blood is pumped into the arteries it exerts a pressure on the artery wall .This pressure is known as blood-pressure.
Blood-pressure is measured in two stages.
(1) Systolic Pressure:- It is the higher limit of blood pressure that shows the state of heart (systole) contraction for man this limit is 120 mm Hg (normal)
(2) Diastolic pressure:- It is the lower limit of B.P. that shows the state of heart relaxation (expansion = Diastole) for man this limit is 80 mm Hg (normal)
The instrument by which we can measure B.P. is called sphygmomanometer.
 Sphygmomanometer
SphygmomanometerIn man B.P. is measured in the brachial artery of arm. [- Normal B.P. of a healthy person is 120/80 mm Hg.]
Hales measured B.P. in horse first of all.
Factors Affecting Blood-Pressure
BP may be affected by following factors:(1) Exercise:- At the time of physical labour. B.P. is increased.
(2) Emotions and Excitement:- In the state of excitement or emotions B.P. is increased in man. At the time of Adrenal secretion at the time of fear and in some hereditary conditions B.P. is increased.
(3) Contraction of Blood Vessels:- B.P. is increased when contraction takes place in arteries and blood capillaries.
(4) Body posture:- In a laying (relaxing) person B.P. is low as compared to a standing man
(5) Sex:- In women, B.P. is slightly low as compared to men.
(6) Obesity:- In obese persons B.P. is increased.
(7) Age : B.P. increases as the age advances due to increase in vasomotor tone.
Note: Pulse is felt in the radial artery present in the wrist of a man. It is also felt in the artery of neck region. The graph of pulse of an artery is marked by an instrument that is called sphygmograph. Pulse pressure is the Pressure difference which generates a pulse. This is systolic minus diastolic B.P.
Disorders of Circulatory System
Hypertension
It is also called high blood pressure. Hypertension or high blood pressure is the occurrence of persistent systolic arterial pressure of more than 140 mm Hg and diastolic arterial pressure of more than 90 mm Hg. Hypertension is of two types primary and secondary.Secondary hypertension is due to an underlying cause like Hormonal or obstructional. Primary hypertension is also called essential hypertension. 90% of the hypertensive patients suffer from this type of hypertension.
It is caused by several factors like arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, varicose veins, obesity, etc.
High blood pressure must be managed. Excessive high blood pressure, say 220/120 mm Hg. is dangerous as it may cause haemorrhages in different parts of body causing blindness (due to optic arteries), nephritis (renal artery), brain stroke or CVA (due to rupturing of cerebral artery). Brain stroke may cause loss of speech, paralysis and other malfunctions of the body. Continued hypertension also affects muscles and valves of the heart. The damage is called hypertensive heart disease. Therefore, regular treatment with controlled diet and reduced salt intake should be undertaken. Excessive physical exercise should be avoided.
Hypotension
It is also called low blood pressure. Hypotension or low blood pressure is the occurrence of persistent systolic arterial pressure of less than 110 mm Hg and diastolic arterial pressure of less than 70 mm Hg. It is caused by persistent vasodilation of arterioles, reduced ventricular pumping, valvular defects, anaemia and deficient diet.Low blood pressure results in weakness, dizziness, blurred vision, etc. It can be corrected only after knowing the cause. However, temporary relief can be obtained through intake of glucose & salt rich drink.
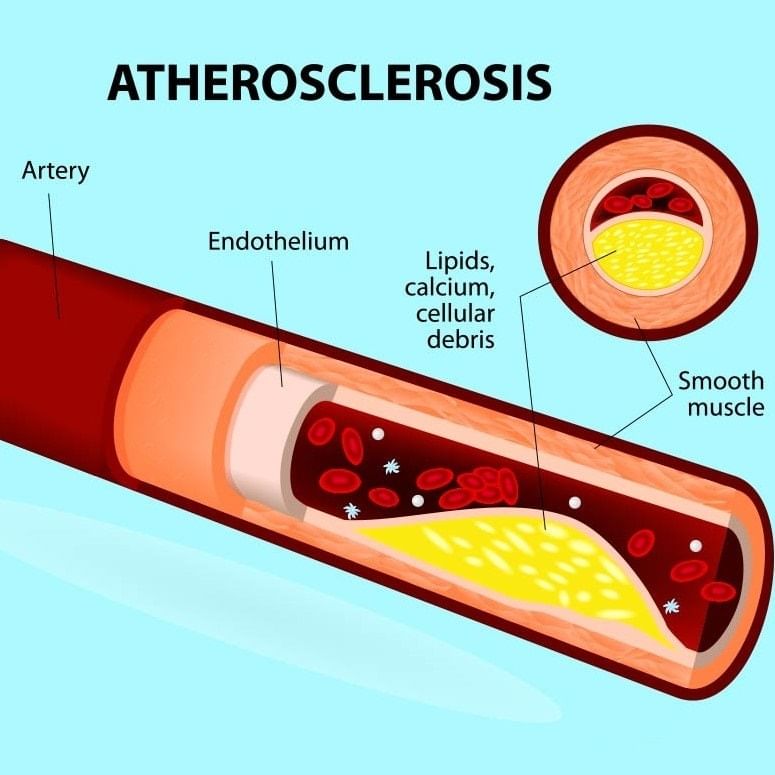
Atherosclerosis

It is irregular thickening of arterial walls and narrowing of their lumen due to deposition of yellow plaques or atheromas in their tunica intima and inner part of tunica media. Atheromas consist of cholesterol and other lipid materials. They are formed from low density lipoproteins or LDL. LDL can pass through endothelium. It gets precipitated inside artery. Normally blood contains an enzymes paraoxonase which prevents LDL precipitation. However, a diet rich in cholesterol (e.g., egg, butter, ghee) overcomes the effect of enzyme and causes deposition of LDL. It slowly brings about atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis causes hypertension due to stenosis or narrowing of arteries, arterial occlusion, kidney damage, brain stroke, reduced limb activity, angina and myocardial infarction. The effect can be reduced by controlling hypertension and lowering body lipid levels through diet and medicines.
Arteriosclerosis
It is a group of degenerative diseases characterised by thickening and loss of elasticity of arterial walls. Typical arteriosclerosis occurs in elderly persons. In one type calcium gets deposited in the tunica media of arteries. In another type the lumen of arterioles becomes narrow. Atherosclerosis is also considered to be a type of arteriosclerosis. Limb arteries suffer the most. It causes pain, cramps, numbness of extremities.
Varicose Veins
On prolonged standing or due to defect in the valves of the veins of the legs. These veins may become dialated, torturous and thickened (Most commonly affected is the saphenous vein). Such veins become clearly visible and prominent. Treatment is surgical removal of such veins.
| Atherosclerosis | Arteriosclerosis |
1. | Deposition of lipids (Cholesterol) on the walls (such depositions are called atheromatous plaque) | Hardening of arteries due to thickening along with deposition of calcium salts with cholesterol |
2. | Takes place in Lumen of large and medium size arteries of body | Can take place in medium to small arteries of limbs |
3. | Plaques are formed due to proliferation of smooth muscles of the inner wall of arteries (due to platelet derived growth factors) | No plaque formation occurs, but the arteries are stiff and rigid due to calcification. |
4. | Encroachment of Lumen of artery is present | There is not much encroachment of Lumen |
5. | Artery Lumen may get blocked resulting in no blood supply. | Artery becomes hard, looses its capacity of distention and may rupture |
|
280 videos|166 docs|147 tests
|
FAQs on Disorders of Circulatory System - Biology A-Level - A Level
| 1. What are the common disorders of the circulatory system? |  |
| 2. How does hypertension affect the circulatory system? |  |
| 3. What is atherosclerosis and how does it impact the circulatory system? |  |
| 4. Can lifestyle changes help prevent circulatory system disorders? |  |
| 5. What are the symptoms of peripheral artery disease? |  |

|
Explore Courses for A Level exam
|

|