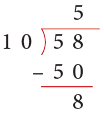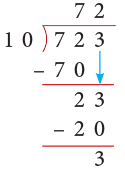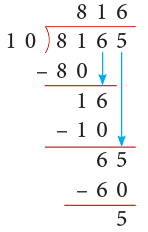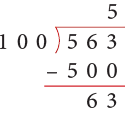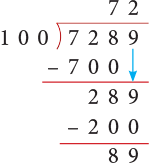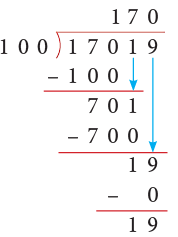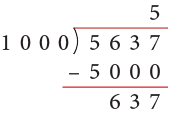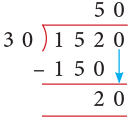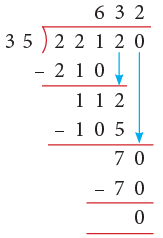Division Class 4 Notes Maths
What is Division?
Division is the process of sharing or splitting a total amount into equal parts.
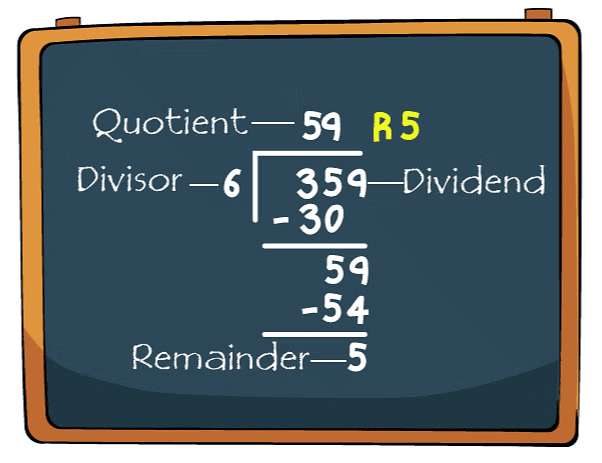 Division
Division
- For example, if you have 12 candies and want to share them with 3 friends, you divide 12 by 3.
- Each friend receives 4 candies, as 12 divided by 3 equals 4.
- Division helps us determine how many equal parts can be made from a total amount.
- In other words, division is about equal sharing or grouping.
 Division helps us figure out how many equal parts we can make from a total amount.
Division helps us figure out how many equal parts we can make from a total amount.
Division means equal sharing or equal grouping.
Terms Related to Division
When we do division, there are different terms to know:
- Dividend: The number that you want to divide. For example, in 20 ÷ 4, the dividend is 20.
- Divisor: The number you divide by. In 20 ÷ 4, the divisor is 4.
- Quotient: The result you get from dividing. For 20 ÷ 4, the quotient is 5.
- Remainder: If there's anything left over after dividing, it's called the remainder. For 22 ÷ 4, the quotient is 5 and the remainder is 2.
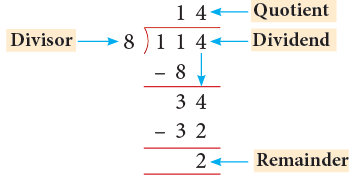
Look at the example above
1. Verifying Division
To check a division result, multiply the quotient by the divisor and add the remainder to this product. The result should be equal to the dividend. Thus, From the above division fact, we have,
From the above division fact, we have,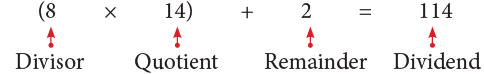 So, our answer is correct.
So, our answer is correct.
2. Some Important Points Related to Division
We always start division from the place of highest value. In case of 2-digit dividends, we start from tens place and in the case of 3-digit dividends, we always start from the hundreds place. The remainder is always smaller than the divisor.
3. Properties of Division
(i) When any number is divided by 1, the quotient is the number itself.
Examples: 62 ÷ 1 = 62, 125 ÷ 1 = 125
(ii) When any number is divided by itself (except 0), the quotient is 1.
Examples: 64 ÷ 64 = 1, 586 ÷ 586 = 1.
(iii) When 0 is divided by any number (except 0), the quotient is always 0.
Examples: 0 ÷ 58 = 0, 0 ÷ 6423 = 0.
(iv) Division by zero is not allowed.
Division of a Number by a 1-Digit Number
Let's Learn with some example
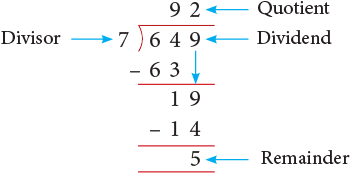
Example 1: Divide 649 by 7.
We divide, as shown alongside.
- Start by looking at the first number in the dividend.
- Find a number in the table of 7 less than or equal to 64.
- So, 9 is the required number. 7 x 9 = 63 , so write 63 below 64.
- Subtract, the number you got by multiplying the divisor,from the number in the dividend.
- 64 minus 63 equals 1. Bring down the next digit, from the number in the dividend.
- Repeat the same process again.
- 7 x 2 equals 14. So use 7.
- Then, subtract. We get 5 left. This 5 is our remainder.
- And the quotient is 92
Thus, 649 ÷ 7 gives Q = 92 and R = 5.Check:
Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
= 7 × 92 + 5 = 644 + 5 = 649
Dividing 4-Digit and 5-Digit Numbers by a 1-Digit Number
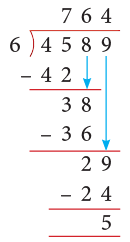
Example 2: Divide 4589 by 6.
- First, consider the thousands place. The divisor 6 does not divide into the first figure 4 of the dividend, as 6 > 4, so consider the first two digits 45 of the dividend. 6 goes into 45, 7 times and yields 3 as remainder.
- Write the quotient 7 above 5 in 45. Then, complete as shown by bringing down the digit 8 and lastly the digit 9 of the dividend.
Check: To check answer, we use the relationship,
Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
- Here, Divisor = 6, Quotient = 764, Remainder = 5 and Dividend = 4589.
So, Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder.
= 6 × 764 + 5 = 4584 + 5 = 4589- Thus, 4589 ÷ 6 gives Q = 764 and R = 5.
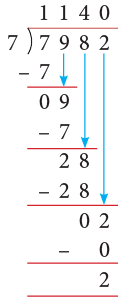
Example 3: Divide 7982 by 7.
Solution:
Thus, 7982 ÷ 7 gives Q = 1140 and R = 2.
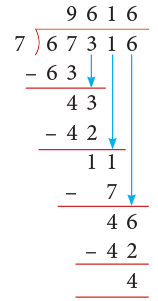
Example 4: Divide 67316 by 7.
Solution:
Thus, 67316 ÷ 7 gives Q = 9616 and R = 4.
EduRev Tip: 7 does not go into 2 so, we put a 0 in the quotient and bring down 2.
Division of a Number by a 2-Digit Number
Let's Learn with some example
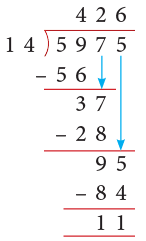
Example 5: Divide 5975 by 14.
Solution:
- Starting from the leftmost digits, we consider 59, the number formed by the first two digits 5 and 9 of the dividend, as divisor is a 2-digit number. 14 < 59.
- Using the multiplication table of 14, we see that 14 goes into 59, 4 times and yields 3 as a remainder. Write the quotient 4 above 9 of 59.
- Then, complete the division as shown by bringing down 7 and lastly the figure 5 of the dividend.
Check: Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
= 14 × 426 + 11
= 5964 + 11 = 5975- Thus, 5975 ÷ 14 gives Q = 426 and R = 11.
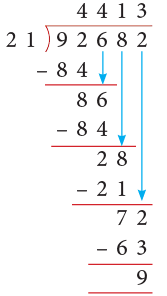
Example 6: Divide 92682 by 21 and check your answer.
Solution:
Thus, 92682 ÷ 21 gives Q = 4413 and R = 9.
Check:
Here, divisor = 21, quotient = 4413, remainder = 9 and dividend = 92682.
We have,
Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
= 21 × 4413 + 9
= 92673 + 9 = 92682
So, the answer is correct.
Division of a Number by 10s, 100s and 1000s
When you divide a number by 10, 100, or 1000, you move the decimal point to the left by 1, 2, or 3 places, respectively. This makes the numbers 10, 100, or 1000 times smaller. For example, 2500 ÷ 100 = 25.
Example 7: Divide each of the following numbers by 10.
(a) 58
(b) 723
(c) 8165
Solution:
(a)
Thus, 58 ÷ 10 gives Q = 5 and R = 8.
(b)
Thus, 723 ÷ 10 gives Q = 72 and R = 3.
(c)
Thus, 8165 ÷ 10 gives Q = 816 and R = 5.
From the above examples, we get the following rule:
Rule: On dividing a number by 10, we remove the digit at the ones place leaving the rest of the digits to form the quotient and the digit we remove from the ones place is the remainder.
Thus,
Example 8: Divide each of the following numbers by 100.
(a) 563
(b) 7289
(c) 17019
Solution:
(a)
Thus, 563 ÷ 100 gives Q = 5 and R = 63.
(b)
Thus, 7289 ÷ 100 gives Q = 72 and R = 89.
(c)
Thus, 17019 ÷ 100 gives Q = 170 and R = 19.
From the above examples, we get the following rule:
Rule: On dividing a number by 100, we remove the digits at the ones and tens places leaving the rest of the digits to form the quotient and the digits we remove from the ones and tens places form the remainder.
Thus,
Example 9: Divide each of the following numbers by 1000.
(a) 5637
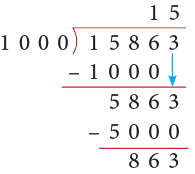
(b) 15863
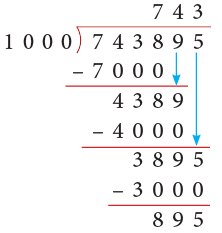
(c) 743895
Solution:
(a)
Thus, 5637 ÷ 1000 gives Q = 5 and R = 637.
(b)
Thus, 15863 ÷ 1000 gives Q = 15 and R = 863.
(c)
Thus, 743895 ÷ 1000 gives Q = 743 and R = 895.
From the above examples, we get the following rule:
Rule: On dividing a number by 1000, we remove the digits at the ones, tens and hundreds of places to get the remainder and the rest of the digits from the quotient.
Thus,
42÷8;Q=5,R=2 A) B) C) D)
Division of a Number by Multiples of 10 and 100
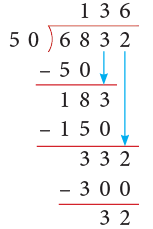
Example 10: Divide 6832 by 50.
Solution:
Thus, 6832 ÷ 50 gives Q = 136 and R = 32.
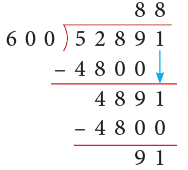
Example 11: Divide 52891 by 600.
Solution:
Thus, 52891 ÷ 600 gives Q = 88 and R = 91.
When you do a division problem, sometimes the remainder forms the part of your answer and sometimes it doesn’t.
Let's Practice
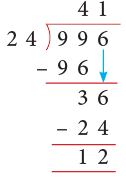
Example 12: 996 students of a school went on a picnic. They boarded buses each of which could hold only 24 students. How many buses were required?
Solution:
- At first, we divide 996 by 24 as shown on the right.
- If we use the quotient 41 as the number of buses needed, then 12 students cannot go for the picnic.
So, we need to have one more bus to answer the question correctly.Thus, 42 buses were needed to take the students for the picnic.
Example 13: The sports teacher is cutting ribbons for the sports medals. How many ribbons of 30 cm length can the teacher get from a roll of ribbon that is 1520 cm long?
Solution:
At first, we divide 1520 by 30.
- Here, we ignore the remainder as the question asks for the number of pieces exactly 30 cm in length.
Thus, the teacher will get 50 pieces each of 30 cm length.
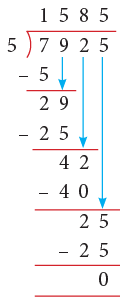
Example 14: Five friends together purchased a cricket kit for ₹ 7925. Find the money contributed by each child.
Solution:
- Money contributed by 5 children = ₹ 7925
- Money contributed by 1 child = ₹ 7925 ÷ 5
= ₹ 1585Thus, the money contributed by each child is ₹ 1585.
Example 15: The product of two numbers is 22120. If one of the numbers is 35, find the other number.
Solution:
- Product of two numbers = 22120
- One of the numbers = 35
- So, the other number = Product ÷ Given number
= 22120 ÷ 35 = 632Thus, the other number is 632.
|
33 videos|168 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Division Class 4 Notes Maths
| 1. What is division and why is it important in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How do you divide a number by a 1-digit number? |  |
| 3. What steps should be followed to divide 4-digit or 5-digit numbers by a 1-digit number? |  |
| 4. How do you perform division of a number by a 2-digit number? |  |
| 5. What are the rules for dividing a number by 10, 100, or 1000? |  |