Drugs and Their Classification - CBSE Chemistry Class 12 PDF Download
Chemistry in Everyday Life
Medicines or Drugs
Chemicals which may be used for the treatment of diseases and for reducing the suffering from pain are called medicines or drugs.
The branch of science which makes use of chemicals for the treatment of diseases [therapeutic effect] is called chemotherapy.
Some important classes of drugs are
Antacid
The chemical substances which neutralize the excess acid in gastric juice and raise the pH to an appropriate level in the stomach are based antacids.
The most commonly used antacids are weak bases such as sodium bicarbonate [sodium hydrogen carbonate, NaHCO3), magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)2] and aluminium hydroxide [Al(OH)3].
Generally, liquid antacids are more effective than tablets because .. have more surface area available for interaction and neutralisation acid.
Milk is a weak antacid.
Histamine stimulates the secretion of pepsin and hydrochloric acid. The drug cimetidine [Tegamet] was designed to prevent the interaction of histamine with the receptors present in the stomach Cimetidine binds to the receptors tbat triggers the release of acid the stomach. This results in release of lesser amount of acid. Now ranitidine (zantac), omeprazole and lansoprazole are used hyperacidity.
Tranquilizers (Psychotherapeutic Drugs)
Chemical substances used for the treatment of stress, anxiety, irritability and mild or even severe mental diseases, are known as tranquilizers. These affect the central nervous system and induce sleep for the patients as well as eliminate the symptoms of emotional distress. They are the common constituents of sleeping pills.
Noradrenaline is one of the neurotransmitter that plays a role in mood change. If the level of noradrenaline is low, the signal sending activity becomes low, and the person suffers from depression. In such situations antidepressant drugs are required. These drugs inhibit the enzymes which catalyse the degradation of noradrenaline. If the enzyme is inhibited, this important neurotransmitter is slowly metabolized and can activate its receptor for longer periods of time, thus counteracting the effect of depression. Iproniazid and phenelzine are two such drugs.
Barbituric acid and its derivatives viz. veronal, amytal, nembutal, luminal, seconal are known as barbiturates. Barbiturates are hypnotic, i.e., sleep producing agents.
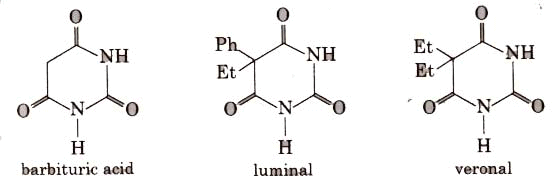
Equanil is used to control depression and hypertension.
Non-hypnotic chlorodiazepoxide and meprobamate are relatively mild tranquilizers suitable for relieving tension.
Analgesics
Medicines used for getting relief from pain are called analgesics. These are of two types :
1. Narcotics
Drugs which produce sleep and unconsciousness are called narcotics. Mhese are habit forming drugs. For example, morphine and codeine. Morphine diacetate is commonly known as heroin.
2. Non-narcotics
These are non-habit forming chemicals which reduce mild to moderate llatn such as headache, toothache, muscle and joint pain, etc. These are also termed as non-addicti,ve. These drugs do not produce sleep unconsciousness. Aspirin (2-acetoxybenzoic acid) is most commonly used analgesic with antipyretic properties. Now these days because its anti-blood clotting action, aspirin is widely used to
heart-attacks.
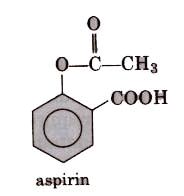
Aspirin is toxic for liver and sometimes also causes bleeding from- stomach. So, naproxen, ibuprofen, paracetamol,dichlorofenac sodium are other widely used analgesics.
Antipyretics
These are the chemical substance which reduce body temperature during high fever. Paracetamol, aspirin, phenacetin (4-hydroxy acetanilide), analgin and novalgin, etc., are common antipyretics. Out of these, paracetamol (4-acetamidophenol) is most common.
Antimicrobials
An antimicrobial tends to kill or prevent development of microbes CII inhibit the pathogenic action of microbes such as bacteria, fungi and virus selectively.
[Sulpha drugs constitute a group of drugs which are derivatives of sulphanilamide and have great antimicrobial capacity, thus, these are widely used against diseases such as dyptheria, dysentry, tubercu losis, etc.]


In structure these drugs are analogues of p-amino benzoic acid Different types of antimicrobial drugs are as follows :
1. Antibiotics
These are the substances (produced wholly or partially by chemical synthesis) which in low concentrations inhibit the growth of microorganisms or destroy them by intervening in their metabolic processes.
Antibiotics are products of microbial growth and thus, antibiotic therapy has been likened to ‘setting on.e thief against another’.
Antibiotics are of two types :
- Bactericidal antibiotics have cidal (killing) effect on microbes. For example, penicillin, ofloxacin, amino glycosides, etc.
- Bacteriostatic antibiotics have a static (inhibitory) effect on microbes. For example, erythromycin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, etc
Penicillin was the first antibiotic discovered (by Alexander Fleming) in 1929. It is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic. Ampicillin and amoxicillin are semi-synthetic Illodifications of penicillin. Penicillin is not suitable to all persons and some Personsare allergic to it. Consequently, it is essential to test the patients for sensitivity (or allergy) to penicillin, before it is administered.
In India, penicillin is manufactured at Pimpri and Rishikesh (Uttarakhand).
Broad-spectrum antibiotics also called antibiotics, are antibiotics which are effective against different types of harmful microorganisms. e.g., Tetracycline, chloramphenicoltgiven in case of typhoid, dysentery, fever ofloxacin, etc.
2. Antiseptics
These are the chemicals which either kill or prevent the growth microorganisms. Antiseptics are applied to the living tissues such wounds, cuts, ulcers and skin diseases in the form of antiseptic creams like furacin and soframycin. e.g., Some important examples of antiseptics are
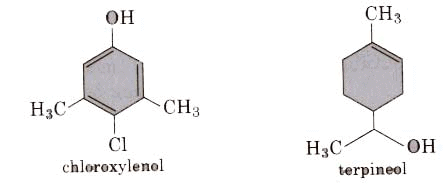
(i) Dettol is a mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol.
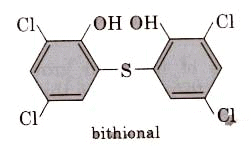
(ii) Bithional is added to soaps to impart antiseptic properties to reduce the odours produced by bacterial organic matter on the skin.
(iii) Tincture of iodine is a 2-3% solution of iodine in alcohol, which is a powerful antiseptic for wounds.
(iv) Iodoform (CHI3) is also used as an antiseptic for wounds.
(v) Boric acid in dilute aqueous solution is weak anIUS4!pa eyes.
3. Disinfectants
These are the chemical substances which kill microorganisms not safe to be applied to the living tissues. They are generally kill the microorganisms present on inanimate objects such as drainage systems, instruments, etc.
Some common examples of disinfectants are as follows :
(i) 1% phenol solution is disinfectant while in lower concentration 0.2% solution of phenol is antiseptic.
(ii) 0.2-0.4 ppm aqueous solution of chlorine is used for sterilisation of water to make it fit for drinking purpose.
(iii) SO2 at very low concentrations behaves like disinfectant.
(iv) Formaldehyde (HCHO) in the disinfecting rooms and operation gaseous theatres forms is used in hospitals. for
Antifertility Drugs
These are the chemical substances used to control the pregnancy. These are also called oral contraceptives. They belong to the class of natural products, known as steroids.
Birth control pills essentially contain a mixture of synthetic estrogen and progesterone derivatives. Norethindrone is widely used as antifertility drug.
FAQs on Drugs and Their Classification - CBSE Chemistry Class 12
| 1. What are the different classes of drugs? |  |
| 2. What are analgesics and how do they work? |  |
| 3. What are the risks of using antimicrobial drugs indiscriminately? |  |
| 4. What are the side effects of using antipsychotic drugs? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between a sedative and a hypnotic? |  |





















