Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > EMF & Potential Difference in Circuits
EMF & Potential Difference in Circuits | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Potential Difference in Series Circuits
- When multiple cells are connected in series, their total EMF equals the sum of individual EMFs.

Potential Difference in Series Circuits
- In a series circuit, the total potential difference across the components equals the EMF of the power supply.
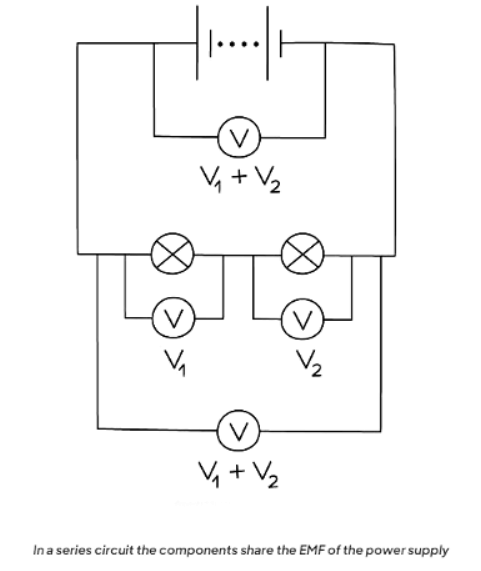
Question for EMF & Potential Difference in CircuitsTry yourself: Which of the following statements is true regarding the potential difference in series circuits?View Solution
Potential Difference in Parallel Circuits
- A parallel circuit includes components connected along separate branches.
- The advantages of parallel circuits are:
- Components can be controlled individually with their own switches.
- If one component fails, others will continue to function.
- The potential difference across each component in parallel is constant.
- Current varies in each branch, unlike the potential difference.
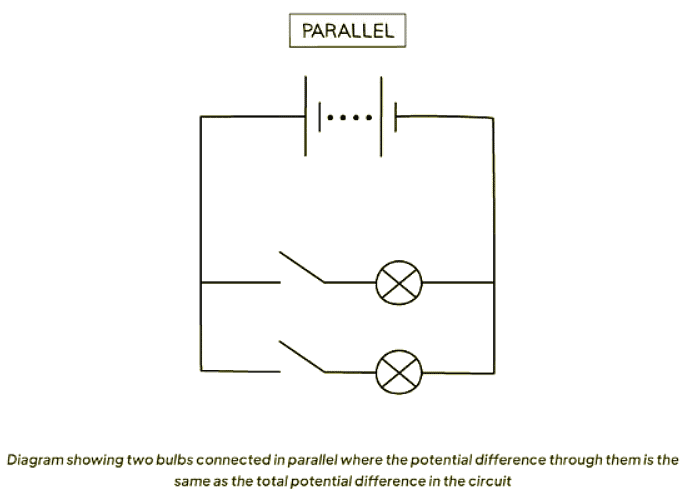

The document EMF & Potential Difference in Circuits | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on EMF & Potential Difference in Circuits - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the difference between EMF and potential difference in circuits? |  |
Ans. EMF (electromotive force) is the total energy supplied per unit charge by the cell or power supply, while potential difference is the energy transferred per unit charge as the charge moves through the circuit.
| 2. How does potential difference behave in series circuits? |  |
Ans. In series circuits, the potential difference is shared between the components, with the total potential difference across all components equal to the sum of the potential differences across each individual component.
| 3. How does potential difference behave in parallel circuits? |  |
Ans. In parallel circuits, the potential difference across each branch is the same, as the branches are connected directly across the power supply. The potential difference across each component in a parallel circuit is equal to the total potential difference of the circuit.
| 4. What are the key concepts of parallel circuits? |  |
Ans. In parallel circuits, the components are connected across the power supply in separate branches, providing multiple paths for the current to flow. The potential difference across each branch is the same, while the total current entering the parallel circuit is equal to the sum of the currents flowing through each branch.
| 5. How does the potential difference affect the flow of current in a circuit? |  |
Ans. The potential difference in a circuit determines the rate at which charge flows through the circuit, with a higher potential difference leading to a greater current flow. The potential difference acts as the driving force for the flow of charge in a circuit.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















