Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE > Economies of Scale
Economies of Scale | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Economies of Scale
- Definition: Economies of scale refer to the cost advantages that a business can achieve as it increases its scale of production. This results in efficiencies that lower the average costs of production.
- Explanation: When a business grows and expands its operations, it can benefit from economies of scale. This means that the cost per unit of production decreases as the volume of output increases.
- Example: For instance, a company that produces smartphones might experience economies of scale when it increases its production capacity. This could lead to lower costs per phone due to efficiencies in the production process.
- Impact on Large Firms: Economies of scale are particularly advantageous for large firms, as they can reduce their costs of production to levels that smaller firms may not be able to achieve.
- Differentiation from Total Costs: It's important to note that while economies of scale can lead to lower average or unit costs, the total costs incurred by the business may still increase. However, this increase occurs at a decreasing rate per unit produced.
Diagram Economies of Scale

Diagram Analysis
- Initially, when the output is low, the average costs for the firm are relatively high.
- As the firm boosts its production, it starts benefiting from economies of scale, resulting in a reduction in the average cost per unit.
- There comes a point where the business achieves the optimal output level, minimizing costs.
- After this point, diseconomies of scale set in, causing the average cost to rise once again.
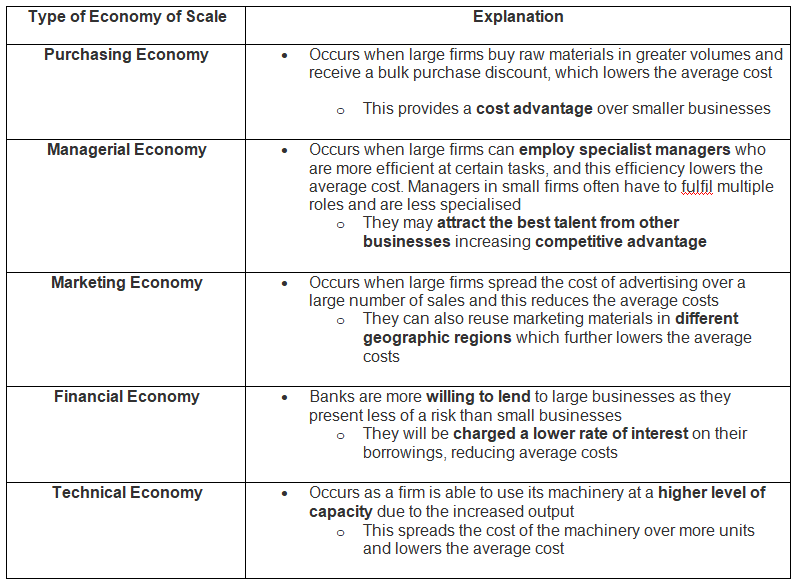
Different Types of Economies of Scale
- Internal factors contribute to the creation of economies of scale, over which businesses have varying degrees of control.
- Businesses strive to capitalize on these economies to reduce costs and boost profits wherever feasible.
Explanation of the Different Economies of Scale
Question for Economies of ScaleTry yourself: How do economies of scale benefit businesses?View Solution
The document Economies of Scale | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
70 videos|94 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Economies of Scale - Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are economies of scale and how do they impact businesses? |  |
Ans. Economies of scale refer to the cost advantages that businesses can achieve due to an increase in production levels. As production increases, the average cost of each unit decreases, leading to higher efficiency and profitability for the business.
| 2. How do economies of scale help businesses remain competitive in the market? |  |
Ans. By taking advantage of economies of scale, businesses can lower their production costs, which allows them to offer competitive prices in the market. This can help them attract more customers and increase market share.
| 3. What are the different types of economies of scale that businesses can benefit from? |  |
Ans. There are various types of economies of scale, including technical, purchasing, financial, marketing, and managerial economies. These different types can arise from various aspects of the business operations, such as production processes, bulk purchasing, financial leverage, and efficient management practices.
| 4. How can businesses achieve economies of scale? |  |
Ans. Businesses can achieve economies of scale by increasing their production levels, improving production processes to reduce costs, investing in technology and automation, and expanding their market reach to increase sales volume.
| 5. What are some challenges that businesses may face when trying to take advantage of economies of scale? |  |
Ans. Some challenges that businesses may face include the need for substantial initial investment in equipment and infrastructure, the risk of overproduction leading to excess inventory, the possibility of reduced flexibility in adapting to market changes, and potential issues with maintaining quality standards as production levels increase.
Related Searches

















