Irodov Solutions: Electric Current | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q. 147. A long cylinder with uniformly charged surface and crosssectional radius a = 1.0 cm moves with a constant velocity v = 10 m/s along its axis. An electric field strength at the surface of the cylinder is equal to E = 0.9 kV/cm. Find the resulting convection current, that is, the current caused by mechanical transfer of a charge.
Solution. 147. The convection current is
 (1)
(1)
here, dq = λ dx, where λ is the linear charge density.
But, from the Gauss’ theorem, electric field at the surface of the cylinder,

Hence, substituting the value of λ and subsequently of dq in Eqs. (1), we get


Q. 148. An air cylindrical capacitor with a dc voltage V = 200 V applied across it is being submerged vertically into a vessel filled with water at a velocity v = 5.0 mm/s. The electrodes of the capacitor are separated by a distance d = 2.0 mm, the mean curvature radius of the electrodes is equal to r = 50 mm. Find the current flowing in this case along lead wires, if d ≪ r.
Solution. 148. Since d << r, the capacitance of the given capacitor can be calculated using the formula for a parallel plate capacitor. Therefore if the water (permittivity ε) is introduced up to a height x and the capacitor is of length l, we have,

Hence charge on the plate at that instant, q = CV
Again we know that the electric current intensity,


But, 
So, 
Q. 149. At the temperature 0°C the electric resistance of conductor 2 is η times that of conductor 1. Their temperature coefficients of resistance are equal to α2 and a1 respectively. Find the temperature coefficient of resistance of a circuit segment consisting of these two conductors when they are connected (a) in series; (b) in parallel.
Solution. 149. We have, Rt = R0 (1 + αf),(1)
where Rt and R0 are resistances at t°C and 0°C respectively and a is the mean temperature coefficient of resistance.
So, 
so  (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
Comparing Eqs. (1) and (2), we conclude that temperature co-efficient of resistance of the circuit,

(b) In parallel combination


Now, neglecting the terms, proportional to the product of temperature coefficients, as being very small, we get,

Q. 150. Find the resistance of a wire frame shaped as a cube (Fig. 3.35) when measured between points
(a) 1- 7; (b) 1- 2; (c) 1- 3.
The resistance of each edge of the frame is R

Solution. 150. (a) The currents are as shown. From Ohm's law applied between 1 and 7 via 1487 (say)



Thus, 
(b) Between 1 and 2 from the loop 14321,

From the loop 48734,

or, 
so 

or 
(c) Between 1 and 3 From the loop 15621


Q. 151. At what value of the resistance Rx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.36 will the total resistance between points A and B be independent of the number of cells?

Solution. 151. Total resistance of the circuit will be independent of the number of cells,

if 
or, 
On solving and rejecting the negative root of the quadratic equation, we have,

Q. 152. Fig. 3.37 shows an infinite circuit formed by the repetition of the same link, consisting of resistance R1 = 4.0Ω and R2 = 3.0 Ω. Find the resistance of this circuit between points A and B.

Solution. 152. Let R0 be the resistance of the network,


On solving we get,

Q. 153. There is an infinite wire grid with square cells (Fig. 3.38). The resistance of each wire between neighbouring joint connections is equal to R0. Find the resistance R of whole grid between points A and B.
Instruction. Make use of principles of symmetry and superposition.

Solution. 153. Suppose that the voltage V is applied between the points A and B then
V = IR = I0 R0,
where R is resistance of whole the grid, l, the current through the grid and I0,the current through the segment AB. Now from symmetry, I/4 is the part of the current, flowing through all the four wire segments, meeting at the point A and similarly the amount of current flowing through the wires, meeting at B is also I/4. Thus a current I/2 flows through the conductor AS, i.e.

Hence, 
Q. 154. A homogeneous poorly conducting medium of resistivity p fills up the space between two thin coaxial ideally conducting cylinders. The radii of the cylinders are equal to a and b, with a < b, the length of each cylinder is l. Neglecting the edge effects, find the resistance of the medium between the cylinders.
Solution. 154. Let us mentally isolate a thin cylindrical layer of inner and outer radii r and r + dr respectively. As lines of current at all the points of this layer are perpendicular to it, such a layer can be treated as a cylindrical conductor of thickness dr and cross-sectional area 2πrl. So, we have,


and integrating between the limits, we get,

Q. 155. A metal ball of radius a is surrounded by a thin concentric metal shell of radius b. The space between these electrodes is filled up with a poorly conducting homogeneous medium of resistivity p. Find the resistance of the interelectrode gap. Analyse the obtained solution at b → ∞.
Solution. 155. Let us mentally isolate a thin spherical layer of inner and outer radii r and r + dr. Lines of current at all the points of the this layer are perpendicular to it and therefore such a layer can be treated as a spherical conductor of thickness dr and cross sectional area 4πr2. So
 (1)
(1)
And integrating (1) between the limits [ay b], we get,

Now, for → ∞, we have

Q. 156. The space between two conducting concentric spheres of radii a and b (a < b) is filled up with homogeneous poorly conducting medium. The capacitance of such a system equals C. Find the resistivity of the medium if the potential difference between the spheres, when they are disconnected from an external voltage, decreases it-fold during the time interval Δt.
Solution. 156. In our system, resistance of the medium 
where p is the resistivity of the medium
The current 
Also ,  as capacitance is constant. (2)
as capacitance is constant. (2)
So, equating (1) and (2) we get,

or, 
or, 
Hence, resistivity of the medium,

Q. 157. Two metal balls of the same radius a are located in a homogeneous poorly conducting medium with resistivity p. Find the resistance of the medium between the balls provided that the separation between them is much greater than the radius of the ball.
Solution. 157. Let us mentally impart the charge +q and - q to the balls respectively. The electric field strength at the surface of a ball will be determined only by its own charge and the charge can be considered to be uniformly distributed over the surface, because the other ball is at infinite distance. Magnitude of the field strength is given by,

So, current density  and electric current
and electric current

But, potential difference between the balls,

Hence, the sought resistance,

Q. 158. A metal ball of radius a is located at a distance l from an infinite ideally conducting plane. The space around the ball is filled with a homogeneous poorly conducting medium with resistivity p. In the case of a ≪ l find:
(a) the current density at the conducting plane as a function of distance r from the ball if the potential difference between the ball and the plane is equal to V;
(b) the electric resistance of the medium between the ball and the plane.
Solution. 158. (a) The potential in the unshaded region beyond the conductor as the potential of the given chaige and its image and has the form


where r1, r2 are HJie distances of the point from the charge and its image. The potential has been taken to be zero on the conducting plane and on the ball

So A ≈ Va. In this calculation the conditions a << l is used to ignore the variation of φ over the ball.
The electric field at P can be calculated similarly. Hie charge on the ball is

and 
Then  normal to the plane.
normal to the plane.
(b) The total current flowing into the conducting plane is



Hence

Q. 159. Two long parallel wires are located in a poorly conducting medium with resistivity p. The distance between the axes of the wires is equal to l, the cross-section radius of each wire equals a. In the case a ≪ l find:
(a) the current density at the point equally removed from the axes of the wires by a distance r if the potential difference between the wires is equal to V;
(b) the electric resistance of the medium per unit length of the wires.
Solution. 159. (a) The wires themselves will be assumed to be perfect conductors so the resistance is entirely due to the medium. If the wire is of length L, the resistance R of the medium is  because different sections of the wire are connected in parallel (by the medium) rather than in series. Thus if R1 is the resistance per unit length of the wire then R = R1/L, Unit of R1 is ohm-meter.
because different sections of the wire are connected in parallel (by the medium) rather than in series. Thus if R1 is the resistance per unit length of the wire then R = R1/L, Unit of R1 is ohm-meter.

The potential at a point P is by symmetry and superposition



or, 
and 
We then calculate the field at a point P which is equidistant from 1 & 2 and at a distance r from both :
Then 

and 
(b) Near either wire 
and 
Then 
Which gives 
Q. 160. The gap between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is filled with glass of resistivity p = 100 GΩ•m. The capacitance of the capacitor equals C = 4.0 nF. Find the leakage current of the capacitor when a voltage V = 2.0 kV is applied to it.
Solution. 160. Let us mentally impart the charges +q and - q to the plates of the capacitor. Then capacitance of the network,
 (1)
(1)
Now, electric current,
 (2)
(2)
Hence, using (1) in (2), we get,

Q. 161. Two conductors of arbitrary shape are embedded into an infinite homogeneous poorly conducting medium with resistivity p and permittivity e. Find the value of a product RG for this system, where R is the resistance of the medium between the conductors, and C is the mutual capacitance of the wires in the presence of the medium.
Solution. 161. Let us mentally impart charges +q and -q to the conductors. As the medium is poorly conducting, the surfaces of the conductors are equipotential and the field configuration is same as in the absence of the medium.
Let us surround, for example, the positively charged conductor, by a closed surface 5, just containing the conductor,
then, 
and 
So, 
Q. 162. A conductor with resistivity p bounds on a dielectric with permittivity a. At a certain point A at the conductor's surface the electric displacement equals D, the vector D being directed away from the conductor and forming an angle α with the normal of the surface. Find the surface density of charges on the conductor at the point A and the current density in the conductor in the vicinity of the same point.
Solution. 162. The dielectric ends in a conductor. It is given that on one side (the dielectric side) the electric displacement D is as shown. Within the conductor, at any point A, there can be no normal component of electric field. For if there were such a field, a current will flow towards depositing charge there which in turn will set up countering electric field causing the normal component to vanish. Then by Gauss theorem, we easily derive
σ = Dn = D cos α where a is the surface charge density at A.

The tangential component is determined from the circulation theorem

It must b e continuous across the surface o f the conductor. Thus, inside the conductor there is a tangential e lectric field o f magnitude,

This implies a current, by Ohm’s law, of

Q. 163. The gap between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is filled up with an inhomogeneous poorly conducting medium whose conductivity varies linearly in the direction perpendicular to the plates from σ1 = 1.0 pS/m to σ2 = 2.0 pS/m. Each plate has an area S = 230 cm2, and the separation between the plates is d = 2.0 mm. Find the current flowing through the capacitor due to a voltage V = 300 V.
Solution. 163. The resistance of a layer of the medium, of thickness dx and at a distance x from the first plate of the capacitor is given by,
 (1)
(1)
Now, since a varies linearly with the distance from the plate. It may be represented as,  at a distance x from any one of the plate.
at a distance x from any one of the plate.
From Eq. (1)

or, 
Hence,

Q. 164. Demonstrate that the law of refraction of direct current lines at the boundary between two conducting media has the form tan α2/tan α1 = σ2/σ1, where σ1 and σ2 are the conductivities of the media, α2 and α1 are the angles between the current lines and the normal of the boundary surface.
Solution. 164. By charge conservation, current j, leaving the medium (1) must enter the medium (2). Thus


which is a consequence of 


Q. 165. Two cylindrical conductors with equal cross-sections and different resistivities p1 and p2 are put end to end. Find the charge at the boundary of the conductors if a current I flows from conductor 1 to conductor 2.
Solution. 165. The electric field in conductor 1 is

and that in 2 is 
Applying Gauss’ theorem to a small cylindrical pill-box at the boundary.

Thus, 
a nd charge at the boundary 
Q. 166. The gap between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is filled up with two dielectric layers 1 and 2 with thicknesses d1 and d2, permittivities ε1 and ε2, and resistivities p1 and p2. A de voltage V is applied to the capacitor, with electric field directed from layer 1 to layer 2. Find σ, the surface density of extraneous charges at the boundary between the dielectric layers, and the condition under which σ = 0.
Solution. 166. 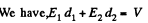
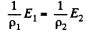
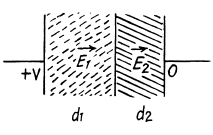
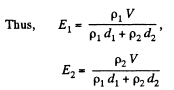
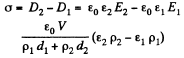
Q. 167. An inhomogeneous poorly conducting medium fills up the space between plates 1 and 2 of a parallel-plate capacitor. Its permittivity and resistivity vary from values ε1, p1 at plate 1 to values ε2, p2 at plate 2. A de voltage is applied to the capacitor through which a steady current I flows from plate 1 to plate 2. Find the total extraneous charge in the given medium.
Solution. 167. By current conservation
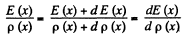
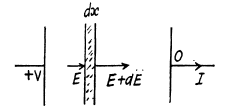
This has the solution,
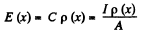
Hence charge induced in the slice per unit area
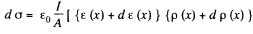
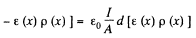
Thus, 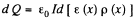
Hence total charge induced, is by integration,
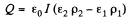
Q. 168. The space between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is filled up with inhomogeneous poorly conducting medium whose resistivity varies linearly in the direction perpendicular to the plates. The ratio of the maximum value of resistivity to the minimum one is equal to η The gap width equals d. Find the volume density of the charge in the gap if a voltage V is applied to the capacitor. ε is assumed to be 1everywhere.
Solution. 168. As in the previous problem
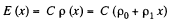
where 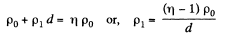
By integration 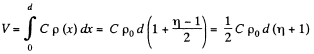
Thus 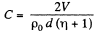
Thus volume density of charge present in the medium
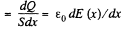
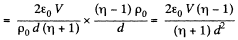
Q. 169. A long round conductor of cross-sectional area S is made of material whose resistivity depends only on a distance r from the axis of the conductor as p = α/r2, where a is α constant. Find:
(a) the resistance per unit length of such a conductor;
(b) the electric field strength in the conductor due to which a current I flows through it.
Solution. 169. (a) Consider a cylinder of unit length and divide it into shells of radius r and thickness dr Different sections are in parallel. For a typical section,
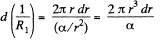
Integrating, 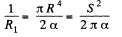
or, 
(b) Suppose the electric filed inside is Ez = E0 (Z axis is along the axiz of the conductor). This electric field cannot depend on r in steady conditions when other components of E are absent, otherwise one violates the circulation theorem
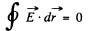
The current through a section between radii (r + dr, r) is
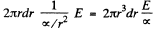
Thus 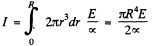
Hence 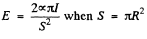
Q. 170. A capacitor with capacitance C = 400 pF is connected via a resistance R = 650 Ω to a source of constant voltage V0. How soon will the voltage developed across the capacitor reach a value V = 0.90 V0?
Solution. 170. The formula is, 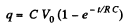
or, 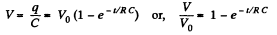
or, 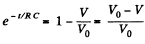
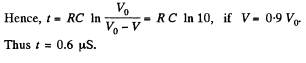
Q. 171. A capacitor filled with dielectric of permittivity e = 2.1 loses half the charge acquired during a time interval τ = 3.0 min. Assuming the charge to leak only through the dielectric filler, calculate its resistivity.
Solution. 171. The charge decays according to the foumula
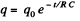
Here, RC = mean life = Half-life/ln 2
So, half life = T = R C In 2
But, 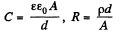
Hence, 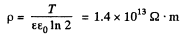
Q. 172. A circuit consists of a source of a constant 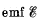 and a resist ante R and a capacitor with capacitance C connected in series. The internal resistance of the source is negligible. At a moment t = 0 the capacitance of the capacitor is abruptly decreased η-fold. Find the current flowing through the circuit as a function of time t.
and a resist ante R and a capacitor with capacitance C connected in series. The internal resistance of the source is negligible. At a moment t = 0 the capacitance of the capacitor is abruptly decreased η-fold. Find the current flowing through the circuit as a function of time t.
Solution. 172. Suppose q is the charge at time t. Initially 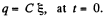
Then at time t,
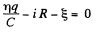
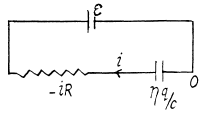
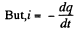 (- sign because charge decreases)
(- sign because charge decreases)
so 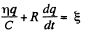
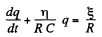
or, 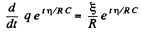
or, 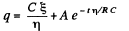
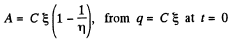
Hence, 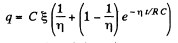
Finally, 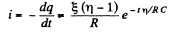
Q. 173. An ammeter and a voltmeter are connected in series to a battery with an emf 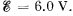 When a certain resistance is connected in parallel with the voltmeter, the readings of the latter decrease η = 2.0 times, whereas the readings of the ammeter increase the same number of times. Find the voltmeter readings after the connection of the resistance.
When a certain resistance is connected in parallel with the voltmeter, the readings of the latter decrease η = 2.0 times, whereas the readings of the ammeter increase the same number of times. Find the voltmeter readings after the connection of the resistance.
Solution. 173. Let r = internal resistance of the battery. We shall take the resistance of the ammeter to be = 0 and that o f voltmeter to be G.
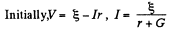
So, 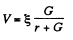 (1)
(1)
After the voltmeter is shunted
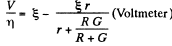 (2)
(2)
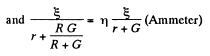 (3)
(3)
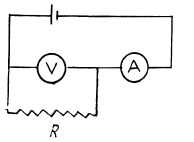
From (2) and (3) we have
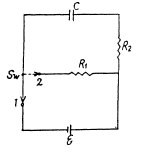
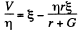 (4)
(4)
From (1) and (4)
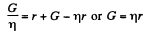
Then (1) gives the required reading
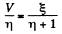
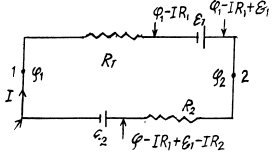
Q. 174. Find a potential difference φ1 — φ2 between points 1 and 2 of the circuit shown in Fig. 3.39 if R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, 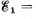 5.0 V, and
5.0 V, and 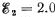 V. The internal resist- ances of the current sources are negligible.
V. The internal resist- ances of the current sources are negligible.
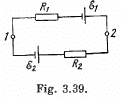
Solution. 174. Assume the current flow, as shown. Then potentials are as shown. Thus,
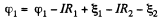
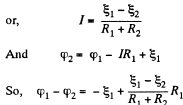
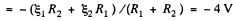
Q. 175. Two sources of current of equal emf are connected in series and have different internal resistances R1 and R2. (R2 > R1). Find the external resistance R at which the potential difference across the terminals of one of the sources (which one in particular?) becomes equal to zero.
Solution. 175. Let, us consider the current i, flowing through the circuit, as shown in the figure. Applying loop rule for the circuit, - Δ φ = 0
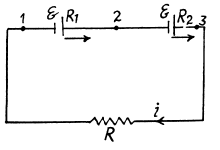
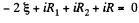
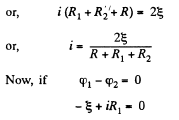
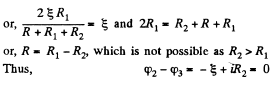
or, 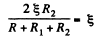
So, 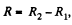 which is the required resistance.
which is the required resistance.
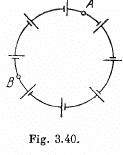
Q. 176. N sources of current with different emf's are connected as shown in Fig. 3.40. The emf's of the sources are proportional to their internal resistances, i.e. 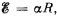 where a is an assigned constant. The lead wire resistance is negligible. Find:
where a is an assigned constant. The lead wire resistance is negligible. Find:
(a) the current in the circuit;
(b) the potential difference between points A and B dividing the circuit in n and N — n links.
Solution. 176. (a) Current, 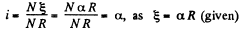
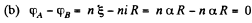
Q. 177. In the circuit shown in Fig. 3.41 the sources have emf's 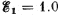 V and
V and 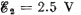 and the resistances have the values R1 = 10 Ω and R2 = 20 Ω. The internal resistances of the sources are negligible. Find a potential difference φA — φB between the plates A and B of the capacitor C.
and the resistances have the values R1 = 10 Ω and R2 = 20 Ω. The internal resistances of the sources are negligible. Find a potential difference φA — φB between the plates A and B of the capacitor C.
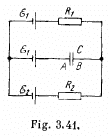
Solution. 177. As the capacitor is fully charged, no current flows through it So, current
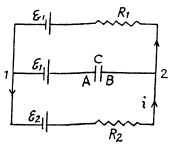
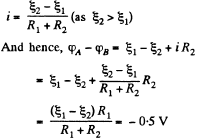
Q. 178. In the circuit shown in Fig. 3.42 the emf of the source is equal to 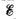 = 5.0 V and the resistances are equal to R1 = 4.0 Ω and R2 = 6.0 Ω. The internal resistance of the source equals R = 0.10 Ω. Find the currents flowing through the resistances R1 and R2.
= 5.0 V and the resistances are equal to R1 = 4.0 Ω and R2 = 6.0 Ω. The internal resistance of the source equals R = 0.10 Ω. Find the currents flowing through the resistances R1 and R2.
Solution. 178. Let us make the current distribution, as shown in the figure.
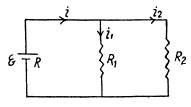
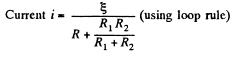
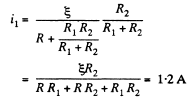
So, current through the resistor R1,
and similary, current through the resistor R2,
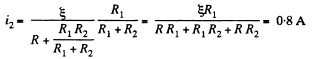
Q. 179. Fig. 3.43 illustrates a potentiometric circuit by means of which we can vary a voltage V applied to a certain device possessing a resistance R. The potentiometer has a length l and a resistance R0, and voltage V0 is applied to its terminals. Find the voltage V fed to the device as a function of distance x. Analyse separately the case R ≫ R0.
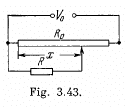
Solution. 179.
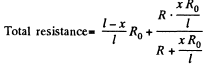
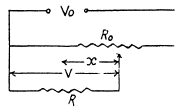
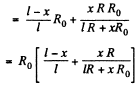
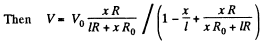
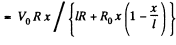
For 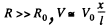
Q. 180. Find the emf and the internal resistance of a source which is equivalent to two batteries connected in parallel whose emf's are equal to 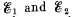 and internal resistances to R1 and R2.
and internal resistances to R1 and R2.
Solution. 180. Let us connect a load of resistance K between the points A and B (Fig.)
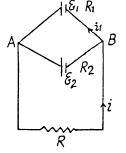
From the loop rule, Δ φ = 0, we obtain
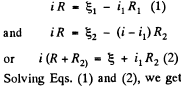
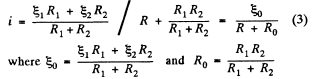
Thus one can replace the given arrangement of the cells by a single cell having the emf 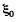 and internal resistance R0.
and internal resistance R0.
Q. 181. Find the magnitude and direction of the current flowing through the resistance R in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.44 if the emf's of the sources are equal to 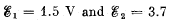 and the resistances are equal to R1 =10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, R = 5.0 Ω. The internal resistances of the sources are negligible.
and the resistances are equal to R1 =10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, R = 5.0 Ω. The internal resistances of the sources are negligible.
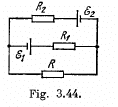
Solution. 181. Make the current distribution, as shown in the diagram
Now, in the loop 12341, applying - Δφ = 0
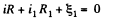 (1)
(1)
and in the loop 23562,
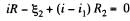 (2)
(2)
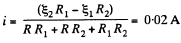
and it is directed from left to the right
Q. 182. In the circuit shown in Fig. 3.45 the sources have emf's 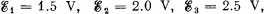 and the resistances are equal to R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, R3 = 30 Ω. The internal resistances of the sources are negligible. Find:
and the resistances are equal to R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, R3 = 30 Ω. The internal resistances of the sources are negligible. Find:
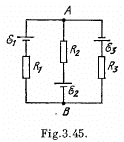
(a) the current flowing through the resistance R1;
(b) a potential difference φA — φB between the points A and B.
Solution. 182. At first indicate the currents in the branches using charge conservation (which also includes the point rule).
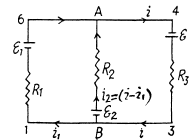
In the loops 1 BA 61 and B34AB from the loop rule, - Δ φ = 0, we get, respectively
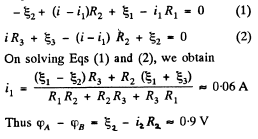
Q. 183. Find the current flowing through the resistance R in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.46. The internal resistances of the batteries are negligible.
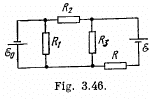
Solution. 183. Indicate the currents in all the branches using charge conservation as shown in the figure. Applying loop rule, - Δφ = 0 in the loops 1A781, 1B681 and B456B, respectively, we get
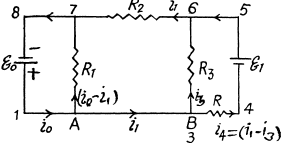
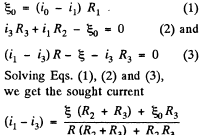
Q. 184. Find a potential difference φA — φB between the plates of a capacitor C in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.47 if the sources have emf's 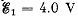 and
and 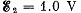 and the resistances are equal to R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, and R3 = 30 Ω. The internal resistances of the sources are negligible.
and the resistances are equal to R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, and R3 = 30 Ω. The internal resistances of the sources are negligible.
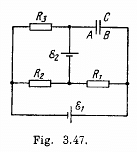
Solution. 184. Indicate the currents in all the branches using charge conservation as shown in the figure. Applying the loop rule (- Δ φ = 0) in the loops 12341 and 15781, we get
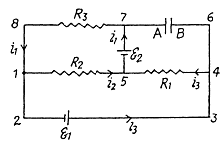
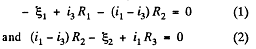
Solving Eqs. (1) and (2), we get
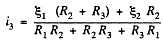
Hence, the sought p.d.
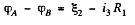
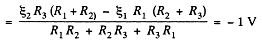
Q. 185. Find the current flowing through the resistance R1 of the circuit shown in Fig. 3.48 if the resistances are equal to R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, and R3 = 30 Ω, and the potentials of points 1, 2, and 3 are equal to φ1 = 10 V, φ2 = 6 V, and φ3 = 5 V
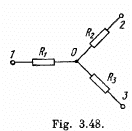
Solution. 185. Let us distribute the currents in the paths as shown in the figure.
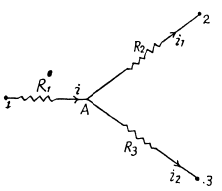
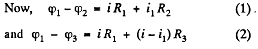
Simplifying Eqs. (1) and (2) we get
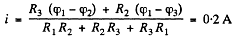
Q. 186. A constant voltage V = 25 V is maintained between points A and B of the circuit (Fig. 3.49). Find the magnitude and direction of the current flowing through the segment CD if the resistances are equal to R1 = 1.0 Ω, R2 = 2.0 Ω, R3 = 3.0 Ω, and R4 = 4.0 Ω.
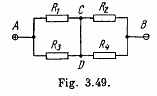
Solution. 186. Current is as shown. From Kirchhoffs Second law
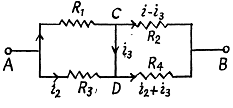
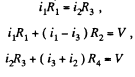
Eliminating i2
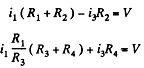
Hence
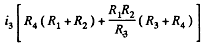
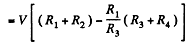
or, 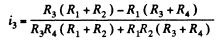
On substitution we get i3 = 1.0 A from C to D
Q. 187. Find the resistance between points A and B of the circuit shown in Fig. 3.50.
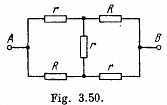
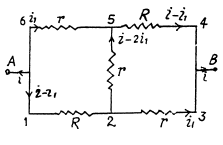
Solution. 187. From the symmetry of the problem, current flow is indicated, as shown in the figure.
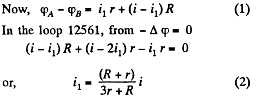
Equivalent resistance between the terminals A and B using (1) and (2),
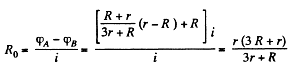
Q. 188. Find how the voltage across the capacitor C varies with time t (Fig. 3.51) after the shorting of the switch Sw at the moment t = 0.
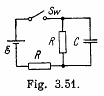
Solution. 188. Let, at any moment of time, charge on the plates be +qr and - q respectively, then voltage across the capacitor, φ = q/C (1)
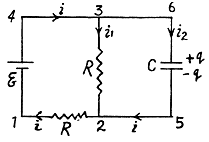
Now, from charge conservation,
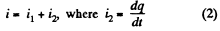
In the loop 65146, using - Δ φ • 0.
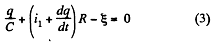
[using (1) and (2)]
In the loop 25632, using - Δ φ = 0
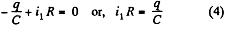
From (1) and (2),
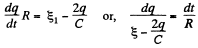 (5)
(5)
On integrating the expression (5) between suitable limits,
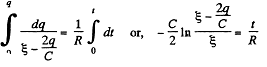
Thus 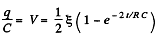
Q. 189. What amount of heat will be generated in a coil of resistance R due to a charge q passing through it if the current in the coil
(a) decreases down to zero uniformly during a time interval Δt;
(b) decreases down to zero halving its value every Δt seconds?
Solution. 189. (a) As current i is linear function of time, and at t = 0 and Δt, it equals i0 and zero respectively, it may be represented as,
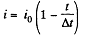
Thus 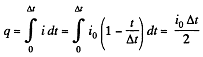
So, 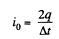
Hence, 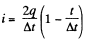
The heat generated.
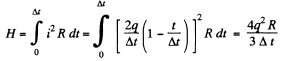
(b) Obviously the current through the coil is given by
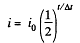
Then charge 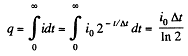
So, 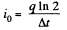
And hence, heat generated in the circuit in the time interval t [0, ∞],
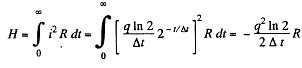
Q. 190. A de source with internal resistance R0 is loaded with three identical resistances R interconnected as shown in Fig. 3.52. At what value of R will the thermal power generated in this circuit be the highest?
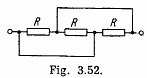
Solution. 190. The equivalent circuit may be drawn as in the figure.
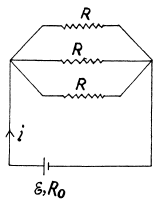
Resistance o f the network 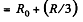
Let, us assume that e.m.f. of the cell is then current
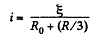
Now, thermal power, generated in the circuit

Q. 191. Make sure that the current distribution over two resistances R1 and R2 connected in parallel corresponds to the minimum thermal power generated in this circuit.
Solution. 191. We assume current conservation but not KirchhofTs second law. Then thermal power dissipated is
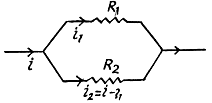
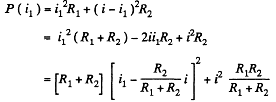
The resistances being positive we see that the power dissipated is minimum when
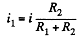
This corresponds to usual distribution of currents over resistance joined is parallel.
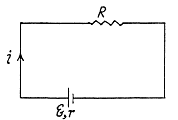
Q. 192. A storage battery with emf 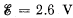 loaded with an external resistance produces a current I = 1.0 A. In this case the potential difference between the terminals of the storage battery equals V = 2.0 V. Find the thermal power generated in the battery and the power developed in it by electric forces.
loaded with an external resistance produces a current I = 1.0 A. In this case the potential difference between the terminals of the storage battery equals V = 2.0 V. Find the thermal power generated in the battery and the power developed in it by electric forces.
Solution. 192. Let, internal resistance of the cell be r, then
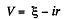 (1)
(1)
where i is the current in the circuit. We know that thermal power generated in the battery.
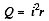
Putting r from (1) in (2), we obtain,
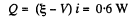
In a battery work is done by electric forces (whose origin lies in the chemical processes going on inside the cell). The work so done is stored and used in the electric circuit outside. Its magnitude just equals the power used in the electric circuit We can say that net power developed by the electric forces is
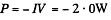
Minus sign means that this is generated not consumed.
Q. 193. A voltage V is applied to a de electric motor. The armature winding resistance is equal to R. At what value of current flowing through the winding will the useful power of the motor be the highest? What is it equal to? What is the motor efficiency in this case?
Solution. 193. As far as motor is concerned the power delivered is dissipated and can.be represented by a load, R0 . Thus
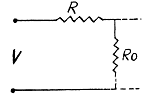
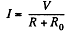
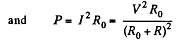
This is maximum when R0 = R and the current / is then
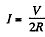
The maximum power delivered is
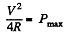
The power input is 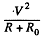 and its value when P is maximum is
and its value when P is maximum is 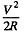
The efficiency then is 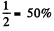
Q. 194. How much (in per cent) has a filament diameter decreased due to evaporation if the maintenance of the previous temperature required an increase of the voltage by η = 1.0%? The amount of heat transferred from the filament into surrounding space is assumed to be proportional to the filament surface area.
Solution. 194. If the wire diameter decreases by δ then by the information given
P = Power input 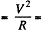 heat lost through the surface, H.
heat lost through the surface, H.
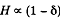 like the surface area and
like the surface area and
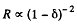
So, 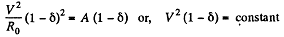
But 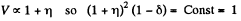
Thus 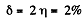
Q. 195. A conductor has a temperature-independent resistance R and a total heat capacity C. At the moment t = 0 it is connected to a de voltage V. Find the time dependence of a conductor's temperature T assuming the thermal power dissipated into surrounding space to vary as q = k (T — T0), where k is a constant, T0 is the environmental temperature (equal to the conductor's temperature at the initial moment)
Solution. 195. The equation of heat balance is
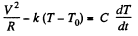
Put 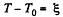
So, 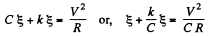
or, 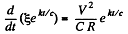
or, 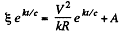
where A is a constant. Clearly
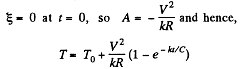
Q. 196. A circuit shown in Fig. 3.53 has resistances R1 = 20Ω and R2 = 30 Q. At what value of the resistance Rx will the thermal power generated in it be practically independent of small variations of that resistance? The voltage between the points A and B is supposed to be constant in this case.
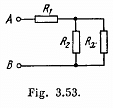
Solution. 196. 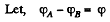
Now, thermal power generated in the resistance Rx,
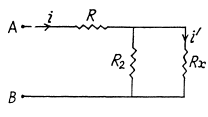
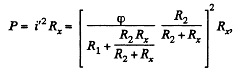
For P to be independent of Rx,
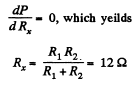
Q. 197. In a circuit shown in Fig. 3.54 resistances R1 and R2 are known, as well as emf's 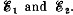 The internal resistances of the sources are negligible. At what value of the resistance R will the thermal power generated in it be the highest? What is it equal to?
The internal resistances of the sources are negligible. At what value of the resistance R will the thermal power generated in it be the highest? What is it equal to?
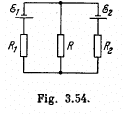
Solution. 197. Indicate the currents in the circuit as shown in the figure. Appying loop rule in the closed loop 12561, - Δφ = 0 we get
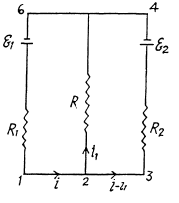
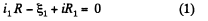
and in the loop 23452,
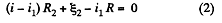
Solving (1) and (2), we get,
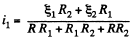
So, thermal power, generated in the resistance R,
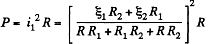
For P to be maximum, 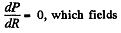
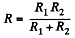
Hence, 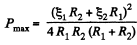
Q. 198. A series-parallel combination battery consisting of a large number N = 300 of identical cells, each with an internal resistance r = 0.3 Ω, is loaded with an external resistance R = 10 Ω. Find the number n of parallel groups consisting of an equal number of cells connected in series, at which the external resistance generates the highest thermal power.
Solution. 198. Let, there are x number of cells, connected in series in each of the n parallel groups
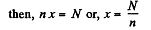 (1)
(1)
Now, for any one of the loop, consisting of x cells and the resistor R, from loop rule
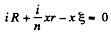
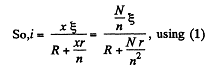
Heat generated in the resistor R,
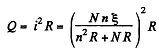 (2)
(2)
and for (2 to be maximum, 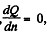 which yields
which yields
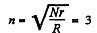
Q. 199. A capacitor of capacitance C = 5.00 µF is connected to a source of constant emf 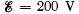 (Fig. 3.55). Then the switch Sw was thrown over from contact 1 to contact 2. Find the amount of heat generated in a resistance R1 = 500 Ω if R2 = 330 Ω.
(Fig. 3.55). Then the switch Sw was thrown over from contact 1 to contact 2. Find the amount of heat generated in a resistance R1 = 500 Ω if R2 = 330 Ω.
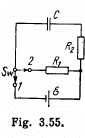
Solution. 199. When switch 1 is closed, maximum chaige accumulated on the capacitor,
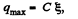 (1)
(1)
and when switch 2 is closed, at any arbitrary instant of time,
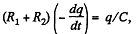
because capacitor is discharging.
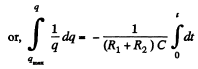
Integrating, we get
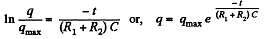 (2)
(2)
Differentiating with respect to time,
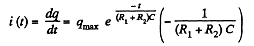
or, 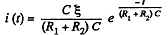
Negative sign is ignored, as we are not interested in the direction of the current.
thus. 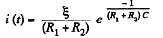 (3)
(3)
When the switch (Sw) is at the position 1, the charge (maximum) accumalated on the capacitor is,
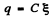
When the Sw is thrown to position 2, the capacitor starts discharging and as a result the electric energy stored in the capacitor totally turns into heat energy tho’ the resistors R1 and R2 (during a very long interval of time). Thus from the energy conservation, the total heat liberated tho the resistors.
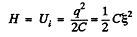
During Hie process of discharging of the capacitor, the current tho’ the resistors and R2 is the same at all the moments of time, thus
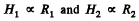
So, 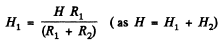
Hence 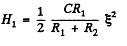
Q. 200. Between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor there is a metallic plate whose thickness takes η = 0.60 of the capacitor gap. When that plate is absent the capacitor has a capacity C = 20 nF. The capacitor is connected to a de voltage source V = 100 V. The metallic plate is slowly extracted from the gap. Find:
(a) the energy increment of the capacitor;
(b) the mechanical work performed in the process of plate extraction.
Solution. 200. When the plate is absent the capacity of the condenser is
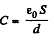
When it is present, the capacity is
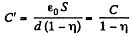
(a) The energy increment is clearly.
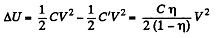
(b) The charge on the plate is
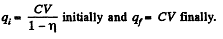
A charge 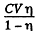 has flown through the battery charging it and withdrawing
has flown through the battery charging it and withdrawing 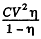 units of energy from the system into the battery. The energy of the capacitor has decreased by just half of this. The remaining half i.e.
units of energy from the system into the battery. The energy of the capacitor has decreased by just half of this. The remaining half i.e. 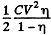 must be the work done by the external agent in withdrawing the plate. This ensures conservation of energy.
must be the work done by the external agent in withdrawing the plate. This ensures conservation of energy.
Q. 201. A glass plate totally fills up the gap between the electrodes of a parallel-plate capacitor whose capacitance in the absence of that glass plate is equal to C = 20 nF. The capacitor is connected to a do voltage source V = 100 V. The plate is slowly, and without friction, extracted from the gap. Find the capacitor energy increment and the mechanical work performed in the process of plate extraction.
Solution. 201. Initially, capacitance of the system = C ε
So, initial energy of the system : 
and finally, energy of the capacitor : 
Hence capacitance energy increment,

From energy conservation

(as there is no heat liberation)



Q. 202. A cylindrical capacitor connected to a de voltage source V touches the surface of water with its end (Fig. 3.56). The separation d between the capacitor electrodes is substantially less than their mean radius. Find a height h to which the water level in the gap will rise. The capillary effects are to be neglected.

Solution. 202. If C0 is the initial capacitance of the condenser before water rises in it then

(R is the mean radius and / is the length of the capacitor plates.)
Suppose the liquid rises to a height h in it. Then the capacitance of the condenser is

and energy of the capacitor and the liquid (including both gravitational and electrosatic contributions) is

If the capacitor were not connected to a battery this energy would have to be minimized.
But the capacitor is connected to the battery and, in effect, the potential energy of the whole system has to be minimized. Suppose we increase h by bh. Then the energy of the capacitor and the liquid increases by

and that of the cell diminishes by the quantity Acell which is the p rod uct o f charge flown and V

In equilibrium, the two must balance; so

Hence 
Q. 203. The radii of spherical capacitor electrodes are equal to a and b, with a < b. The interelectrode space is filled with homogeneous substance of permittivity ε and resistivity p. Initially the capacitor is not charged. At the moment t = 0 the internal electrode gets a charge q0. Find:
(a) the time variation of the charge on the internal electrode;
(b) the amount of heat generated during the spreading of the charge.
Solution. 203. (a) Let us mentally islolate a thin spherical layer with inner and outer radii r and r + dr respectively. Lines of current at all the points of this layer are perpendicular to it and therefore such a layer can be treated as a spherical conductor of thickness dr and cross sectional area 4 πr2 . Now, we know that resistance,
 (1)
(1)
Integrating expression (1) between the limits,
 (2)
(2)
Capacitance of the network,  (3)
(3)
and  (4)
(4)
also,  (5)
(5)
From Eqs. (2), (3), (4) and (5) we get,

Integrating 
Hence 
(b) From energy conservation heat generated, during the spreading of the charge,

Q. 204. The electrodes of a capacitor of capacitance C = 2.00 μF carry opposite charges q0 = 1.00 mC. Then the electrodes are interconnected through a resistance R = 5.0 MΩ. Find:
(a) the charge flowing through that resistance during a time interval τ = 2.00 s;
(b) the amount of heat generated in the resistance during the same interval.
Solution. 204. (a) Let, at any moment of time, charge on the plates be (q0 - q) then current through the resistor,  because the capacitor is discharging.
because the capacitor is discharging.
or, 

Now, applying loop rule in the circuit,

or, 
or, 
At t = 0, q = 0 and at t = τ, q = q
So, 
Thus 
(b) Amount of heat generated = decrement in capacitance energy

Q. 205. In a circuit shown in Fig. 3.57 the capacitance of each capacitor is equal to C and the resistance, to R. One of the capacitors was connected to a voltage V0 and then at the moment t = 0 was shorted by means of the switch Sw. Find:
(a) a current I in the circuit as a function of time t;
(b) the amount of generated heat provided a dependence I (t) is known.

Solution. 205. Let, at any moment of time, charge flown be q then current 
Applying loop rule in the circuit, 



Hence, 
Now, heat liberaled,

Q. 206. A coil of radius r = 25 cm wound of a thin copper wire of length l = 500 m rotates with an angular velocity ω = 300 rad/s about its axis. The coil is connected to a ballistic galvanometer by means of sliding contacts. The total resistance of the circuit is equal to R = 21 Ω. Find the specific charge of current carriers in copper if a sudden stoppage of the coil makes a charge q = 10 nC flow through the galvanometer.
Solution. 206. in a rotating frame, to first order in ω, the main effect is a coriolis force  This unbalanced force will cause electrons to react by setting up a magnetic field
This unbalanced force will cause electrons to react by setting up a magnetic field  that the magnetic force
that the magnetic force  balances the coriolis force.
balances the coriolis force.
Thus 
The flux associated with this is

where  is the number of turns of the ring. If ω changes (and there is time for the electron to rearrange) then B also changes and so
is the number of turns of the ring. If ω changes (and there is time for the electron to rearrange) then B also changes and so  An emf will be induced and a current will flow. This is
An emf will be induced and a current will flow. This is

The total charge flowing through the ballastic galvanometer, as the ring is stopped, is

So, 
Q. 207. Find the total momentum of electrons in a straight wire of length l = 1000 m carrying a current I = 70 A.
Solution. 207. Let, n0 be the total number of electoms then, total momentum of electoms,
 (1)
(1)
Now, 
Here Sx = Cross sectional area, p = electron charge density, V = volume of sample From (1) and (2)

Q. 208. A copper wire carries a current of density j = 1.0 A/mm2. Assuming that one free electron corresponds to each copper atom, evaluate the distance which will be covered by an electron during its displacement l = 10 mm along the wire.
Solution. 208. By definition
ne vd = j (where vd is drift velocity, n is number density of electrons.)
Then 
So distance actually travelled

(<v> = mean velocity of thermal motion of an electron)
Q. 209. A straight copper wire of length l = 1000 m and crosssectional area S = 1.0 mm2 carries a current I = 4.5 A. Assuming that one free electron corresponds to each copper atom, find:
(a) the time it takes an electron to displace from one end of the wire to the other;
(b) the sum of electric forces acting on all free electrons in the given wire.
Solution. 209. Let, n be the volume density of electrons, then from 

So, 
(b) Sum of electric forces
 where p is resistivity of die material.
where p is resistivity of die material.

Q. 210. A homogeneous proton beam accelerated by a potential difference V = 600 kV has a round cross-section of radius r = 5.0 mm. Find the electric field strength on the surface of the beam and the potential difference between the surface and the axis of the beam if the beam current is equal to I = 50 mA.
Solution. 210. From Gauss theorem field strength at a surface of a cylindrical shape equals,  where X is the linear chaige density.
where X is the linear chaige density.
Now, 
Also, 
or, 
Hence 
(b) For the point, inside the solid charged cylinder, applying Gauss’ theorem,

or, 
So,from 

or, 
Hence, 
Q. 211. Two large parallel plates are located in vacuum. One of them serves as a cathode, a source of electrons whose initial velocity is negligible. An electron flow directed toward the opposite plate produces a space charge causing the potential in the gap between the plates to vary as φ = ax4/3, where a is a positive constant, and x is the distance from the cathode. Find:
(a) the volume density of the space charge as a function of x;
(b) the current density.
Solution. 211. Between the plates 
or, 

or, 
Let the charge on the electron be - e,
then 
as the electron is initially emitted with neligible energy.

So, 
(j is measued from the anode to cathode, so the - ve sign.)
Q. 212. The air between two parallel plates separated by a distance d = 20 mm is ionized by X-ray radiation. Each plate has an area S = 500 cm2. Find the concentration of positive ions if at a voltage V = 100 V a current I = 3.0 μ,A flows between the plates, which is well below the saturation current. The air ion mobilities are  = 1.37 cm2/(V•s) and
= 1.37 cm2/(V•s) and = 1.91 cm2/(V•s).
= 1.91 cm2/(V•s).
Solution. 212.

So by the definition of the mobility

and 
(The negative ions move towards the anode and the positive ion towards the cathode and the total current is the sum of the currents due to them.) On the other hand, in equilibrium n+ = n_
So, 

Q. 213. A gas is ionized in the immediate vicinity of the surface of plane electrode l (Fig. 3.58) separated from electrode 2 by a distance l. An alternating voltage varying with time t as V = V0 sin cot is applied to the electrodes. On decreasing the frequency ω it was observed that the galvano- meter G indicates a current only at ω < ω0 where ω0 is a certain cut-off frequency. Find the mobility of ions reaching electrode 2 under these conditions.

Solution. 213. Velocity = mobility x field
 which is positive for 0 < ω t < π
which is positive for 0 < ω t < π
So, maximum displacement in one direction is


Thus 
Q. 214. The air between two closely located plates is uniformly ionized by ultraviolet radiation. The air volume between the plates is equal to V = 500 cm3, the observed saturation current is equal to Isat = 0.48 μA. Find :
(a) the number of ion pairs produced in a unit volume per unit time;
(b) the equilibrium concentration of ion pairs if the recombination coefficient for air ions is equal to r = 1.67.10-6 cm3/s.
Solution. 214. When the current is saturated, all the ions, produced, reach the plate.
Then, 
(Both positive ions and negative ions are counted here)
The equation of balance is 
The first term on the right is the production rate and the second term is the recombination rate which by the usual statistical arguments is proportional to n2 (= no of positive ions x no. of -ve ion). In eauilibrium.

so, 
Q. 215. Having been operated long enough, the ionizer producing ni = 3.5.109 cm-3 •s -1 of ion pairs per unit volume of air per unit time was switched off. Assuming that the only process tending to reduce the number of ions in air is their recombination with coefficient r = 1.67.10-6 cm3/s, find how soon after the ionizer's switching off the ion concentration decreases η= 2.0 times.
Solution. 215. Initially 
Since we can assume that the long exposure to the ionizer has caused equilibrium to be set up. Afer the ionizer is switched off,

or 
But 
The concentration will decrease by a factor η when

or, 
Q. 216. A parallel-plate air capacitor whose plates are separated by a distance d = 5.0 mm is first -charged to a potential difference V = 90 V and then disconnected from a de voltage source. Find the time interval during which the voltage across the capacitor decreases by η = 1.0%, taking into account that the average number of ion pairs formed in air under standard conditions per unit volume per unit time is equal to ni = 5.0 cm-3 •s-1 and that the given voltage corresponds to the saturation current.
Solution. 216. Ions produced will cause charge to decay. Clearly,
 decrease of charge
decrease of charge 
or, 
Note , that ni, here, is the number of ion pairs produced.
Q. 217. The gap between two plane plates of a capacitor equal to d is filled with a gas. One of the plates emits v0 electrons per second which, moving in an electric field, ionize gas molecules; this way each electron produces α new electrons (and ions) along a unit length of its path. Find the electronic current at the opposite plate, neglecting the ionization of gas molecules by formed ions.
Solution. 217. If v = number of electrons moving to the anode at distance x, then

Assuming saturation, 
Q. 218. The gas between the capacitor plates separated by a dist- ance d is uniformly ionized by ultraviolet radiation so that ni electrons per unit volume per second are formed. These electrons moving in the electric field of the capacitor ionize gas molecules, each electron producing α new electrons (and ions) per unit length of its path. Neglecting the ionization by ions, find the electronic current density at the plate possessing a higher potential.
Solution. 218. Since the electrons are produced uniformly through the volume, the total current attaining saturation is clearly,

Thus, 
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Electric Current - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is electric current and how is it measured? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of electric currents? |  |
| 3. How does electric current affect resistance in a circuit? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between electric current and electric potential? |  |
| 5. How does the resistance of a wire depend on its length and cross-sectional area? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|


















