Electrostatic Potential | Electricity & Magnetism - Physics PDF Download
Electric potential, in simple terms, is a way to describe how much electric energy a charged object has based on its position relative to other charged objects. It's similar to how we describe a ball's gravitational potential energy based on its height. Electric potential helps us understand how charges interact and move in electric fields. In this document, we will understand the mathematical interpretation of electric potential.
Curl of Electric field
Consider a point charge at the origin, then the electric field at a distance r is given by,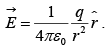 Now we will calculate the line integral of this field from some point a to some other point:
Now we will calculate the line integral of this field from some point a to some other point: 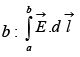 In spherical coordinates,
In spherical coordinates,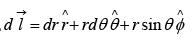
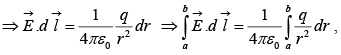
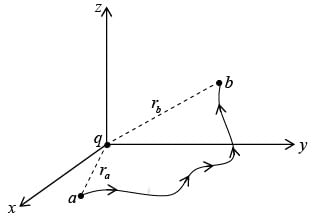
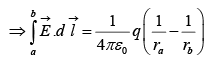
where ra is the distance from the origin to point a and rb is the distance to b.
Then integral around a closed path is zero i.e.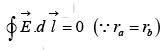 This line integral is independent of the path. It depends on two endpoints.
This line integral is independent of the path. It depends on two endpoints.
Applying Stokes theorem, we get 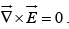 The electric field is not just any vector but only those vectors whose curl is zero. If we have many charges, the principle of superposition states that the total field is the vector sum of their fields:
The electric field is not just any vector but only those vectors whose curl is zero. If we have many charges, the principle of superposition states that the total field is the vector sum of their fields:
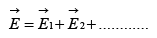 So,
So,
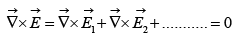 Since
Since 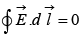 the line integral is independent of the path.
the line integral is independent of the path.
So, we can define a function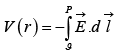 where ϑ is some standard reference point V and then depends only on the point r. It is called the electric potential.
where ϑ is some standard reference point V and then depends only on the point r. It is called the electric potential.
The potential difference between two points a and b is
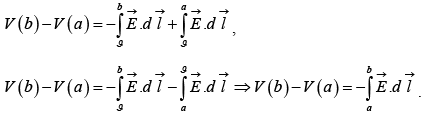
Now, the fundamental theorem for gradients states that
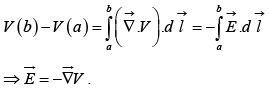
Potential obeys the superposition principle.
The potential of localized charges
The potential of a point charge q is 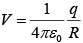 where R is the distance from the charge.
where R is the distance from the charge.
The potential of a collection of point charges is 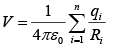
For continuous volume charge distribution 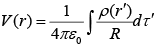
The potential of line and surface charges are 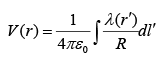 and
and
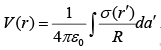
Example 1: Which one of these is an impossible electrostatic field?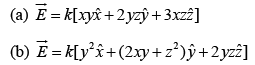
(a)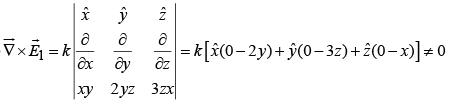 So,
So, 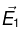 is an impossible electrostatic field.
is an impossible electrostatic field.
(b) 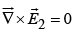 so
so 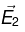 is a possible electrostatic field.
is a possible electrostatic field.
Example 2: Find the potential inside and outside a spherical shell of radius R, charge q.
From Gauss's law the field
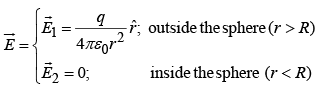
Potential outside ( r >R) is: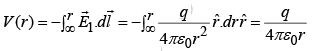
Potential inside ( r <R) is: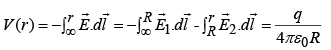
So potential inside the spherical shell is constant.
Thus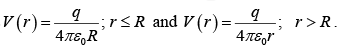
Example 3: Find the potential inside and outside a uniformly charged solid sphere whose radius is R and whose total charge is q.
From Gauss's law the field 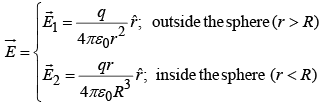
Potential outside ( r >R) is: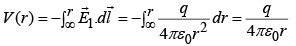
Potential inside ( r <R) is: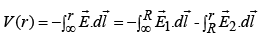
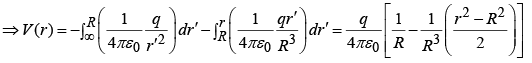
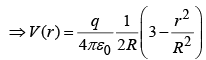
Example 4: Find the potential distance r from an infinitely long straight wire that carries a uniform line charge λ.
Since 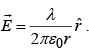 In this case, we cannot set the reference point at ∞ , since the charge
In this case, we cannot set the reference point at ∞ , since the charge
itself extends to ∞ . Let’s set it at r =a
Then, 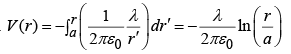
|
82 videos|32 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Electrostatic Potential - Electricity & Magnetism - Physics
| 1. What is the significance of the curl of the electric field in electrostatics? |  |
| 2. What are the electrostatic boundary conditions and why are they important? |  |
| 3. How is work and energy related to electrostatics? |  |
| 4. What are the basic properties of conductors in electrostatics? |  |
| 5. How do electric field, potential, and boundary conditions relate in IIT JAM preparation? |  |





















