Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Energy from Fuels
Energy from Fuels | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Fossil Fuels
- Fossil fuels refer to coal, natural gas (predominantly methane) utilized in household heating systems and cookers, and crude oil that undergoes refinement to produce petrol, diesel, and various other fuels.

- Fossil fuels are created from the remnants of plants and animals.
- Chemical energy stored in fossil fuels originally derived from sunlight.
- Energy from the sun was converted to the chemical energy store of plants through photosynthesis.
- Animals consumed the plants, transferring the energy to their chemical store.
Advantages
- Current transportation and electricity systems heavily depend on fossil fuels due to their abundant availability.
- Historically, fossil fuels were pivotal for large-scale energy production, but their reliability is shifting with depleting supplies and escalating prices.
Disadvantages
- Fossil fuels take millions of years to form, rendering them non-renewable resources.
- The escalating demand coupled with a diminishing supply leads to price hikes, with predictions indicating a complete depletion within the next 200 years.
- The combustion of fossil fuels releases harmful gases like carbon dioxide, contributing to the greenhouse effect, and sulphur dioxide, which leads to acid rain.
- While technologies exist to capture these gases before they are released into the atmosphere, the process is costly.
Usage of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels serve various purposes:
- Transportation
- Electricity generation
- Heating
Transport
- Most vehicles globally run on petroleum derivatives like gasoline, diesel, and kerosene, all derived from crude oil, a fossil fuel.
- An increasing number of vehicles are adopting electric power.
- The benefit of electric vehicles is their zero carbon emissions during operation.
- However, a drawback is that during charging, they rely on the National Grid, which currently employs both renewable and non-renewable energy sources.
Electricity Generation
- Fossil fuels like coal and oil are utilized for generating energy instantly as needed.
- When coal is burned, energy is released from its stored chemicals.
- This energy is then employed to heat water, producing steam.
- The steam is directed through a turbine, which sets coils in motion within a magnetic field in the generator.
- As a result, electricity is generated in the process.
- Finally, the electricity is transmitted via a step-up transformer and conveyed through electrical lines.
- The steam produced in the turbine is condensed and then cycled back into the boiler for reuse.

- The demand for electricity is at an all-time high due to the global population of nearly 8 billion people.
- Meeting this demand requires a diverse mix of energy resources.
- The high demand for electricity necessitates the use of all available energy resources.
- However, a significant portion (84%) of the world's energy is derived from non-renewable sources that harm the environment.
- Efforts are underway to develop more sustainable methods of electricity production using carbon-neutral resources.

Heating
- Most residences in colder regions use central heating systems that run on natural gas to warm water, circulated through radiators for home heating.
- These systems efficiently utilize natural gas for heating purposes.
Bio Fuels
- Biofuels are derived from plant materials where the energy from sunlight is captured and stored in the plants.
- This stored energy can be converted into fuels like ethanol or methane, which can be used as alternatives to traditional fossil fuels.
- However, it's important to note that biofuels only have about half the energy density of fossil fuels.
Advantages
- Biofuels are considered a renewable resource since they are derived from plant matter.
- Vehicles can be powered by biofuels, reducing the dependence on non-renewable fossil fuels.
- Additionally, biofuels are often deemed carbon-neutral, meaning they do not contribute to net carbon emissions in the atmosphere.
- Unlike the burning of fossil fuels, the use of biofuels does not produce sulfur dioxide, a harmful air pollutant.
Disadvantages
- Cultivating biofuel-producing crops requires a significant amount of time.
- This cultivation demands extensive land and resources that could otherwise be allocated to food production.
- Combusting biofuels emits carbon dioxide into the air.
- Despite this, it's deemed carbon neutral as plants absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.

Question for Energy from FuelsTry yourself: What is the primary disadvantage of fossil fuels?View Solution
Nuclear Fuel
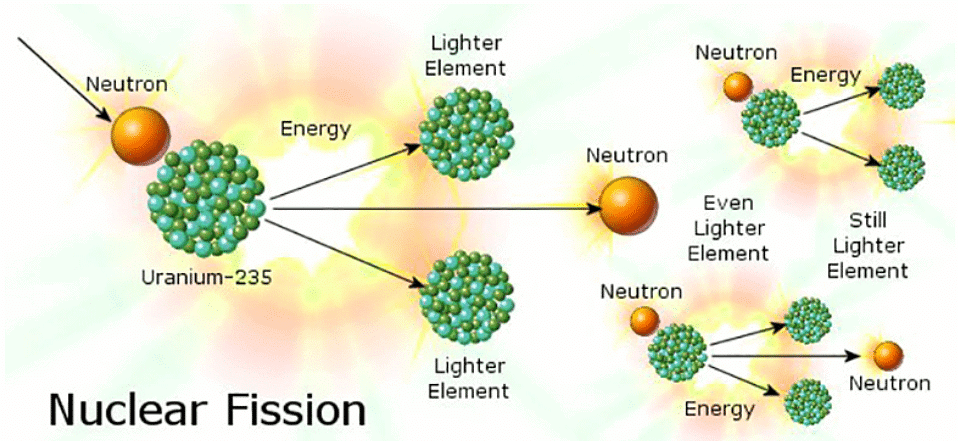
- Energy stored within atomic nuclei can be released through nuclear fission, where a nucleus splits into two, releasing energy.

- Nuclear power plants employ fission reactions to heat water, which in turn drives turbines to produce electricity.
Advantages
- No pollution is released into the atmosphere by nuclear power.
- Nuclear reactors are safe when functioning correctly and following stringent safety procedures.
- Regular rigorous safety checks are essential for nuclear power plants.
- Nuclear power stations can reliably produce large-scale electricity as needed.
Disadvantages
- Uranium ore found in the ground is utilized for fission reactions, contributing to the generation of nuclear power. However, due to its limited availability, nuclear power is classified as a non-renewable resource.
- Nuclear fuels, integral to the process, lead to the production of radioactive waste. This waste necessitates long-term storage for thousands of years, which comes at a considerable cost.
- In the event of an accident at a nuclear reactor, there is a risk of radioactive waste leakage, potentially impacting vast areas and posing significant environmental hazards.
Question for Energy from FuelsTry yourself: What is the main advantage of nuclear power?View Solution
The document Energy from Fuels | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Energy from Fuels - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are fossil fuels and how are they formed? |  |
Ans. Fossil fuels are natural resources such as coal, oil, and natural gas that are formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals that were buried and subjected to high heat and pressure over millions of years.
| 2. What are biofuels and how are they different from fossil fuels? |  |
Ans. Biofuels are renewable fuels derived from organic materials such as plants and algae. Unlike fossil fuels, biofuels are considered to be more environmentally friendly as they produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions when burned.
| 3. How is nuclear fuel different from fossil fuels and biofuels? |  |
Ans. Nuclear fuel is a non-renewable energy source that is derived from uranium and other radioactive elements. Unlike fossil fuels and biofuels, nuclear fuel does not produce greenhouse gas emissions during energy production, but it does pose risks related to radioactive waste disposal and potential accidents.
| 4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using fossil fuels as an energy source? |  |
Ans. Some advantages of using fossil fuels include their abundance, affordability, and reliability. However, the disadvantages include their contribution to air pollution, climate change, and environmental degradation.
| 5. How can we reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and transition to alternative energy sources? |  |
Ans. To reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, we can invest in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. Additionally, implementing energy efficiency measures and promoting sustainable practices can help in transitioning to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches