Environment Audit | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
What is Environmental Audit?
An environmental audit is a systematic process used to assess an organization’s environmental performance. It helps management identify potential environmental hazards and impacts and implement appropriate measures to address them. This process also highlights areas where the organization can improve its environmental performance and shows its commitment to sustainable development.
The environmental audit involves a thorough review of an organization’s activities, operations, and systems to evaluate its environmental impact. This includes checking compliance with environmental regulations, identifying risk areas and opportunities, and assessing the effectiveness of the organization’s environmental management systems.
Types of Environmental Audit
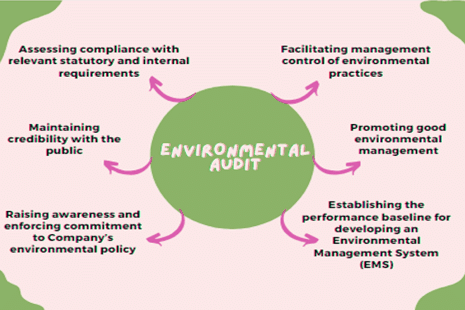
Environmental audits are thorough evaluations designed to assess an organization’s compliance with environmental regulations, identify potential risks, and evaluate the effectiveness of its environmental management systems. There are various types of environmental audits, each focusing on different aspects of environmental performance and regulatory compliance:
Compliance Audit This audit reviews an organization’s adherence to environmental laws, regulations, permits, and internal policies. It identifies non-compliance issues, potential liabilities, and necessary corrective actions to ensure legal compliance with regulations related to air quality, water management, hazardous waste disposal, noise pollution, and other environmental concerns.
Management System Audit A management system audit evaluates the effectiveness of an organization's Environmental Management System (EMS), often based on standards like ISO 14001. It assesses how well the EMS is implemented, maintained, and improved to meet environmental objectives. This includes reviewing documentation, management commitment, operational controls, emergency preparedness, training, and internal audits.
Due Diligence Audit Conducted during mergers, acquisitions, or property transactions, this audit assesses potential environmental liabilities and risks associated with the transaction. It identifies environmental liabilities, compliance status, and financial implications to support informed decision-making. Areas of focus include historical land use, contamination risks, regulatory compliance, environmental permits, and potential cleanup costs.
Risk Assessment Audit This audit evaluates environmental risks linked to specific activities, processes, or facilities. It identifies and prioritizes environmental risks, assesses their potential impacts, and recommends risk management strategies. Key areas include hazardous materials handling, pollution prevention, emergency response plans, and ecological impact assessments.
Energy Audit An energy audit examines energy consumption, identifies opportunities for improving energy efficiency, and promotes sustainable energy practices. It aims to reduce energy use, lower operational costs, and minimize greenhouse gas emissions. The audit covers energy usage patterns, efficiency measures, renewable energy options, and recommendations for energy-saving technologies.
Waste Audit A waste audit assesses an organization’s waste generation, management practices, and potential for waste reduction and recycling. It identifies waste streams, evaluates waste management effectiveness, and suggests strategies for minimizing waste and enhancing recycling rates. This includes waste characterization, segregation practices, waste minimization initiatives, recycling programs, and disposal methods.
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) An EIA evaluates the potential environmental impacts of proposed projects, developments, or policies before they are implemented. It predicts environmental effects, identifies mitigation measures, and ensures sustainable development practices. The assessment includes air quality, water resources, biodiversity, soil quality, socio-economic impacts, and public consultation.
Sustainability Audit This audit assesses an organization’s overall environmental, social, and economic performance against sustainability goals and standards. It evaluates sustainable practices, identifies areas for improvement, and supports corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. Key aspects include environmental footprint, resource efficiency, community engagement, stakeholder relations, ethical business practices, and sustainable supply chain management.
Importance of Environmental Audit
Environmental audits play a crucial role in corporate sustainability by systematically evaluating a company’s environmental performance, policies, and procedures. These audits help businesses meet legal requirements, enhance sustainability efforts, and strengthen their reputation. Here’s why periodic environmental audits are important for companies:
- Regulatory Compliance: Companies conduct environmental audits to ensure they comply with complex and diverse environmental regulations. Regular audits are necessary to confirm adherence to relevant laws and regulations. Non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties, damage to reputation, and legal consequences.
- Identification of Environmental Risks: Environmental audits help identify potential risks associated with company operations, such as air and water pollution, hazardous waste, and carbon emissions. Recognizing these risks is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate them. Addressing environmental risks helps prevent accidents, reduce environmental impact, and avoid legal and reputational issues.
- Opportunities for Improvement: Audits also reveal opportunities for enhancing environmental performance. They can highlight areas where companies can reduce resource consumption, improve efficiency, and lower their carbon footprint. By identifying these areas, businesses can implement sustainability initiatives such as adopting energy-efficient practices, reducing waste, and utilizing renewable energy sources.
- Enhanced Reputation: Conducting environmental audits can boost a company’s reputation. Today, stakeholders—including customers, investors, and the public—are increasingly focused on environmental sustainability. Companies that demonstrate commitment to environmental stewardship and transparency through audits build trust and credibility, which can enhance brand value, foster customer loyalty, and provide a competitive edge.
The Process of Environmental Audit
The environmental audit process involves a systematic and thorough assessment of an organization’s environmental management systems, actions, and outcomes. The key steps in conducting an environmental audit are as follows:
- Step 1: Planning and Preparation: This initial phase involves defining the scope and objectives of the audit. It includes selecting the audit team, and developing the procedures and protocols for the assessment.
- Step 2: Conducting the Audit: During this stage, the audit team gathers data, reviews records, and conducts interviews. Site inspections and sample collection may also be carried out to assess compliance with environmental regulations and standards.
- Step 3: Analyzing the Findings: The team then analyzes the collected data to pinpoint areas of non-compliance and opportunities for improvement. They compile a detailed audit report that includes findings, recommendations, and proposed corrective actions.
- Step 4: Reporting and Follow-up: The final report is presented to management and stakeholders. The organization then formulates a plan to implement the recommendations and corrective actions outlined in the report.
Environmental audits are essential for organizations to enhance their environmental impact and sustainability performance.
What Do Environmental Auditors Do?
 Environmental auditors are professionals trained in environmental management, law, and science who assess and evaluate an organization’s environmental performance. They work with businesses, government agencies, and other entities to ensure environmental regulations are met and to identify areas for improvement.
Environmental auditors are professionals trained in environmental management, law, and science who assess and evaluate an organization’s environmental performance. They work with businesses, government agencies, and other entities to ensure environmental regulations are met and to identify areas for improvement.
Responsibilities of Environmental Auditors:
Environmental auditors have a crucial role in managing environmental impacts. Their key responsibilities include:
- Conducting environmental audits to assess compliance with regulations and standards.
- Identifying potential environmental risks and opportunities for performance enhancement.
- Developing recommendations and corrective actions to address environmental issues.
- Offering advice and guidance on environmental management systems and practices.
- Assisting with environmental reporting and disclosure requirements.
Limitations of Environmental Audits
While valuable, environmental audits have limitations that must be considered to ensure their effectiveness:Limited Scope: Audits often focus on specific facilities or operations, which may not capture the full environmental impact, such as supply chain effects or product disposal. Audits should cover all relevant aspects of an organization’s environmental impact.
Limited Standards: Existing standards like ISO 14001 may not cover every aspect of an organization's environmental impact. Additional criteria may be needed for a comprehensive assessment.
Subjectivity: Audits are subject to the auditor's interpretation, which can lead to inconsistent conclusions. Personal biases or client interests may also affect outcomes. Rigorous training and certification for auditors are crucial to minimize these issues.
Reliance on Self-Reporting: Audits depend on data provided by the organization, which may be misrepresented. Spot checks and independent verification are necessary to ensure data accuracy.
Scope of Environmental Audit
The scope of an environmental audit typically includes:
Regulatory Compliance: Evaluating adherence to environmental laws and standards, reviewing permits, and inspecting compliance with emission limits and operational requirements.
Environmental Management Systems (EMS): Assessing the effectiveness of the EMS, including its design, implementation, and continuous improvement against standards like ISO 14001.
Operational Practices and Procedures: Examining daily operations that impact the environment, such as resource use, waste generation, and pollution prevention. Identifying opportunities for improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
Environmental Risk Assessment: Identifying and prioritizing environmental risks associated with activities, processes, and facilities, and evaluating hazardous materials management and emergency preparedness.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication: Assessing how the organization communicates environmental performance and risks to stakeholders, enhancing transparency, and ensuring effective engagement and feedback mechanisms.
Environmental Audit Report
An environmental audit report summarizes the findings, observations, and recommendations from the audit. It is a critical tool for evaluating performance, ensuring compliance, and driving improvements in environmental management. The report provides a roadmap for addressing environmental challenges and demonstrating commitment to sustainability.
Conclusion
Environmental audits are essential for evaluating and improving a company’s environmental impact. Regular audits help companies reduce their carbon footprint, enhance sustainability efforts, and ensure regulatory compliance. By proactively addressing environmental issues, companies can achieve financial benefits through waste reduction and improved resource efficiency.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Environment Audit - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is the importance of conducting an Environmental Audit? |  |
| 2. What are the types of Environmental Audits? |  |
| 3. What is the process of conducting an Environmental Audit? |  |
| 4. What do Environmental Auditors do? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of Environmental Audits? |  |
















