SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year > Environment Pollution
Environment Pollution | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Air Pollution |

|
| Water Pollution |

|
| Soil Pollution |

|
| Noise Pollution |

|
| Radio Active Pollution |

|
| E-Waste |

|
| Solid Waste |

|
| Bioremediation |

|
Introduction
- Defined as 'an addition or excessive addition of certain materials to the physical environment (water, air and lands), making it less fit or unfit for life'.
- Pollutants are the materials or factors, which cause adverse effect on the natural quality of any component of the environment.

Classifications
- According to the form in which they persist after release into the environment.
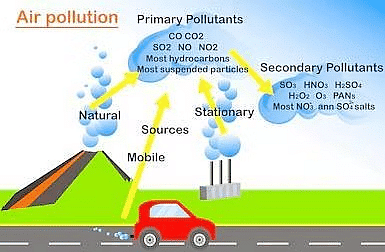
(i) Primary pollutants: These persist in the form in which they are added to the environment. Example: DDT, plastic.
(ii) Secondary Pollutants: These are formed by interaction among the primary pollutants. For example, peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) is formed by the interaction of nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons. - According to their existence in nature.
(i) Quantitative Pollutants: These occur in nature and become pollutant when their concentration reaches beyond a threshold level. Example: carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide.
(ii) Qualitative Pollutants: These do not occur in nature and are man-made. Example: fungicides, herbicides, DDT etc. - According to their nature of disposal.
(i) Biodegradable Pollutants: Waste products, which are degraded by microbial action. Example: sewage.
(ii) Non-biodegradable Pollutants: Pollutants, which are not decomposed by microbial action. Example: plastics, glass, DDT, salts of heavy metals, radioactive substances etc. - According to origin
(i) Natural
(ii) Anthropogenic
Air Pollution
- Aggravated because of four developments: Increasing traffic, growing cities, rapid economic development, and industrialization contamination of air by the discharge of harmful substances.
➢
Major air pollutants and their sources
1. Carbon monoxide (CO)
- It is a colourless, odourless gas that is produced by the incomplete burning of carbon - based fuels including petrol, diesel, and wood.
- It is also produced from the combustion of natural and synthetic products such as cigarettes.
- It lowers the amount of oxygen that enters our blood. It can slow our reflexes and make us confused and sleepy.
2. Carbon dioxide CO2
- Principe greenhouse gas
3. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC)
- Gases that are released mainly from air-conditioning systems and refrigeration.
- When released into the air, CFCs rise to the stratosphere, where they come in contact with few other gases, which lead to a reduction of the ozone layer that protects the earth from the harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun.
4. Lead
- Present in petrol, diesel, lead batteries, paints, hair dye products, etc.
- Affects children in particular.
- Cause nervous system damage and digestive problems and, in some cases, cause cancer.
5. Ozone
- Occurs naturally in the upper layers of the atmosphere.
- At-the ground level, it is a pollutant with highly toxic effects.
- Vehicles and industries are the major source of ground-level ozone emissions.
- Ozone makes our eyes itch, burn, and water. It lowers our resistance to cold and pneumonia.
6. Nitrogen oxide (Nox)
- Causes smog and acid rain. It is produced from burning fuels including petrol, diesel, and Coal.
- Nitrogen oxide can make children susceptible to respiratory diseases in winters.
7. Suspended particulate matter (SPM)
- Consists of solids in the air in the form of smoke, dust, and vapour that can remain suspended for extended periods
- The finer of these particles when breathed in can lodge in our lungs and cause lung damage and respiratory problems.
8. Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
- A gas produced from burning coal, mainly in thermal power plants.
- Some industrial processes, such as production of paper and smelting of metals, produce sulphur dioxide.
- A major contributor to smog and acid rain.
- Sulphur dioxide can lead to lung diseases
9. Smog
- A combination of the words fog and smoke. Smog is a condition of fog that had soot or smoke in it.
- Interaction of sunlight with certain chemicals in the atmosphere.
- Primary components of photochemical smog is ozone.
- Oxides, and sunlight. It is formed when pollutants released from gasoline.
- Ozone is formed through a complex reaction involving hydrocarbons, nitrogen diesel- powered vehicles and oil-based solvents react with heat and sunlight from biofuels, the four most serious pollutants are particulates, carbon monoxide, polycyclic organic matter, and formaldehyde.
Pollutants
1. Volatile organic compounds
- The main indoor sources are perfumes, hair sprays, furniture polish, glues, air fresheners, moth repellents, wood preservatives, and other products.
- Biological pollutants - It includes pollen from plants, mite, and hair from pets, fungi, parasites, and some bacteria.
2. Formaldehyde
Mainly from carpets, particle boards, and insulation foam. It causes irritation to the eyes and nose and allergies.
3. Radon
It is a gas that is emitted naturally by the soil. Due to modern houses having poor ventilation, it is confined inside the house and causes lung cancers.
Fly Ash
Ash is produced whenever combustion of solid material takes place.
- Aluminium silicate (in large amounts)
- Silicon dioxide (SiO2) and
- Calcium oxide (CaO)
Fly ash particles are oxide rich and consist of silica, alumina, oxides of iron, calcium, and magnesium and toxic heavy metals like lead, arsenic, cobalt, and coppers.
Policy measures of MoEF
- The Ministry of Environment and Forests vide its notification in 2009, has made it mandatory to use Fly Ash based products in all construction projects, road embankment works and low lying land filling works within 100 kms radius of Thermal Power Station.
- To use Fly Ash in mine filling activities within 50 kms radius of Thermal Power Stations.
- Arresters: These are used to separate particulate matters from contaminated air.
- Scrubbers: These are used to clean air for both dusts and gases by passing it through a dry or wet packing material.
Government Initiatives
National Air Quality Monitoring Programme
- In India, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has been executing a nationwide programme of ambient air quality monitoring known as National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP).
- The National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP) is undertaken in India:
(i) To determine status and trends of ambient air quality.
(ii) to ascertain the compliance of NAAQS.
(iii) to identify non-attainment cities.
(iv) to understand the natural process of cleaning in the atmosphere; and
(v) to undertake preventive and corrective measures. - Annual average concentration of SOx levels are within the prescribed National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS).
- National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAas) were notified in the year 1982, duly revised in 1994 based on health criteria and land uses.
- The NAAQS have been revisited and revised in November 2009 for 12 pollutants, which include, Sulphur dioxide (S02), nitrogen dioxide (N02), particulate matter having size less than 10 micron.
- (PM 10),particulate matter having size less than 2.5micron (PM2.5), ozone, lead, carbon monoxide (CO), arsenic, nickel, benzene, ammonia, and. Benzopyrene.
Water Pollution
- Addition of certain substances to the water such as organic, inorganic, biological, radiological, heat, which degrades the quality of water so that it becomes unfit for use.

- Putrescibility is the process of decomposition of organic matter present in water by microorganisms using oxygen.
- Water having DO (dissolved oxygen) content below 8.0 mg/L may be considered as contaminated. Water having DO content below. 4.0 mg/L is considered to be highly polluted.
- Water pollution by organic wastes is measured in terms of Biochemical Oxygen Demand-(BOD). BOD is the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by bacteria in decomposing the organic wastes present in water.
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is a slightly better mode used to measure pollution load in water. It is the measure of oxygen equivalent to the requirement of oxidation of total organic matter (i.e. biodegradable and non- biodegradable) present in water.
- A crippling deformity called Minamata disease due to consumption of fish captured from mercury contaminated Minamata Bay.
- Water contaminated with cadmium can cause itai-itai disease also called ouch-ouch disease (a painful disease of bones and joints) and cancer of lungs and liver.
- The compounds of lead cause anaemia, headache, loss of muscle power and bluish line around the gum.
- Excess nitrate in drinking water reacts with hemoglobin to form non -functional methaemoglobin, and impairs oxygen transport. This condition is called methemoglobinemia or blue baby syndrome.
- Over exploitation of ground water may lead to leaching of arsenic from soil and rock sources and contaminate ground water. Chronic exposure to arsenic causes black foot disease. It also causes diarrhoea, -peripheral neuritis, hyperkeratosis and also lung and skin cancer.

Soil Pollution
- Industrial waste includes chemicals such as mercury, lead, copper, zinc, cadmium, cyanides, thiocynates, chromates, acids, alkalies, organic substances etc.
- Four R’s: Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle.
Noise Pollution
- Sound is measured in decibels (dB). An increase of about 10 dB is approximately double the increase in loudness.
- A person's hearing can be damaged if exposed to noise levels over 75 dB over a prolonged period of time.
- The World Health Organization recommends that the sound level indoors should be less than 30 dB .

- Noise Level Monitoring - Noise Pollution (Control and Regulation) Rules, 2000 define ambient noise levels for various areas as follows-
(i) Industrial Area- 75DB to 70Db (Day time-6 am to 10 pm and night time 10pm to 6am..75 is day time and 70 is night time)
(ii) Commercial Area- 65 to 55
(iii) Residential Area- 55 to 45
(iv) Silence Zone- 50 to 40 - The Government of India on Mar 2011 launched a Real time Ambient Noise Monitoring Network.
- Under this network, in phase- 1, five Remote Noise Monitoring Terminals each have been installed in different noise zones in seven metros (Delhi, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai and Lucknow).
- In Phase II another 35 monitoring stations will be installed in the same seven cities.
- Phase III will cover installing 90 stations in 18 other cities.
- Phase-II cities are Kanpur, Pune, Surat, Ahmedabad, Nagpur, Jaipur, Indore, Bhopal, Ludhiana, Guwahati, Dehradun, Thiruvananthapuram, Bhubaneswar, Patna, Gandhinagar, Ranchi, Amritsar and Raipur.
- Silence Zone is an area comprising not less than 100 metres around hospitals, educational institutions, courts, religious places or any other t area declared as such by a competent authority.
Radio Active Pollution
- Non-ionising radiations affect only those components which absorb them and have low penetrability. They include short-wave radiations such as ultraviolet rays, which forms a part of solar radiation. Sunburns is due to these radiation
- Ionising radiations have high penetration power & cause breakage of macro molecules They include X-rays, cosmic rays and atomic radiations -(radiations emitted by radioactive elements
- Alpha particles, can be blocked by a piece of paper and human skin. Beta particles can penetrate through skin, while can be blocked by some pieces of glass
- Gamma rays can penetrate easily to human skin and damage cells on its way through, and metal.
- Reaching far, and can only be blocked by a very thick, strong, massive piece of concrete radium-224, uranium-238, thorium-232, potassium-40, carbon-14, etc.
- The nuclear arms use uranium-235 and plutonium-239 for fission and hydrogen or lithium as fusion material
- The radio nuclides with long half-time are the chief source of environmental radioactive pollution.
E-Waste
- E-waste is not hazardous if it is stocked in safe storage or recycled by scientific methods or transported from one place to the other in parts or in totality in the formal sector. The e-waste can be considered hazardous if recycled by primitive methods
- Survey was carried out by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) during 2005
- In India, among top ten cities; Mumbai ranks first in generating e-waste followed by Delhi, Bangalore, Chennai, Kolkata, Ahmadabad, Hyderabad, Pune, Surat and Nagpur.
Solid Waste
- The discarded (abandoned or considered waste-like) materials in irrigation return flows or industrial discharges, Conventional plastics have been associated with reproductive problems in both.
- Does not include solid or dissolved materials in domestic sewage, or solid or dissolved humans and wildlife.
 Solid Waste Management
Solid Waste Management - Dioxin (highly carcinogenic and toxic) by-product of the manufacturing process is one of the chemicals believed to be passed on through breast milk to the nursing infant.
- Burning of plastics, especially PVC releases this dioxin and also furan into the atmosphere.
- Pyrolysis-It is a process of combustion in absence of oxygen or the material burnt under controlled atmosphere of oxygen. It is an alternative to incineration. The gas and liquid thus obtained can be used as fuels.
Waste Minimization Circles (WMC)
- Helps Small and Medium Industrial Clusters in waste minimization in their industrial plants, assisted by the World Bank with the Ministry of Environment and Forests acting as the nodal ministry.
- Being implemented with the assistance of National Productivity Council (NPC), New Delhi.
- Aims to realise the objectives of the Policy Statement for Abatement of Pollution (1992), which states that the government should educate citizens about environmental risks, the economic and health dangers of resource degradation and the real economic cost of natural resources.
Bioremediation
The use of microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) to degrade the environmental contaminants into less toxic forms. Phytoremediation is use of plants to remove contaminants from soil and water.
Rhizofiltration
A water remediation technique that involves the uptake of contaminants by plant roots. Used to reduce contamination in natural wetlands and estuary areas.
The document Environment Pollution | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year is a part of the SSC CGL Course SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
1365 videos|1312 docs|1010 tests
|
|
1365 videos|1312 docs|1010 tests
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for SSC CGL exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches