Enzyme Kinetics & Photochemical Processes | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
Michaelis-Menten Enzyme Kinetics.
Enzyme are protein molecules that serve as catalysts in a chemical reaction.
The kinetic mechanism of enzyme catalyst can be described using the Michaelis-Menten mechanism.
The kinetic mechanism of enzyme catalyst can be described using the Michaelis-Menten mechanism.
But in this mechanism substrate concentration is greater than that of enzyme i.e.
[S]0 >> [E0]
then rate of formation of product in enzyme catalyst is
…(1)
The co mposite constant km is referred to as the Michaelis constant in enzyme kinet ics and the equation is referred to as the Michaelis-Menten rate law.
When [S]0 >> km, the Michaelis constant can be neglected, resulting new expressio n for the rate.
R0 = k2[E]0 = Rmax
The reciprocal equation of equation (1) is the Lineweaver-Burk equation i.e.
…(2)
This equation is known as Lineweaver-Burk equation.
The plot of reciprocal of rate is known as Linewearver-Burk plot. k2 is known as turn over numberof the enzyme. “The turn over number is the maximum number of substrate molecules per uit time that can be converted into product.”
This is Linewearver-Burk plot.
We know that
Case I. ` [S]0 >> km
i.e. rate is maximum due to all enzyme are present
R = Rmax = k2[E]0
This is zero order w.r.t. substrate.
Case II. If [S]0 = km
Case III. If [S] << km
This is first order w.r.t. substrate.
This is graph between initial rate and concentration of substrate.
G.S. Eadie Plot
We know that,
Multiplying with R,
Multiplying with
or
Photochemical Processes
The following are the most common forms of phases of Photochemical Processes
- Initiation (formation of active particles or chain carriers, often free radicals, in a photochemical step)
- Propagation (can contain many elementary or simple steps in a cycle, where the reactive particle through chemical reaction forms another reactive particle that continues the chain of reaction by entering the next elementary or simple step). In addition, the active particle acts as a catalyst for the propagation cycle's overall reaction. The following are examples of special cases:
Chain Branching - It's a phase in the propagation process where one reactive particle enters and two or more are formed.
Chain transfer (a propagation step in which the active particle is a growing polymer chain which reacts to form an inactive polymer whose growth is terminated and an active small A radical, for example, is a particle that can react to produce a new polymer chain.
Termination (simple or elementary step in which the reactive particle loses its reactivity; e. g. by recombination of two free radicals).
- The chain length is equal to the overall reaction rate divided by the initiation rate and is defined as the average number of times the propagation cycle is repeated.Complex rate equations of fractional order or mixed order kinetics can be used in certain chain reactions.
Examples of Chain Reactions
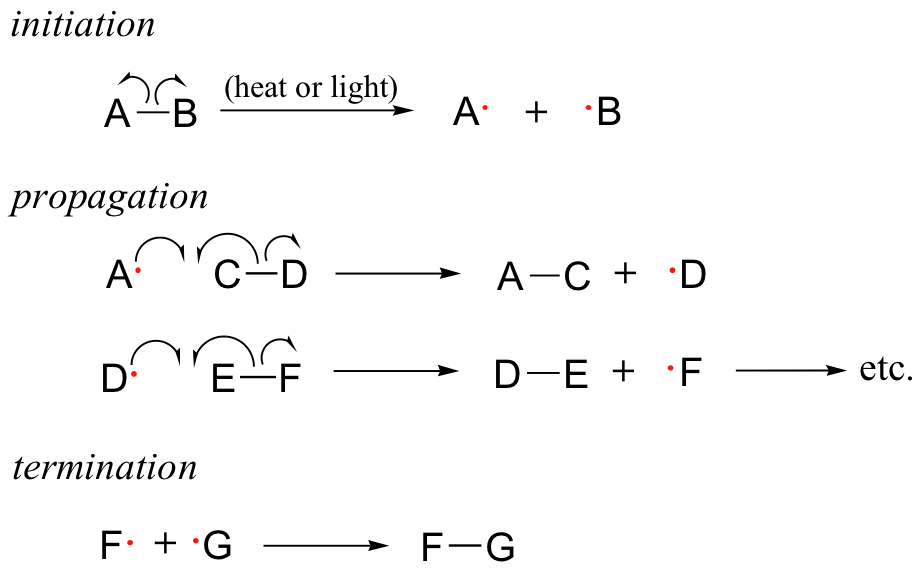
|
84 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Enzyme Kinetics & Photochemical Processes - Physical Chemistry
| 1. What is enzyme kinetics and how is it related to photochemical processes? |  |
| 2. How do enzymes participate in photochemical processes? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed photochemical processes? |  |
| 4. How can enzyme kinetics be measured in photochemical processes? |  |
| 5. What applications does the study of enzyme kinetics in photochemical processes have? |  |





















