Even, Odd functions & Half-Range Expansion | Mathematical Methods - Physics PDF Download
Even & Odd function
A function g (x) is said to be even if g (-x) = g (x), so that its graph is symmetrical with respect to vertical axis.
A function h (x) is said to be even ifh (-x) = -h (x).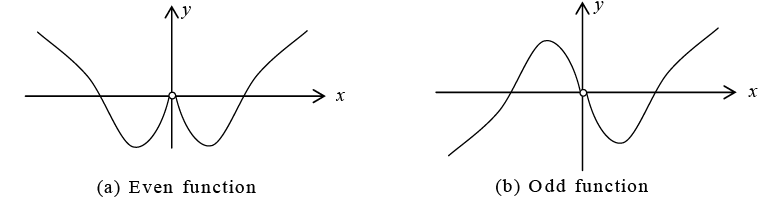
Since the definite integral of a function gives the area under the curve of the function between the limits of integration, we have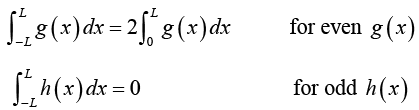
Fourier Cosine Series and Fourier Sine Series
Fourier series of an even function of period 2L, is a “Fourier cosine series”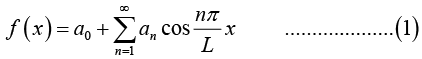
with coefficients( note integration from 0 to L)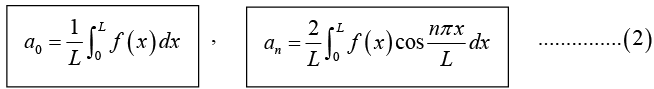
Fourier series of an odd function of period 2L, is a “Fourier sine series”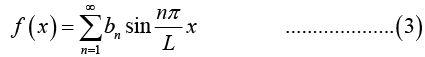
with coefficients 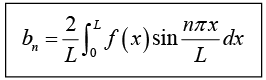
NOTE:
(i) For even function f (x);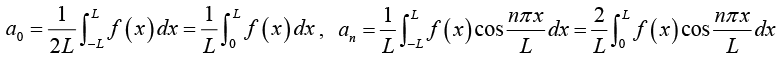
and 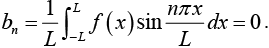
(ii) For odd function f (x);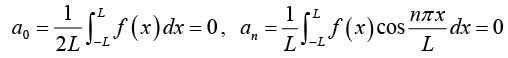
The Case of Period 2π
If L = π, and f(x) is even function then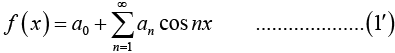
with coefficients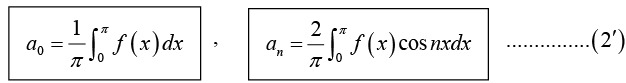
If f(x) is odd function then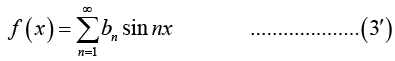
with coefficients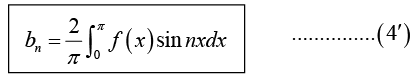
Sum and Scalar Multiple
(a) The Fourier coefficients of a sum f1 + f2 are the sums of the corresponding Fourier coefficients of f1 and f2.
(b) The Fourier coefficients of cf are c times the corresponding Fourier coefficients of f.
Example 4: Find the Fourier series of the periodic function f (x) as shown in figure: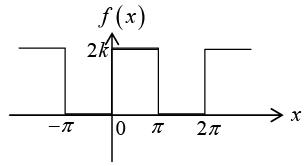
We have already calculated the Fourier series of the periodic function f (x) as shown in figure:
The Fourier series is
The function given in the problem can be obtained by adding k to the above function. Thus the Fourier series of a sum k+ /'(x) are the sums of the corresponding Fourierseries of k and /(x).
The Fourier series is f
Example 5: Find the Fourier series of the periodic function
f (x) = x + π ; ( - π < x < π) having period 2π
Let f(x) = f1 + f2 where f1 = x and f2 = π.
The Fourier coefficient of f2 = π is a0 = π, an= 0 and bn = 0 . The Fourier coefficient of f1 = x is
Thus the Fourier series of f (x) is
Half-Range Expansion
Half-range expansions are Fourier series. The idea is simple and useful. We could extend f (x) as a function of period L and develop the extended function into a Fourier series. But this series would in general contain both cosine and sine terms.
We can do better and get simpler series. For our given function f (x) we can calculate
Fourier cosine series coefficient(a0 and an ) . This is the even periodic extension f1(x) of f (x) in figure (b).
For our given function f (x) we can calculate Fourier sine series coefficient (bn ). This
is the odd periodic extension f2 (x) off (x) in figure (c).
Both extensions have period 2L . Note that f(x) is given only on half the range, half the
interval of periodicity of length 2L .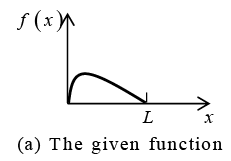
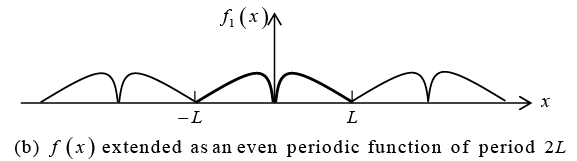
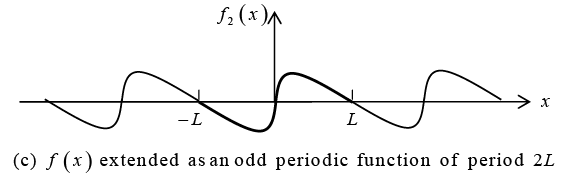
Example 6: Find the two half-range expansion of the function f (x) as shown in figure below.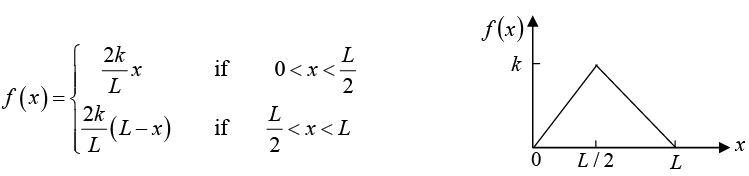
Even periodic extension
Let us calculate the integral
and
Hence the first half-range expansion of f (x) is
This Fourier cosine series represents the even periodic extension of the given function/ (x), of period 2 L as shown in figure.Odd periodic extension
Let us calculate the integral
Hence the other half-range expansion of f (x) is
This Fourier sine series represents the odd periodic extension of the given function f (x).
of period 2L as shown in figure.
Complex Fourier series
The Fourier series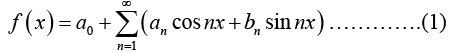
can be written in complex form, which sometimes simplifies calculations.
∵ einx = cos nx + i sin nx and e-inx = cos nx -i sin nx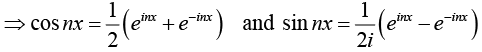
Thus 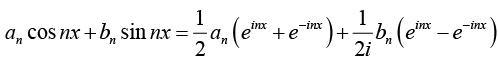
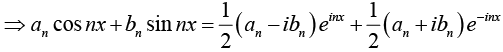
Lets take 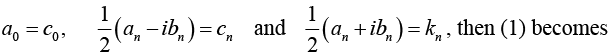
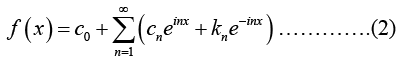
where coefficients c0, cn and kn are given by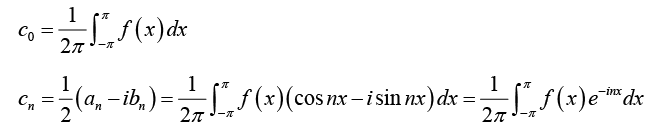
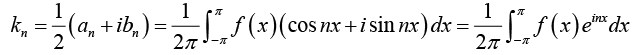
We can also write (2) as (take kn = c-n)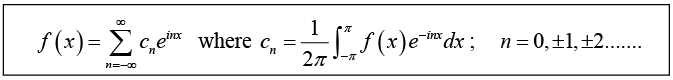
This is so called complex form of the Fourier series or, complex Fourier series off (x) .
The cn are called complex Fourier series coefficients of f (x).
For a function of period 2L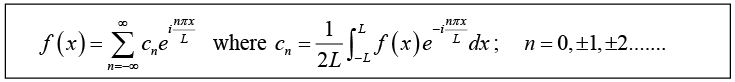
Example 7: Find the complex Fourier series of the periodic function
f (x) = ex; ( - π < x < π), having period 2π
Let Fourier series is f(x) =
Thus Fourier series is
Let us derive the real Fourier series
∵ (1 + in) einx = (1 + in) (cos nx + i sin nx) = (cos nx - nsin nx) + i (cos nx + sin nx)
∵ n varies from -∞ to + ∞, equation (1) has corresponding term with -n instead of n .
Thus∵ (1 -in) e-inx = (1 -in) (cos nx - i sin nx) = (cos nx-n sin nx) - i (cos nx+sin nx)
Let’s add these two expressions;
(1 + in) einx + (1 - in)e-inx = 2 (cos nx - n sin nx), n = 1,2,3........
For n = 0,
Thus
Example 8: Consider the periodic function f(t) with time period T as shown in the figure below.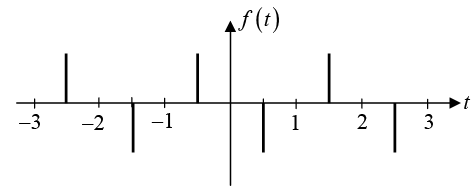
The spikes, located at 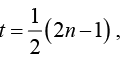 where n = 0,±1,±2,..., are Dirac-delta function of strength +1 . Find the amplitudes an in the Fourier expansion of
where n = 0,±1,±2,..., are Dirac-delta function of strength +1 . Find the amplitudes an in the Fourier expansion of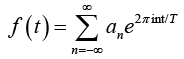
and Range: [-1,1] hence 2L = 2.
Comparing with
Approximation by Trignometric Polynomials
Fourier series have major applications in approximation theory, that is, the approximation of functions by simpler functions.
Let f (x)be a periodic function, of period 2π for simplicity that can be represented by a Fourier series. Then the Nth partial sum of the series is an approximation to f (x) :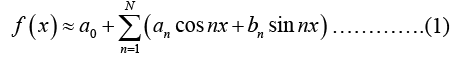
We have to see whether (1) is the "best” approximation to f by a trignometric polynomial of degree N, that is , by a function of the form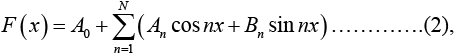
where "best” means that the "error” of approximation is minimum.
The total square error of F relative to / on the interval -π < x < π is given by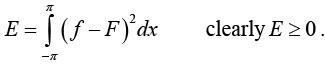
The function F is a good approximation to f but |f - F| is large at a point of discontinuity x0.
Minimum square error
The total square error of F relative to f on the interval - π < x < n is minimum if and only if the coefficients of f(x) are the Fourier coefficients of f(x). This minimum value E* is given by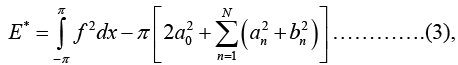
From (3) we can see that E* cannot increase as N increases, but may decrease. Hence with increasing N the partial sums of the Fourier series of f yields better and better approximations to f.
Parseval’s Identity
Since E* > 0 and equation (3) holds for every N, we obtain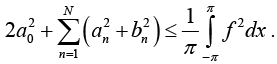
Now Parseval’s Identity is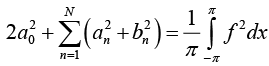
Example 9: Compute the total square error of F with N = 3 relative to
f (x) = x + π (- π < x < π)
on the interval - π < x < π .
Fourier coefficients are a0 = π, an = 0 and bn =
Its Fourier series is given by
Hence,
Although |f (x) - f(x)| is large at x = ± π . where f is discontinuous, F approximates f quite well on the whole interval.
|
78 videos|18 docs|24 tests
|
FAQs on Even, Odd functions & Half-Range Expansion - Mathematical Methods - Physics
| 1. What is a complex Fourier series? |  |
| 2. How does the approximation of a function by trigonometric polynomials work? |  |
| 3. What are even and odd functions in the context of Fourier series? |  |
| 4. What is the concept of half-range expansion in Fourier series? |  |
| 5. How can the concepts of complex Fourier series, approximation by trigonometric polynomials, even and odd functions, and half-range expansion be applied in IIT JAM exam? |  |





































 and Range: [-1,1] hence 2L = 2.
and Range: [-1,1] hence 2L = 2.


























