Evolution, Variations & Darwin's Theory | Biology for Grade 10 PDF Download
Evolution
 The term evolution has been derived from the Latin word 'evolvere' means unroll.
The term evolution has been derived from the Latin word 'evolvere' means unroll.
Evolution can be defined as a sequence of gradual development of complex form of life from simple form of life over the course of geological time "Descent with modification."
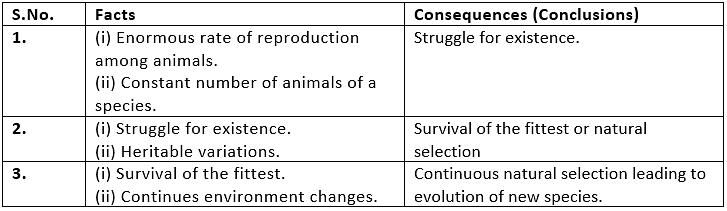
Charles Darwin's theory of evolution states that evolution happens by natural selection. Individuals in a species show variation in physical characteristics. This variation is because of differences in their genes.
Types of Evolution
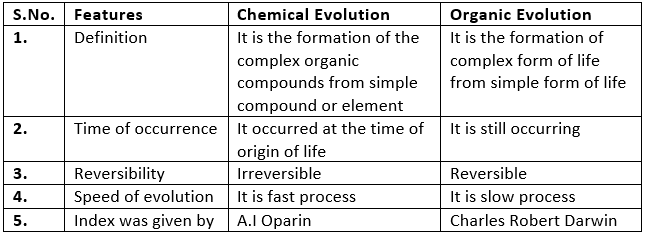
Evolution is of two types:
- Chemical evolution
- Organic evolution
After origin of a living cell the next questions that arose was how did so many different species of complex life forms come into existence?
Here are various view points:
- Carolus Linnaeous: Said that no species is new i.e. each species originates from pre-existing species. In Systema Naturae, Linnaeus classified nature into a hierarchy. He proposed that there were three broad groups, called kingdoms, into which the whole of nature could fit. These kingdoms were animals, plants, and minerals. He divided each of these kingdoms into classes.

- Jeans baptist Lamarck: Explained in his book namely "philosophie zoologique", the theory of inheritance of acquired characters or Lamarkism. This theory states that use and disuse of an organ leads to change in the organ, which is inherited by the offsprings. The favourable variations which remain for longer period of time results in evolution of new species.
This theory was discarded by August Weismann as he experimentally proved that even after cutting tails of mice for 21 generation tailless mice was never born.
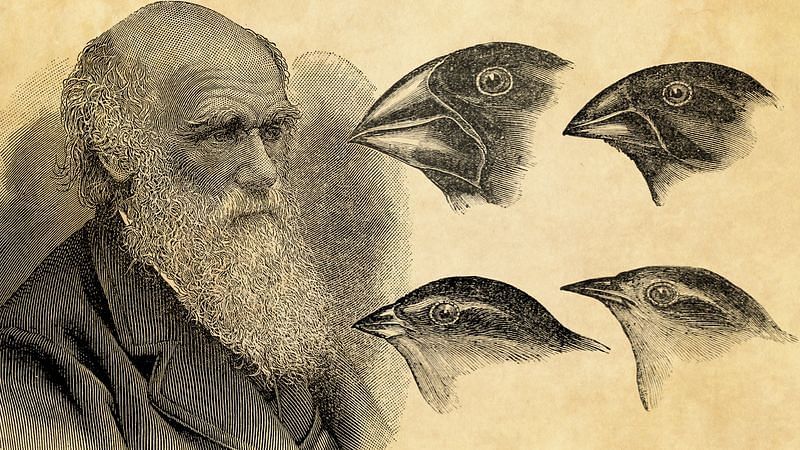
- Darwinism: Charles Robert Darwin was born on 12 Feb, 1809 in England. He travelled by HMS Beagle ship along with Dr. Henslow. He visited many islands of south America, South Africa, Australia and Galapagos Islands. Darwin was influenced by two books. "Principal of population" of Malthus. "Principal of Geology" of Charls Leyell.

 In his book origin of species he answered this questions. The theory presented by him is called theory of natural selection or Darwinism.
In his book origin of species he answered this questions. The theory presented by him is called theory of natural selection or Darwinism. - Alfred Russel Wallace: He travelled south eastern Asia and South America. The idea of natural selection striked in his mind. Wallace wrote an essay and sent it to Darwin. On the tendency of varieties to depart indefinitely from original type, there is striking similarity between the views of Darwin and Wallace.
 Charles Darwin explained the mechanism of origin of new species by natural selection. But he failed to explain the mechanism of source of heritable variations. This was explained by Hugo De Vries, a Dutch botanist. According to him, heritable variations arise when there is a change in genes of the germplasm (protoplasm of germcell). He called it mutation.
Charles Darwin explained the mechanism of origin of new species by natural selection. But he failed to explain the mechanism of source of heritable variations. This was explained by Hugo De Vries, a Dutch botanist. According to him, heritable variations arise when there is a change in genes of the germplasm (protoplasm of germcell). He called it mutation.
Variations
Variations are the structural, functional or behavioral changes from the normal characters developed in living organisms. There is an inbuild tendency to variation during reproduction. Both because of errors in DNA copying as a result of sexual reproduction.
Variations provide raw materials for evolution. These may be inheritable or non-inheritable, only inheritable variations participate in evolution.
- Genetic Variations: The differences in the DNA sequences among every organism leading to the diverse gene pool are called genetic variations. These differences lead to different/varied physical characters or biochemical pathways.
- Natural Selection: It is the phenomenon by which a favourable trait in a population of a species is selected. Changing natural conditions exert equal pressure on all the existing species. The species/organisms which are better adapted to the changing conditions survive and reproduce i.e. selected by nature and species/organisms which cannot adapt perish i.e. rejected by nature.
Type of Variations
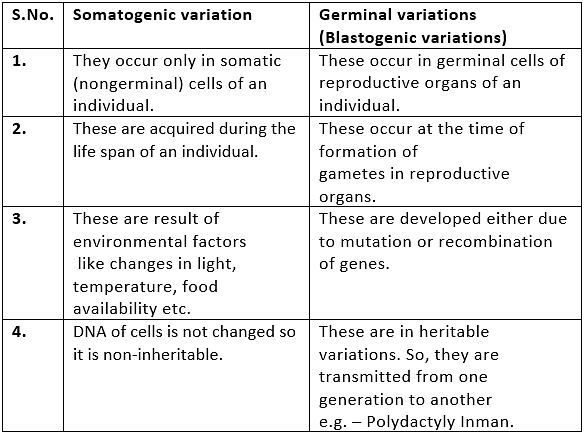
On the basis of nature of cells where variations occur, variations are of two types:
- Somatogenic variations or Acquired traits
- Germinal (Blastogenic) variations.

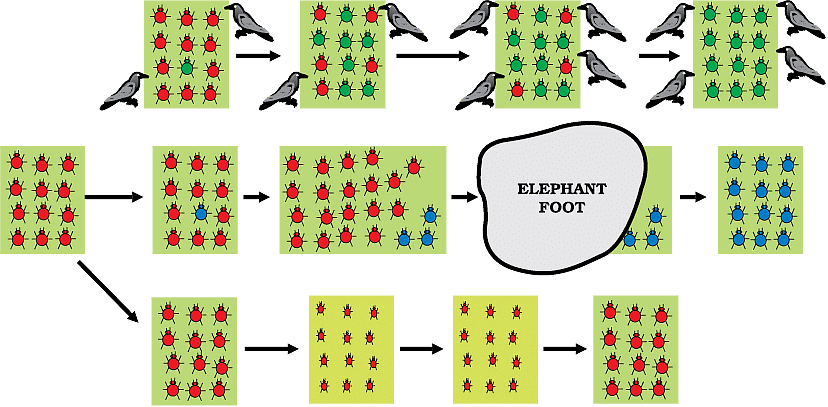
An Illustration
Consider the following example:
- A group of twelve red beetles living in bushes with green leaves.
- Beetles in the population can generate variations because these are reproducing sexually.
- Crow can eat the beetles. The more beetles the crow eat, the fewer beetles are left for reproduction.


Variation in a population inherited and otherwise.
Now consider the following situations: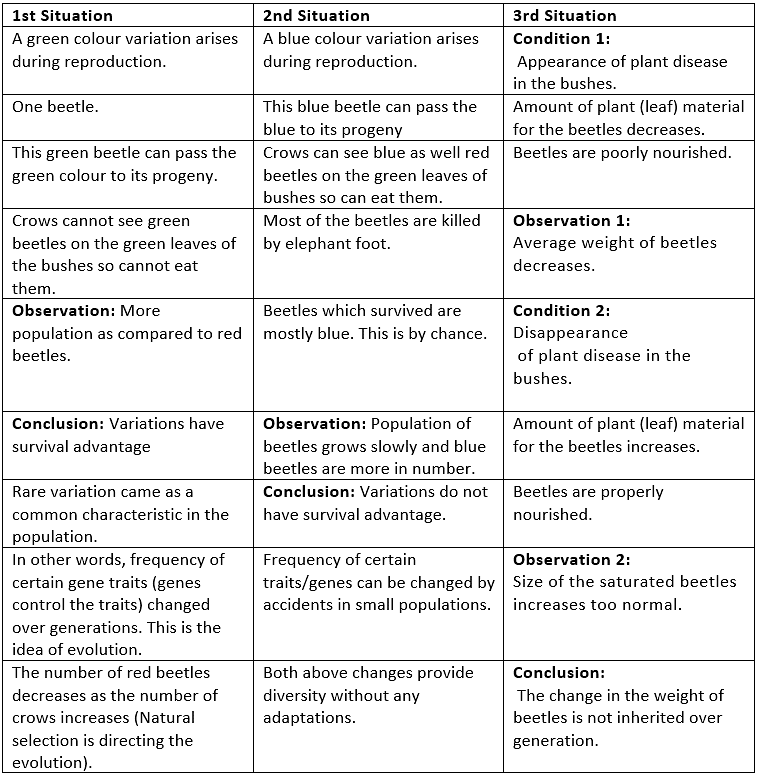
Acquired and Inherited Traits
- Acquired characters: The traits that are acquired by an organism over the period of its lifetime are termed as acquired characters. These characters may or may not get transferred to the next generation.
- Inherited characters: The traits that are inherited from the parents are called inherited characters. These traits always get transferred to the next generation, but depending on the dominance or recessiveness it may or may not be expressed. Examples are height, skin colour and eye colour.
Heritable Variation
The reason why organisms resemble their parents lie in the precise copying of their genes, which carry hereditary characters from one generation to the next. On the other hand no two offspring have exactly the same genes.
This is because offspring of sexually reproducing organisms receive varying combination of genetic material from both parents such variations result from mutations (errors in DNA copying). Variations also result from genetic recombination during sexual reproduction.
Genetic Drift
The random changes in the gene frequency occurring by chance alone. The effect of genetic drift is very small in large population and large in small populations. Genetic drift is a mechanism of evolution. It refers to random fluctuations in the frequencies of alleles from generation to generation due to chance events. Genetic drift can cause traits to be dominant or disappear from a population. The effects of genetic drift are most pronounced in small populations.
|
110 videos|93 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Evolution, Variations & Darwin's Theory - Biology for Grade 10
| 1. What is evolution? |  |
| 2. What are variations in the context of evolution? |  |
| 3. What is Darwin's theory of evolution? |  |
| 4. How does natural selection contribute to evolution? |  |
| 5. Can evolution be observed in real-time? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Grade 10 exam
|

|