NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 - Linear Equations in Two Variables
Exercise 4.1
Q1. The cost of a notebook is twice the cost of a pen. Write a linear equation in two variables to represent this statement. (Take the cost of a notebook to be ₹ x and that of a pen to be ₹ y)
Ans: Let the cost of a notebook be = ₹ x
Let the cost of a pen be = ₹ y
According to the question,
The cost of a notebook is twice the cost of a pen.
i.e., cost of a notebook = 2×cost of a pen
x = 2 × y
x = 2y
x - 2y = 0
x - 2y = 0 is the linear equation in two variables to represent the statement, ‘The cost of a notebook is twice the cost of a pen.’
Q2. Express the following linear equations in the form ax + by + c = 0 and indicate the values of a, b and c in each case:
(i) 2x + 3y= 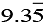
Ans: Consider 2x + 3y= 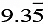 Equation (1)
Equation (1)
⇒ 2x + 3y - 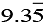 = 0
= 0
Comparing this equation with the standard form of the linear equation in two variables, ax + by + c = 0 we have,
a = 2
b = 3
c = -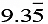
(ii) x – (y/5) – 10 = 0
Ans: The equation x –(y/5)-10 = 0 can be written as,
(1)x+(-1/5)y +(–10) = 0
Now comparing x+(-1/5)y+(–10) = 0 with ax+by+c = 0
We get,
a = 1
b = -(1/5)
c = -10
(iii) –2x + 3y = 6
Ans: –2x+3y = 6
Re-arranging the equation, we get,
–2x+3y–6 = 0
The equation –2x+3y–6 = 0 can be written as,
(–2)x+(3)y+(– 6) = 0
Now, comparing (–2)x+(3)y+(–6) = 0 with ax+by+c = 0
We get, a = –2
b = 3
c =-6
(iv) x = 3y
Ans: x = 3y
Re-arranging the equation, we get,
x-3y = 0
The equation x-3y=0 can be written as,
(1)x+(-3)y+(0)c = 0
Now comparing 1x+(-3)y+(0)c = 0 with ax+by+c = 0
We get a = 1
b = -3
c = 0
(v) 2x = –5y
Ans: 2x = –5y
Re-arranging the equation, we get,
2x+5y = 0
The equation 2x+5y = 0 can be written as,
2x+5y+0 = 0
Now, comparing (2)x+(5)y+0= 0 with ax+by+c = 0
We get a = 2
b = 5
c = 0
(vi) 3x + 2 = 0
Ans: 3x+2 = 0
The equation 3x+2 = 0 can be written as,
3x+0y+2 = 0
Now comparing 3x+0+2= 0 with ax+by+c = 0
We get a = 3
b = 0
c = 2
(vii) y–2 = 0
Ans: y–2 = 0
The equation y–2 = 0 can be written as,
(0)x+(1)y+(–2) = 0
Now comparing (0)x+(1)y+(–2) = 0with ax+by+c = 0
We get a = 0
b = 1
c = –2
(viii) 5 = 2x
Ans: 5 = 2x
Re-arranging the equation, we get,
2x = 5
i.e., 2x–5 = 0
The equation 2x–5 = 0 can be written as,
2x+0y–5 = 0
Now comparing 2x+0y–5 = 0 with ax+by+c = 0
We get a = 2
b = 0
c = -5
Exercise 4.2
Q1. Which one of the following options is true, and why?
y = 3x + 5 has
(i) A unique solution
(ii) Only two solutions
(iii) Infinitely many solutions
Ans: Let us substitute different values for x in the linear equation y = 3x + 5,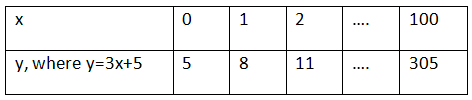
From the table, it is clear that x can have infinite values, and for all the infinite values of x, there are infinite values of y as well.
Hence, (iii) infinitely many solutions is the only option true.
Q2. Write four solutions for each of the following equations:
(i) 2x + y = 7
Ans: To find the four solutions of 2x + y =7 we substitute different values for x and y
Let x = 0
Then,
2x + y = 7
(2)(0) + y = 7
y = 7
(0, 7)
Let x = 1
Then,
2x + y = 7
(2 × 1) + y = 7
2 + y = 7
y = 7 - 2
y = 5
(1, 5)
Let y = 1
Then,
2x + y = 7
(2x) + 1 = 7
2x = 7 - 1
2x = 6
x = 6/2
x = 3
(3, 1)
Let x = 2
Then,
2x + y = 7
(2 × 2) + y = 7
4 + y = 7
y =7 - 4
y = 3
(2, 3)
The solutions are (0, 7), (1, 5), (3, 1), (2, 3)
(ii) πx + y = 9
Ans: To find the four solutions of πx+y = 9 we substitute different values for x and y
Let x = 0
Then,
πx + y = 9
(π)(0) + y = 9
y = 9
(0, 9)
Let x = 1
Then,
πx + y = 9
(π × 1) + y = 9
π + y = 9
y = 9-π
(1, 9-π)
Let y = 0
Then,
πx + y = 9
πx + 0 = 9
πx = 9
x = 9/π
(9/π,0)
Let x = -1
Then,
πx + y = 9
π(-1)+y = 9
-π+y=9
y = 9 + π
(-1, 9+π)
The solutions are (0, 9), (1, 9-π), (9/π, 0), (-1, 9+π)
(iii) x = 4y
Ans: To find the four solutions of x = 4y we substitute different values for x and y
Let x = 0
Then,
x = 4y
0 = 4y
4y = 0
y = 0/4
y = 0
(0, 0)
Let x = 1
Then,
x = 4y
1 = 4y
4y = 1
y = 1/4
(1, 1/4)
Let y = 4
Then,
x = 4y
x= 4 × 4
x = 16
(16, 4)
Let y =
Then,
x = 4y
x = 4×1
x = 4
(4,1)
The solutions are (0,0), (1,1/4), (16,4), (4,1)
Q3. Check which of the following are solutions of the equation x–2y = 4 and which are not:
(i) (0, 2)
Ans: (x, y) = (0, 2)
Here, x = 0 and y = 2
Substituting the values of x and y in the equation x – 2y = 4, we get,
x – 2y = 4
⟹ 0 – (2 × 2) = 4
But, -4 ≠4
Therefore, (0, 2) is not a solution of the equation x – 2y = 4
(ii) (2, 0)
Ans: (x,y) = (2, 0)
Here, x = 2 and y = 0
Substituting the values of x and y in the equation x - 2y = 4, we get,
x - 2y = 4
⟹ 2-(2 × 0) = 4
⟹ 2 - 0 = 4
But, 2 ≠ 4
(2, 0) is not a solution of the equation x - 2y = 4
(iii) (4, 0)
Ans: (x, y) = (4, 0)
Here, x = 4 and y = 0
Substituting the values of x and y in the equation x - 2y = 4, we get,
x – 2y = 4
⟹ 4 – 2 × 0 = 4
⟹ 4-0 = 4
⟹ 4 = 4
(4, 0) is a solution of the equation x – 2y = 4
(iv) (√2, 4√2)
Ans: (x, y) = (√2, 4√2)
Here, x = √2 and y = 4√2
Substituting the values of x and y in the equation x – 2y = 4, we get,
x –2y = 4
⟹ √2-(2×4√2) = 4
√2-8√2 = 4
But, -7√2 ≠ 4
(√2, 4√2) is not a solution of the equation x – 2y = 4
(v) (1, 1)
Ans: (x, y) = (1, 1)
Here, x = 1 and y = 1
Substituting the values of x and y in the equation x – 2y = 4, we get,
x – 2y = 4
⟹ 1 -(2 × 1) = 4
⟹ 1 - 2 = 4
But, -1 ≠ 4
(1, 1) is not a solution of the equation x–2y = 4
Q4. Find the value of k, if x = 2, y = 1 is a solution of the equation 2x+3y = k.
Ans: The given equation is
2x + 3y = k
According to the question, x = 2 and y = 1.
Now, Substituting the values of x and y in the equation 2x + 3y = k,
We get,
(2 × 2)+(3 × 1) = k
⟹ 4 + 3 = k
⟹ 7 = k
k = 7
The value of k, if x = 2, y = 1 is a solution of the equation 2x + 3y = k, is 7.
|
44 videos|412 docs|54 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 - Linear Equations in Two Variables
| 1. What are linear equations in two variables? |  |
| 2. How do you solve a linear equation in two variables? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of linear equations in two variables? |  |
| 4. Can linear equations in two variables have more than one solution? |  |
| 5. How can linear equations in two variables be graphically represented? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















