Experiments with Water Class 5 Notes EVS Chapter 7
| Table of contents |

|
| What Floats – What Sinks? |

|
| Is It Magic? |

|
| What Dissolved, What Did Not? |

|
| Racing Drops |

|
| Where did the water go? |

|
| Dandi March |

|
| Making of Salt |

|
In this part of our learning, we'll talk about water and why things either sink or float in it. We'll do some fun experiments to understand more about water and liquids. It's going to be interesting and easy to learn, so let's get started!
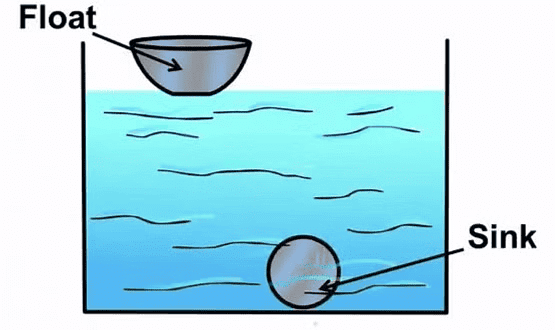 Floating and Sinking in Water
Floating and Sinking in Water
What Floats – What Sinks?
In this section, we will learn why some things float in water while others sink.
- Ayesha eagerly awaits dinner as her mother prepares her favorite meal—puri and spicy potatoes.
- Ayesha watches her mother roll out puris and then place them in hot oil for frying.
The Behavior of Puri in Oil
- Initially, the puris sink to the bottom of the pan.
- As they cook, the puris puff up and begin to float on the oil.
- One puri does not puff up and remains submerged, prompting Ayesha's curiosity.
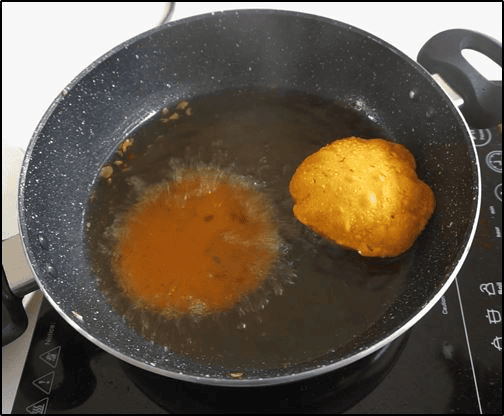 Puffed Up Puris
Puffed Up Puris
Ayesha’s Experiment
- Curious about the behavior of the puris, Ayesha takes some dough.
- She rolls the dough into a ball and flattens it.
- When placed in a bowl of water, the flattened dough sinks to the bottom and stays there.
Evening Bath Incident
- Later, Ayesha goes for a bath. After her bath, her mother points out the soap that has been dropped in the water.
- Ayesha accidentally drops the soap case, which starts floating on the water.
 Soap dropped in water
Soap dropped in water
Observation with Soap
- Ayesha gently places the soap into the floating soap case.
- Despite the added weight of the soap, the soap case continues to float on the water.
 Floating soap case on water
Floating soap case on water
Key Concepts of Floatation and Submersion:
- Through her experiences with both the puris and the soap, Ayesha observes that some objects float while others sink.
- These observations prompt her to think critically about the reasons behind why things float or sink in water.
- Objects that are less dense than the liquid will float (e.g., puffed puris, soap case).
- Objects that are denser than the liquid will sink (e.g., raw puris, flattened dough)
- Here are some more examples:
Is It Magic?
In this section, we will discover how salt affects the density of water, allowing heavy objects like eggs to float.
- Ayesha wakes up to find her mother, Ammi, has a fever.
- Abbu makes tea and gives medicines to Ammi. He asks Ayesha to boil eggs and add some salt to the water.
Experiment with Eggs:
- Ayesha fills a pot with water but accidentally adds too much salt.
- To her surprise, the eggs at the bottom of the pot begin to rise and float in the salty water.
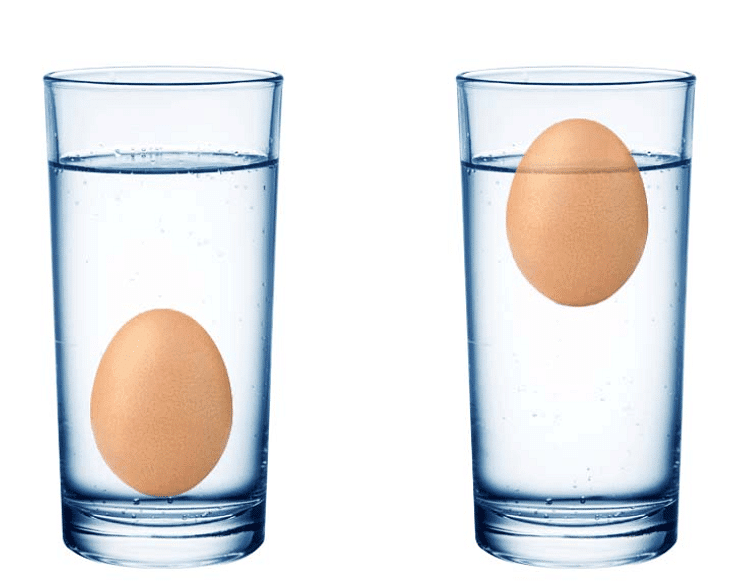 Eggs begin to float in Salty Water
Eggs begin to float in Salty Water
Key Concepts: How Salt Makes Things Float
Salt helps heavy things float by making the water denser. When salt dissolves in water, it mixes in and makes the water thicker (denser).
- Salt Makes Heavier Objects Float: Normally, objects that are heavier than water will sink, but with salt, the water becomes heavy enough to make even things like eggs or lemons float.
- Eggs in Salty Water: When boiling eggs with salt in the water, the eggs start to float because the salty water is denser than plain water.
- The Dead Sea: The Dead Sea is a famous example of water with a very high salt content. While all oceans and seas have some salt, the Dead Sea has the most.

- Nature’s Floating Pool: Because the Dead Sea is so salty, even people who can't swim won’t sink—they float easily. There’s about 300 grams of salt in every litre of Dead Sea water, making it much saltier than any other body of water!
What Dissolved, What Did Not?
In this section, we will explore which substances dissolve in water and which do not, through experiments with sugar, oil, and water, and learn key methods for dissolving substances effectively.
Mixing Sugar in Water:
- On Sunday, Ayesha’s cousin Hamid visits her house to play.
- Hamid asks Ammi to make his favorite sweet dish, shakkarpara.
- Ammi tells Hamid to help her by taking two glasses of water and mixing in a bowl of sugar until it dissolves.
Q. How to Dissolve Things Quickly in Water?
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Stir Continuously: Keep stirring the solution while adding soluble substances.
- Heat the Mixture: Applying heat can help dissolve substances more quickly

Experiment with Oil and Water:
- While mixing, Ayesha and Hamid argue about the experiment.
- Ayesha's Claim: She believes the oil dissolves in water after stirring.
- Hamid's Counterargument: He disagrees, pointing out that tiny yellow oil drops are still visible in the water.
- Resolution: Ayesha suggests waiting for some time to see what happens.
- Conclusion: Oil does not dissolve in water; it separates and forms droplets that float on top.
Key Concepts: Soluble and Insoluble Substances
- Soluble Substances: Some substances disappear in water when mixed; these are called soluble substances. Examples include salt, sugar, glucose, vinegar, and lemon juice.
Insoluble Substances: Other substances do not dissolve in water; instead, they settle at the bottom. These are known as insoluble substances. Examples include sand, pebbles, chalk powder, and cemen
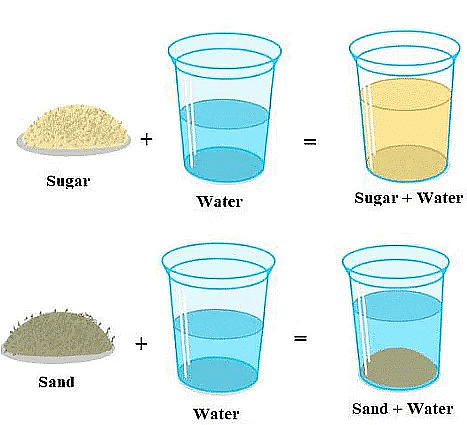 Soluble & Insoluble Substances
Soluble & Insoluble Substances
Take a look at the table given below:
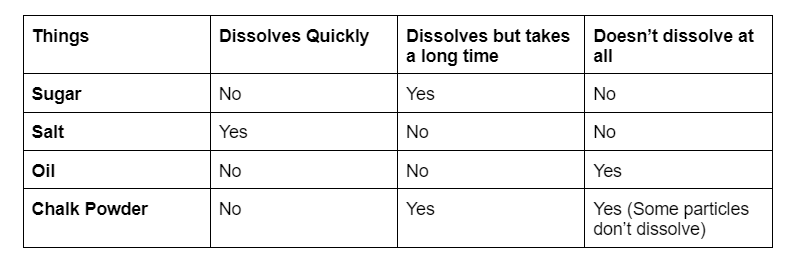
Racing Drops
When we tilt a tiffin box lid with drops of water, oil, and sugar solutions, the water slides faster. The oil and sugar drops stick to the lid, slowing them down.
- Clean water moves quickly.
- Water with things added or mixed in it moves slowly.
- Liquids that are heavy move slowly.
- Oil does not mix with water because it is an immiscible liquid and forms a layer on the surface of the water.
 Oil in Water
Oil in Water
Where did the water go?
Experiment with Boiling Water:- Ayesha's mother boiled water for tea but forgot about it.
- When she checked, she found very little water left in the pan.
Where Did the Water Go?
 View Answer
View Answer 
The water evaporated into the air as steam due to heating.
Evaporation
When a liquid, like water, turns into a gas because of heat, we call it evaporation. So, if you heat water, it goes up into the air.
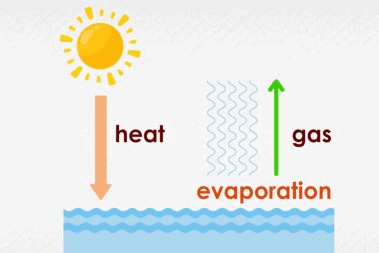 Evaporation
Evaporation
Dandi March
- Now, let's talk about an event in 1930 called Dandi March.
- Before India became independent, the British government made rules that stopped people from making their own salt.
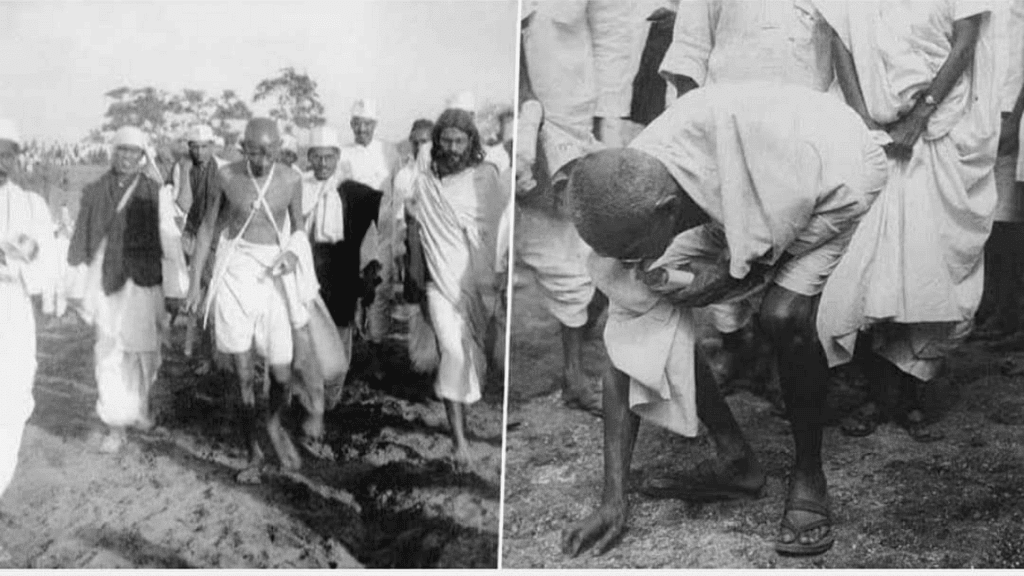 Dandi March
Dandi March - They also put a high tax on salt, making it illegal for people to make it at home.
- To protest against these rules, Mahatma Gandhi (whom people lovingly call Gandhiji) and a group of others went on a long walk from Ahmedabad to the Dandi seashore in Gujarat.
- They did this to show they didn't agree with the law about salt and wanted to make a statement.
Making of Salt
- People gather seawater in flat, sandy areas.
 Making of Salt
Making of Salt - They let the sun dry the water.
- After the water is gone, salt is left behind on the ground.
|
37 videos|410 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Experiments with Water Class 5 Notes EVS Chapter 7
| 1. What are some examples of objects that float and sink in water? |  |
| 2. How can we demonstrate that some substances dissolve in water while others do not? |  |
| 3. What is the 'Dandi March' and how is it related to water? |  |
| 4. How can we investigate where the water goes when it evaporates? |  |
| 5. What can we do to make our own salt at home? |  |





















