Class 9 History Chapter 1 Question Answers - The French Revolution
Q.1. When did the French Revolution begin?
Or
When was the Bastille Prison stormed?
Ans. It began on 14th July 1789 with the storming of the Bastille prison just outside Paris.
Q.2. Louis XVI belonged to which dynasty?
Or
Which ruler came to power in France in 1774?
Ans. Louis XVI belonged to the Bourbon dynasty. He became the king of France in 1774.
Q.3. Who belonged to the third estate?
Or
Which estate of the French society paid all taxes?
Ans. The third estate comprised all the people of France except the clergy (first estate) and the nobility (second estate), i.e., all those who paid taxes.
Q.4. The new Constitution of France drafted in 1791 immediately after the revolution made France what kind of state?
Ans. It made France a Constitutional monarchy, with the powers of the king severely limited.
Q.5. Who was the leader of the Jacobin club?
Ans. The leader of the Jacobin club was Maximilian Robespierre.
Q.6. Who was the author of the pamphlet called 'What is the Third Estate'?
Ans. Abbe Sieyes, originally a priest, wrote an influential pamphlet called 'What is the Third Estate'.
Q.7. Who was the editor of the paper called "L'ami du peuple" (The friend of the people)?
Ans. The revolutionary journalist Jean-Paul Marat was the editor.

Q.8. What was the charge on which King Louis XVI was sentenced to death?
Ans. Louis XVI was sentenced to death by a court on the charge of treason. On 21st January, 1793, he was executed publicly at the Place de la Concorde.
Q.9. What was the name of the assembly which was called in France in 1792?
Or
Which new Assembly was formed by Jacobins?
Or
Who abolished the monarchy in France and declared it a republic, and when?
Ans. On 21st September 1792, the Convention, the newly elected assembly, abolished the monarchy and declared France a republic.
Q.10. A triangular slave trade was held between which areas of the world during the 18th century?
Or
Between which three continents triangular slave trade was held?
Ans. A triangular slave trade was held between Europe, Africa and the Americas to meet a shortage of labor on the plantations in the Americas.
Q.11. When did Napoleon Bonaparte crowned himself Emperor of France?
Or
When did Napoleon Bonaparte become Emperor of France?
Ans. He crowned himself Emperor of France in 1804.
Q.12. When and where was Napoleon Bonaparte finally defeated?
Or
In which famous war was Napoleon Bonaparte defeated?
Ans. Napoleon was finally defeated at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815.
Q.13. Name the French port cities related to the slave trade.
Or
Name the French ports through which the slave trade was done.
Ans. Bordeaux and Nantes were the places from where the French merchants sailed to the African coast, where they bought slaves from local chieftains.
Q.14. Who seized power after the fall of the Jacobin government?
Ans. The fall of the Jacobin government allowed the wealthier middle classes to seize power in the form of a political body called the Directory.
Q.15. Who did lead the representatives of the third estate in Versailles on 20th June 1789?
Ans. The representatives of the third estate were led by Mirabeau and Abbe Sieyes.
Q.16. Which social groups emerged in the 18th century?
Ans. The 18th century witnessed the emergence of social groups, termed the middle class, as well as lawyers and administrative officials.
Q.17. What was the name of the direct tax collected by the state from the peasants in 18th-century France?
Or
What was taille?
Ans. These included A direct tax, called taille was collected by the state.
Q.18. Name the French colonies in the Caribbean.
Ans. The French colonies in the Caribbean were Martinique, Guadeloupe and San Domingo.
Q.19. When was slavery finally abolished in the French colonies?
Ans. Slavery was finally abolished in the French colonies in 1848.
Q.20. Who wrote a 'Declaration of the Rights of Women and Citizens'?
Ans. Olympe de Gouges wrote a 'Declaration of the Rights of Women and Citizens' in 1791.
Q.21. When did the women in France get the right to vote?
Or
When did women in France finally get the right to vote in France?
Ans. In 1946, the women in France won the right to vote.
Q.22. Name the symbol of eternity in French society.
Ans. A snake biting its tail to form a ring is the symbol of eternity in French society.
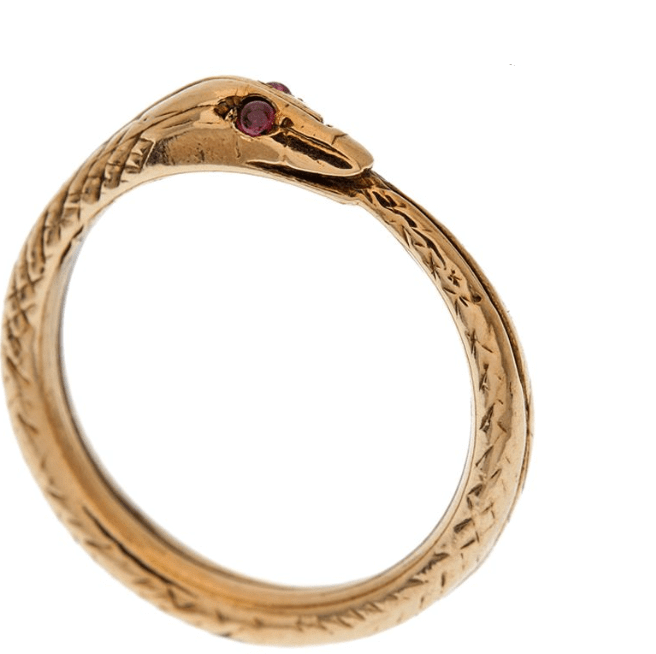 Snake biting its tail to form a ring: Symbol of Eternity. A ring has neither a beginning nor an end.
Snake biting its tail to form a ring: Symbol of Eternity. A ring has neither a beginning nor an end.
Q.23. Which section of French society was forced to give up its power after the French Revolution?
Ans. The first and second estates were forced to give up their power after the French Revolution.
Q.24. Whom did Louis XVI get married to?
Ans. Louis XVI was married to Princess Marie Antoinette of Austria.
Q.25. Why was the Bastille hated by all?
Or
What did the fall of the Bastille signify?
Ans. The Bastille, the fortress prison, was hated by all because it stood for the despotic power of the king.
Q.26. Name the classes which formed the privileged estates.
Ans. The clergy and the nobility constituted the privileged estates.
Q.27. When was monarchy abolished and France declared a republic?
Ans. On 21st September 1792, the monarchy was abolished, and France became a republic.
Q.28. Name the authors of the following books.
(i) The Social Contract
(ii) The Spirit of Laws
Ans.
(i) 'The Social Contract' was written by Jean Jacques Rousseau.
(ii) 'The Spirit of Laws' was written by Montesquieu.
Q.29. Explain the terms Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity of the French Revolution.
Ans. The term 'Liberty' means freedom, Equality stands for being equal and Fraternity stands for brotherhood.
Q.30. Name the European countries which share common boundaries with France.
Ans. The countries that share common boundaries with France are Spain, Italy, Switzerland, Germany, Luxembourg, and Belgium.
Q.31. What was the most important legacy of the French Revolution?
Ans. The ideas of liberty and democratic rights were the most important legacy of the French Revolution.
Or
LEF (liberty, equality and fraternity)
Q.32. When was slavery finally abolished in France?
Ans. Slavery was finally abolished in 1848 in France.
Q.33. Name the important political clubs formed by women in France to fight for their political rights.
Ans. The Society of Revolutionary and The Republican Women.
Q.34. What was 'Directory'?
Ans. The directory was an executive made up of five members. They were appointed by two elected legislative councils.
Q.35. How Robespierre's end came?
Ans. Robespierre was convicted by a court in July 1794, arrested and on the next day sent to the guillotine and killed in the same manner he punished guilty people.
Q.36. What was Guillotine?
Ans. A guillotine was a device consisting of two poles and a blade with which a person is beheaded. It was named after Dr. Guillotine, who invented it.
Q.37. Who introduced 'Reign of terror' in France?
Ans. Robespierre introduced Reign to Terror when he followed a policy of severe control and punishment in France.
Q.38. Who were 'Sans-Culottes'?
Ans. Those Jacobins were known as Sans-Culottes, who were without knee breeches and wore red caps to symbolize liberty.
Q.39. What were political clubs?
Ans. Political clubs were formed by people to discuss government policies and plan their own forms of action. Women, too, formed such clubs.
Q.40. What was 'Marseillaise'?
Ans. It was a patriotic song sung by volunteers of Marseilles as they marched into Paris. Marseillaise is now the national anthem of France.
Q.41. Who could qualify as an Elector?
Or
Who were the electors?
Ans. To qualify as an elector and then as a member of the Assembly, a man had to belong to the highest bracket of taxpayers.
Q.42. When was the draft of the National Assembly's constitution completed, and what was its main objective?
Ans. The draft of the constitution was completed in 1791 and its main objective was to limit the powers of the monarch.
Q.43. What was tithe?
Ans. It was a tax levied by the church, comprising at least one-tenth of the agricultural produce by the farmers.
Q.44. What was a 'Manor'?
Ans. A manor was an estate consisting of the lord's lands and his mansion.
Q.45. What does 'Chateau' mean?
Ans. It was a castle or stately residence belonging to a king or a nobleman.
Q.46. What do you know about Abbe Sieyes?
Ans. Abbe Sieves was originally a priest. He wrote an influential pamphlet called 'What is the Third Estate'.
Q.47. What was the Estates General?
Ans. The Estates General was a political body to which the three estates sent their representatives.
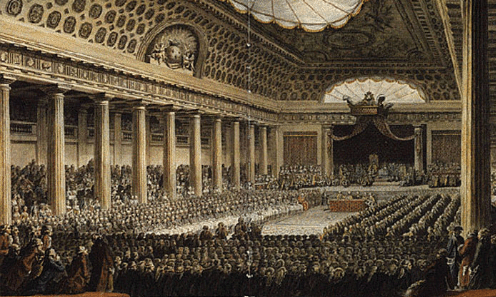 Estates General
Estates General
Q.48. How was the division of power suggested by philosopher Montesquieu?
Ans. Montesquieu proposed a division of power within the government between the legislative, the executive, and the judiciary.
Q.49. Why was Bastille Prison attacked?
Ans. The revolutionaries stormed the Bastille prison with the hope of finding hoarded ammunition for the revolution.
Q.50. What does 'subsistence crisis' mean?
Ans. It is an extreme situation where the basic means of livelihood are endangered.
|
53 videos|437 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 History Chapter 1 Question Answers - The French Revolution
| 1. Quelles étaient les principales causes de la Révolution française ? |  |
| 2. Quels événements importants ont marqué le déroulement de la Révolution française ? |  |
| 3. Quel rôle a joué Napoléon Bonaparte dans la Révolution française ? |  |
| 4. Comment la Révolution française a-t-elle influencé d'autres pays à travers le monde ? |  |
| 5. Quels étaient les résultats à long terme de la Révolution française sur la société et la politique françaises ? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















