Factors Limiting the Insurability of Risk | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Insurable Risks |

|
| Understanding Insurable Risks |

|
| Types of Insurable Risks |

|
| Factors Limiting the Insurability of Risk |

|
Introduction
It’s crucial for both businesses and individuals to prepare for potential losses, as unforeseen events such as theft or fire can result in significant financial setbacks. Having a contingency plan is essential, and this is where insurance plays a vital role. Insurance provides financial protection by covering losses associated with specific events. By paying premiums, individuals and businesses ensure they receive compensation if a covered event occurs. However, there are certain factors that limit the insurability of risks, which can affect the extent of protection and may result in some events not being covered by insurance companies.
Insurable Risks

- Insurable risks are those that insurance companies are willing to cover.
- Examples of insurable risks include theft, death, fire, and life-threatening situations.
- When such an event occurs and meets the policy’s conditions, the policyholder is entitled to a claim.
- For instance, if a policyholder is hospitalized due to an accident, their medical bills may be covered by the insurance.
- Both companies and individuals can insure against various risks.
- Businesses might insure against theft, fire, or loss during transportation.
- Individuals may secure policies for health, life, property, and more.
- It's essential to understand the factors that limit the insurability of risks.
- These factors can prevent a risk from being insured or might increase the premium.
- For instance, if someone intentionally causes an event to claim insurance, such as setting fire to their own property, they would not be eligible for the claim.
- This is because the event was not accidental.
Understanding Insurable Risks
- Insurable risks are typically pure risks, meaning they carry the potential for financial loss without the possibility of gain.
- These events are uncertain, and insurance companies cover them by charging premiums.
- However, not all risks are insurable, particularly those with speculative outcomes that involve the possibility of both loss and gain.
- Insuring such risks would expose the insurance company to significant potential losses, which is why factors limiting the insurability of risks exist.
- For example, a gambler faces the possibility of both winning and losing money, making this a speculative risk that is not insurable.
- Similarly, events like earthquakes, which can affect many people simultaneously, are generally not insurable.
- They could result in massive financial losses for the insurance company due to the volume of claims.
Types of Insurable Risks
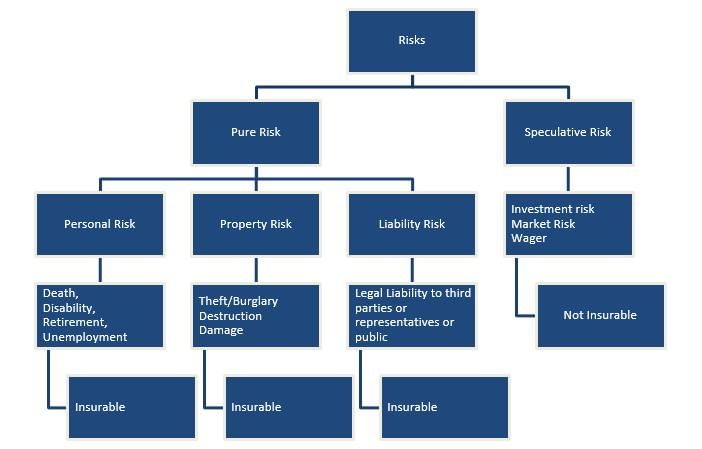 Insurable risks can be categorized into three types:
Insurable risks can be categorized into three types:
Personal Risk: These are risks that affect individuals, such as health issues, life threats, accidents, identity theft, or bankruptcy. These events can result in financial loss for the individual. For example, a person involved in an accidental injury can claim compensation for medical expenses, provided the accident was not intentional.
Property Risk: These risks involve loss or damage to property, such as homes, businesses, cars, or land, due to theft, fire, or other hazards. Insurance covers the financial loss associated with these risks. For instance, if someone’s car is stolen, they can file a claim, provided they were not negligent, such as leaving the car unlocked intentionally.
Liability Risk: This type of risk occurs when the insured is responsible for causing damage or loss to a third party. The insurance company covers the loss. For example, if the insured is at fault in a car accident that damages another person’s vehicle, the insurance company will cover the damages.
These types of risks are typically insurable, but other cases might involve higher premiums or may not be insurable at all, depending on the factors limiting the insurability of risk.
Factors Limiting the Insurability of Risk
Certain factors make it less likely for an insurance company to cover a risk. These include:
Moral Hazard: This occurs when individuals become less cautious because they know they are insured. For example, a person might drive recklessly, assuming they won’t face financial loss because they have insurance. Similarly, failing to take basic precautions, such as installing a fire alarm, can also lead to higher payouts by the insurance company, making the risk less insurable.
Adverse Selection: This happens when there is an information imbalance between the insurer and the insured. If the insured person withholds critical information, such as a pre-existing health condition, the insurance company might end up covering a higher risk than anticipated. For instance, a person with diabetes might face higher health insurance premiums, but if they hide this condition, it could adversely affect the insurer.
Premium Loads: When the risk of loss is higher, the insurance company might charge a premium load, which is an additional amount over the base premium. For example, insuring a home in a high-crime area might result in a higher premium due to the increased likelihood of theft or damage.
To better understand the factors limiting the insurability of risk, consider the following examples:
- A person purchases a house in an area prone to earthquakes. Due to the high risk of damage from frequent earthquakes, insurance companies may refuse to insure the property.
- An individual with a history of heart disease and high blood pressure applies for health insurance. Due to the high risk associated with their health condition, they might either be denied coverage or face significantly higher premiums compared to a healthier individual.
Conclusion
Understanding the factors limiting the insurability of risk is essential for anyone considering insurance. These factors determine whether a risk can be insured and at what cost. Being aware of these factors can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions when selecting insurance policies and evaluating potential premium costs.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Factors Limiting the Insurability of Risk - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What are some common factors that limit the insurability of risk? |  |
| 2. How do factors such as severity of risk impact the insurability of risk? |  |
| 3. What role does uncertainty play in limiting the insurability of risk? |  |
| 4. How does the lack of historical data impact the insurability of risk? |  |
| 5. Can you explain how moral hazard and adverse selection impact the insurability of risk? |  |




















