Facts that Matter: Lines & Angles | Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 PDF Download
- Two adjacent angles are said to form a linear pair of angles if their non-common arms are two opposite rays.
- If a ray stands on a line then the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is 180º.
- The sum of all the angles formed on the same side of a line at a given point on the line is 180º.
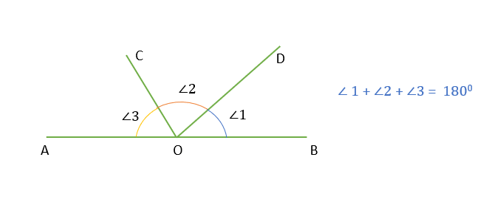 Sum of angles on one side of a straight line
Sum of angles on one side of a straight line - If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the angles of any
(i) Pair of corresponding angles are equal.
(ii) Pair of alternate interior angles are equal.
(iii) Pair of interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary. - If a transversal intersects two lines in such a manner that either
(i) angles of a pair of corresponding angles are equal, or
(ii) angles of a pair of alternate interior angles are equal, or
(iii) angles of a pair of interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary, then the lines are parallel. - If two lines intersect each other, then the vertically opposite angles are equal.
- Lines which are parallel to a given line are parallel to each other.
- The sum of the three angles of a triangle is 180º.
- If a side of a triangle is produced the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
Basic Terms & Definitions
Recall that a point is an exact location. We denote a point by a capital letter such as A, B, C, P and Q etc. The straight path between two points A and B is called a line segment AB. We denote it as. It has a definite length. A line segment
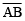 when extended indefinitely in one direction is called a ray AB. It is denoted by
when extended indefinitely in one direction is called a ray AB. It is denoted byhas one end-point A. A line segment
when extended indefinitely in both directions is called a line AB. It is denoted by
. It has no definite length and it is labelled by small letters ℓ, m, n, p, q, etc.
Note:
If three or more points lie on the same line they are called collinear points otherwise they are called non-collinear points.
Angle
An angle is formed when two rays originate from the same end-point. The rays making the angle are called arms of the angle and the endpoint is called the vertex of the angle.
Types of Angles
(i) An acute angle measures between 0º and 90º.
(ii) An angle that is exactly equal to 90º is called a right angle.
(iii) An angle greater than 90º but less than 180º is called an obtuse angle.
(iv) An angle that is exactly equal to 180º is called a straight angle.
(v) An angle that is greater than 180º and less than 360º is called a reflex angle.
(vi) An angle that is exactly equal to 360º is called a complete angle.
Note:
If the sum of two angles is 90º then they are called complementary angles whereas if the sum of two angles is 180º then they are called the supplementary angles.
Pairs of Angles [Having Common Vertex]
(i) Adjacent Angles
Two angles are said to be adjacent angles, if
(i) They have the same vertex
(ii) They have a common arm.
(iii) Their non-common arms are on either side of the common arm.
In the figure, ∠BOA and ∠COB are adjacent angles.
(ii) Linear Pair of Angles
Two adjacent angles are said to form a linear pair of angles if their non-common arms are two opposite rays. In the figure, ∠AOC and ∠BOC form a linear pair of angles.
Note:
If the sum of two adjacent angles is 180º, then the non-common arms of the angles form a straight line.
(iii) Vertically Opposite Angles
When two lines intersect each other at a point then they form two pairs of vertically opposite angles. In the figure AB and CD intersect at O and form ∠AOD and ∠BOC one pair of vertically opposite angles whereas ∠AOC and ∠BOD is the other pair.
Remember
The vertically opposite angles are always equal.
|
40 videos|471 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Facts that Matter: Lines & Angles - Mathematics (Maths) Class 9
| 1. What is a line in geometry? |  |
| 2. How are lines classified in geometry? |  |
| 3. What are angles in geometry? |  |
| 4. How are angles classified in geometry? |  |
| 5. How are lines and angles related in geometry? |  |






















