Financial Market : Money Market and Capital Market | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Financial Market Overview |

|
| Main Functions of the Financial Market |

|
| Classification of Financial Markets |

|
| Money Market in India |

|
| Capital Market Overview |

|
Financial Market Overview
A financial market is a system that facilitates the transfer of funds between investors or lenders and borrowers or users. It serves as a mechanism for channeling funds from those who have surplus money (investors or lenders) to those who need it (borrowers or businesses). This market is composed of individual investors, financial institutions, and intermediaries, all connected through formal trading rules and communication networks for the exchange of financial assets and credit instruments, such as bills of exchange, shares, debentures, and bonds.
Fund Raising by Businesses
Businesses often need to secure both short-term and long-term funds to support their working and fixed capital requirements. These funds can be obtained from investors or lenders. Essentially, surplus funds flow from investors or lenders to businesses to finance the production and sale of goods and services. Thus, the financial market brings together two key groups: those who invest or lend money and those who borrow or use it.
Main Functions of the Financial Market
- Facilitates Interaction: Provides a platform for investors and borrowers to interact.
- Pricing Information: Delivers pricing details based on market transactions between buyers and sellers of financial assets.
- Security: Ensures the security of transactions in financial assets.
- Liquidity: Offers mechanisms for investors to sell their financial assets, ensuring liquidity.
- Low Transaction Costs: Reduces transaction and information costs.
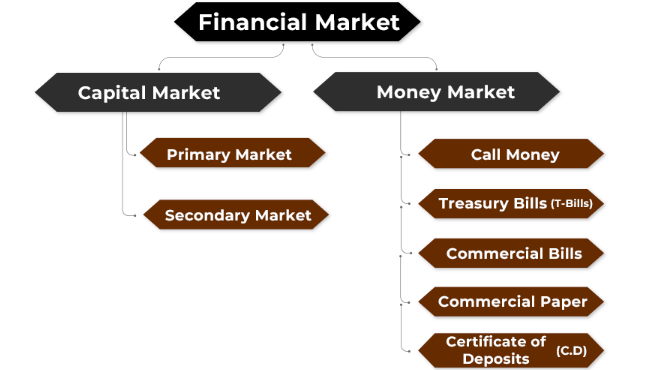
Classification of Financial Markets
Financial markets can be broadly divided into two segments:
Money Market
Deals with short-term credit and financial assets with maturities of up to one year. It includes instruments such as call money, treasury bills, commercial paper, certificates of deposit, and trade bills. The money market does not handle cash directly but provides a market for credit instruments.
Capital Market
Handles medium- and long-term credit and is further subdivided into:
Securities Market:
- Primary Market: Includes IPOs, book building, and private placements.
- Secondary Market: Comprises equity markets, debt markets, commodity markets, and futures and options markets. The secondary market can be split into spot and forward markets, with forward markets including futures and options (put and call options).
Non-Securities Market: Includes mutual funds, fixed deposits, savings deposits, post office savings, and insurance.
Money Market in India
- The Indian money market is a short-term credit market involving instruments with maturities up to one year.
- It does not deal in actual cash but provides a platform for credit instruments like bills of exchange, promissory notes, commercial paper, and treasury bills, which act as substitutes for money.
- Key participants include the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), commercial banks, co-operative banks, and specialized financial institutions such as LIC, GIC, and UTI.
- The RBI plays a leading role in the Indian money market.
Capital Market Overview
The capital market is a financial system designed for borrowing medium- and long-term funds and facilitates the marketing and trading of securities. It encompasses long-term borrowings from banks and financial institutions, international markets, and raising capital through the issuance of various securities such as shares, debentures, and bonds. The capital market is divided into two primary segments: the primary market and the secondary market.
Primary Market vs. Secondary Market
Primary Market: This segment is focused on obtaining long-term funds by issuing new shares and debentures. It is where companies raise capital directly from investors through the issuance of new securities.
Secondary Market: Also known as the stock exchange, this market provides a platform for buying and selling existing long-term securities. It ensures that securities like shares, debentures, bonds, and government securities can be traded regularly. The secondary market is organized and regulated according to the rules and regulations of stock exchanges.
Functions and Benefits of Stock Exchanges
Stock exchanges serve several key functions:
- Liquidity: They provide a continuous and ready market for securities.
- Price Information: They offer information about prices and sales.
- Safety: They ensure the security of transactions and investments.
- Capital Formation: They aid in mobilizing savings and contributing to capital formation.
- Economic Indicator: They act as a barometer for economic and business conditions.
Despite their advantages, stock exchanges can also face issues such as speculative trading and price fluctuations driven by rumors or unpredictable events. Currently, India has 21 stock exchanges, including BSE, NSE, and OTCEI. These exchanges are regulated by the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act and overseen by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which has implemented reforms to enhance market regulation and protect investor interests. This includes stricter listing and trading requirements.
Secondary Market Components
The secondary market includes two main components:
- Spot Market: Where securities are traded for immediate delivery and payment.
- Forward Market: Where securities are traded for future delivery and payment, further divided into:
- Futures Market: Trades securities for conditional future delivery.
- Options Market: Trades options, which provide the right but not the obligation to buy (call option) or sell (put option) a security at a predetermined price before a specific date.
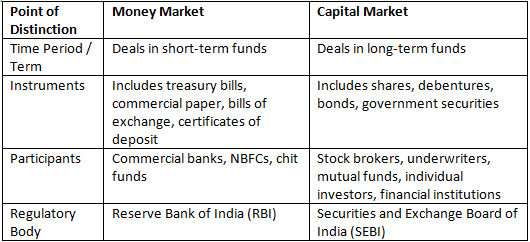
Comparison: Money Market vs. Capital Market
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Financial Market : Money Market and Capital Market - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What are the main functions of the financial market? |  |
| 2. How are financial markets classified? |  |
| 3. What is the money market in India? |  |
| 4. What is the capital market overview? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions related to the financial market for the UGC NET exam? |  |




















