Financial Statement Analysis | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
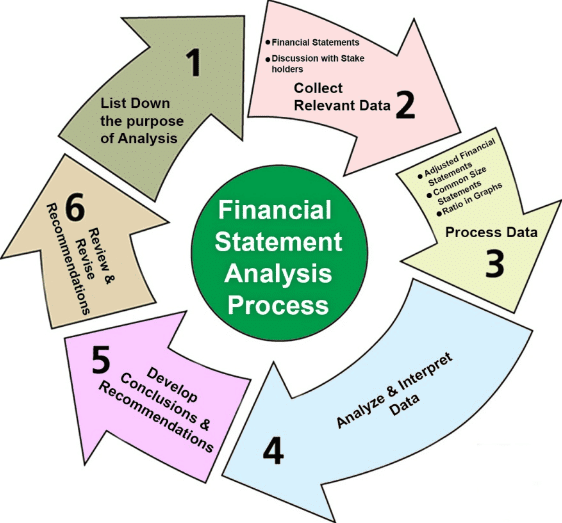
Financial Statement Analysis refers to the systematic numerical evaluation of the relationship between various financial aspects of a business. This analysis is conducted to assess a company's profitability, solvency, operational efficiency, and growth prospects.
Financial Statement Analysis involves breaking down financial records according to a specific plan, organizing them into sections, and presenting them in a way that is easy to understand.
Purpose of Financial Statement Analysis
The primary purposes of financial statement analysis include:
- Assessing the financial health of the business
- Evaluating the profitability (earning capacity) of the business
- Making comparisons within the firm (intra-firm) and with other firms (inter-firm)
- Determining the business's ability to pay interest, dividends, and other obligations
- Assessing the performance of management
- Measuring the firm's short-term and long-term solvency
Types of Financial Analysis
The key types of financial statement analysis are:
Horizontal Analysis:
- Examines the changes in financial statement figures over time.
- Compares one financial item with another over different periods.
- Analyzes financial trends from one year to the next.
Vertical Analysis:
- Analyzes the relationship between various items on a financial statement during a specific accounting period.
- Expresses these relationships as percentages.
Liquidity Analysis:
- Uses ratios to assess a company’s ability to repay debts and cover expenses.
- Helps businesses foresee potential financial difficulties and provides lenders and creditors with insights into a business's financial health before extending credit.
Profitability Analysis:
- Evaluates a company’s return on investment.
- Measures the balance between costs and revenues over a given period.
- Includes margin ratios and return ratios.
Variance Analysis:
- Involves comparing budgeted financial figures with actual outcomes to identify discrepancies.
- For example, if a business budgeted for sales of INR 10,000 but actually sold goods worth INR 4,500, the variance would be INR 5,500.
Valuation Analysis:
- Assesses the current value of a business.
- Useful for scenarios such as mergers and acquisitions.
- Compares current ratios with past ratios and those of competitors.
Scenario and Sensitivity Analysis:
- Evaluates the value of an investment based on current scenarios and potential changes.
- Helps predict outcomes under different variables.
Importance and Uses of Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis is crucial for various stakeholders, including:
- Management: To evaluate profitability, liquidity, and solvency, measure decision-making effectiveness, and take corrective actions.
- Investors: To assess the business’s earning capacity, future growth prospects, and the safety and reliability of their investment returns.
- Creditors: To evaluate the business's liquidity and solvency position.
- Government: To determine the profitability required for taxation and make decisions about price regulations.
- Customers: To assess the business's longevity.
- Employees: To understand the company’s progress, which impacts bonuses, wage increases, job stability, and other factors.
Tools of Financial Statement Analysis
Several tools are used in financial statement analysis to evaluate and interpret a company’s financial statements for planning, investment, and performance purposes. These include:
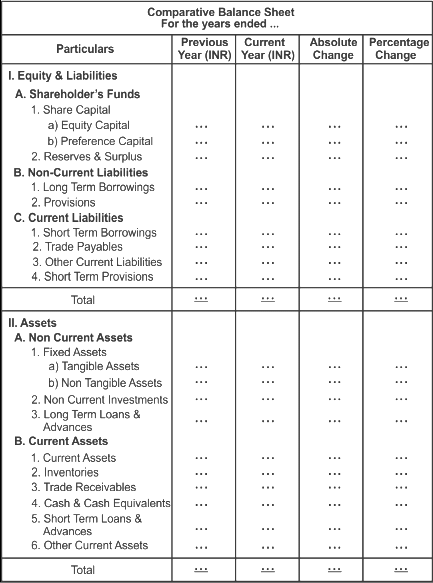
- Comparative Statement: Compares financial statements over two years, calculating differences in absolute and percentage terms (a form of horizontal analysis).
- Common Size Statement: A vertical analysis tool that shows each item on a financial statement as a percentage of a base figure.
- Ratio Analysis: A quantitative analysis tool that evaluates relationships between different financial statement items.
- Cash Flow Analysis: Analyzes the inflows and outflows of cash within a business.
- Trend Analysis: Examines patterns over a period to predict future financial performance.
Format of Comparative Income Statement
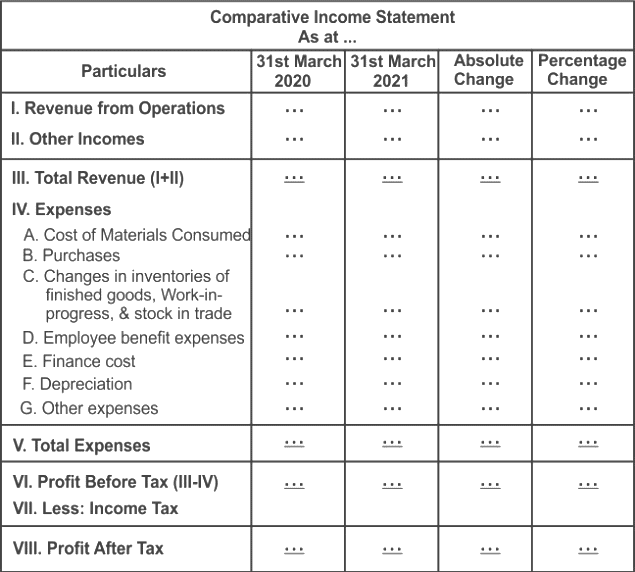
The above statement shows in percentage terms the total of income earned and the expenses incurred during two or more accounting periods.
Format of Comparative Balance Sheet
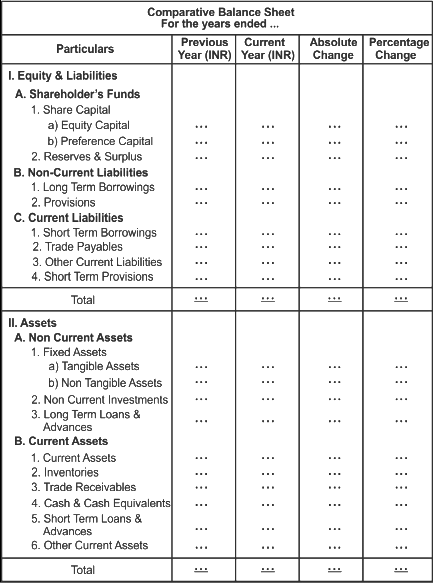
A Common Size Statement provides a way to analyze and compare financial statements by converting the figures into percentages of a common base. This makes it easier to see the relative size of each item and compare it across periods or with other businesses.
Common Size Income Statement
In a Common Size Income Statement, each line item is expressed as a percentage of total sales or revenue. This allows for easier comparison of financial performance across different periods or companies, regardless of size.
Format of Common Size Income Statement
Here’s a general format of a Common Size Income Statement:
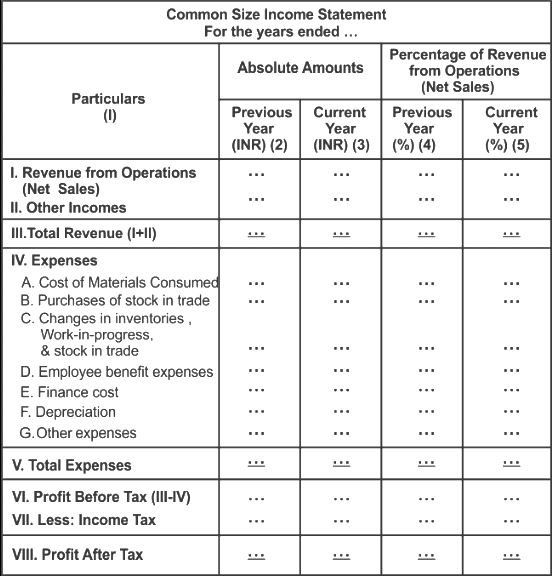
The above Common Size Income Statement shows the sales figure to be 100 and all other figures expressed as a percentage of sales.
Format of Common Size Balance Sheet
The common-size balance sheet shows the total of assets or liabilities to be assumed as 100 and the figures are expressed as a percentage of the total.
Ratio Analysis
Ratio Analysis involves examining the relationship between various items in financial statements to assess a company's financial performance. By calculating financial ratios, such as profitability, liquidity, efficiency, and solvency ratios, stakeholders can gain insights into different aspects of the business, such as how effectively it is managing its assets, how well it is generating profit, and how capable it is of meeting its short- and long-term obligations. These ratios provide a quick way to evaluate the company's financial health and compare it with industry standards or competitors.
Cash Flow Statement
A Cash Flow Statement details the inflows and outflows of cash and cash equivalents within a business over a specific period. This statement is crucial for understanding the liquidity of the company, as it highlights how cash is generated and used in operating, investing, and financing activities. Analyzing the cash flow statement helps identify the causes of changes in the company’s cash position between two balance sheet dates, providing insight into the company's ability to generate cash and manage its financial obligations. It is particularly useful for assessing whether the business has sufficient cash flow to sustain operations and meet its short-term liabilities.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Financial Statement Analysis - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is the purpose of financial statement analysis? |  |
| 2. What are the types of financial analysis? |  |
| 3. Why is financial statement analysis important? |  |
| 4. What are the key tools used in financial statement analysis? |  |
| 5. How can ratio analysis help in financial statement analysis? |  |





















