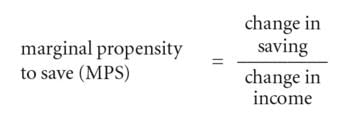|
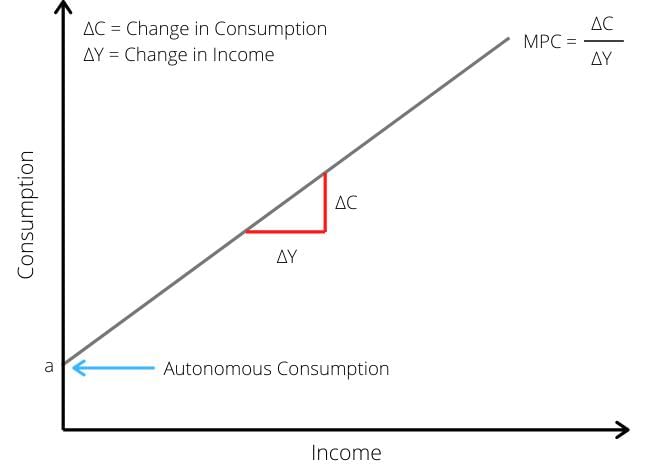
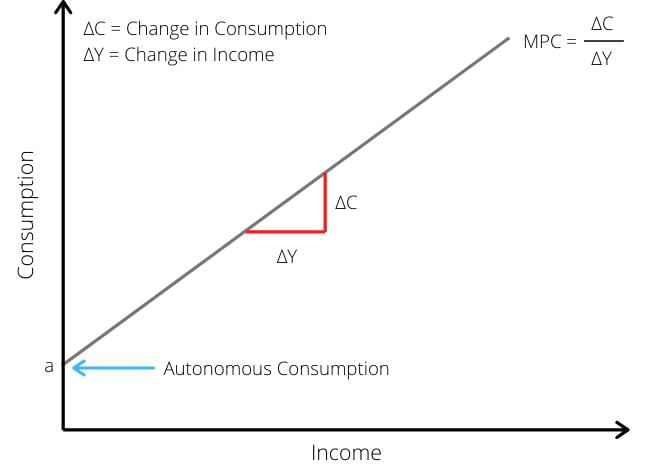
Induced consumption changes with disposable income, while autonomous consumption remains constant regardless of income. |
Card: 6 / 48 |
|
The Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) indicates the change in consumption when income changes. What is the range of MPC? |
Card: 7 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The sum of autonomous and induced consumption is referred to as ___ demand. |
Card: 9 / 48 |
|
Riddle: I can be positive or zero, but never negative. I tell you how much of your income you choose to spend. What am I? |
Card: 11 / 48 |
|
True or False: An increase in income leads to a decrease in consumption expenditure. |
Card: 15 / 48 |
|
False. An increase in income generally results in an increase in consumption expenditure. |
Card: 16 / 48 |
|
True or False: The Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) is the portion of additional income that is saved. |
Card: 19 / 48 |
|
Investment goods differ from intermediate goods in that they are considered ___ goods. |
Card: 21 / 48 |
|
It enhances the future productive capacity by increasing the stock of physical capital. |
Card: 24 / 48 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Riddle: I am the increase in the stock of capital that builds the future, but I am not labor. What am I? |
Card: 25 / 48 |
|
The Average Propensity to Save (APS) measures savings per unit change in ___ . |
Card: 27 / 48 |
|
Explain the difference between induced consumption and autonomous consumption. |
Card: 29 / 48 |
|
Induced consumption varies with income changes, while autonomous consumption remains constant regardless of income level. |
Card: 30 / 48 |
|
Income can be defined as the money earned or received from ___, ___, or ___ activities. |
Card: 31 / 48 |
|
Government expenditure adds to aggregate demand by spending on final goods and services. |
Card: 38 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: National income can be calculated by adding up all the income earned by individuals, firms, and ___ from various economic activities. |
Card: 39 / 48 |
|
Riddle: I can be measured by the total output of goods and services, but I am not a physical product. What am I? |
Card: 41 / 48 |
|
Induced consumption after taxes decreases overall income because higher taxes reduce disposable income, leading to lower consumption expenditure. |
Card: 44 / 48 |
|
Income is influenced by aggregate demand, as higher aggregate demand typically leads to increased production and income for individuals and firms. |
Card: 46 / 48 |