|
What were the primary goals of British economic policies in India during colonial rule? |
Card: 1 / 48 |
|
The primary goals were to benefit British industries by reducing India to a supplier of raw materials and a market for finished goods from Britain.
|
Card: 2 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: Before British rule, India had a thriving economy characterized by ___ and strong agriculture. |
Card: 3 / 48 |
|
True or False: The British government made sincere efforts to estimate India's national and per capita income during colonial rule. |
Card: 5 / 48 |
|
False. The British government did not make sincere efforts to estimate India's national and per capita income. 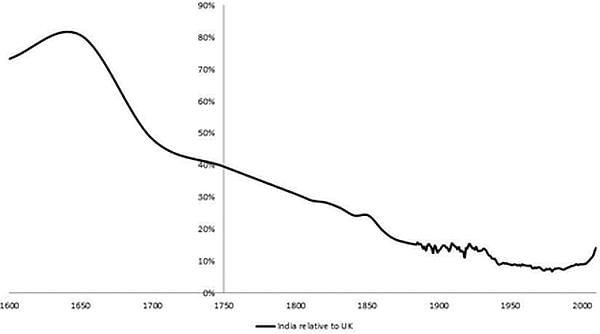 |
Card: 6 / 48 |
|
Riddle: I was known for my fine quality cotton textiles and had a royal texture. What am I? |
Card: 7 / 48 |
|
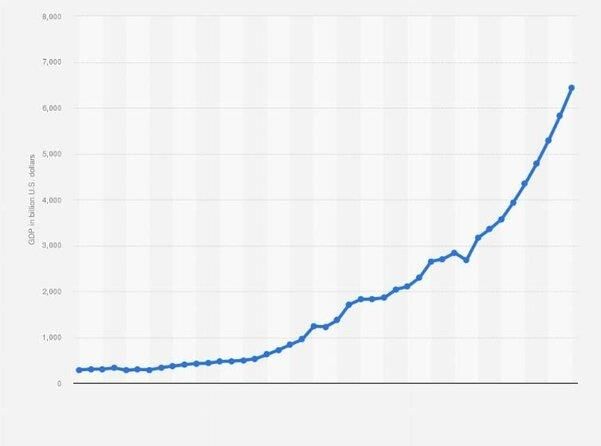
What was the estimated growth rate of aggregate real output in India during the first half of the 20th century? |
Card: 9 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The increased problems in farming during British rule were a direct result of policies aimed at transforming India into a supplier of ___ for British industries. |
Card: 11 / 48 |
|
British rule led to the downfall of local industries by focusing on the extraction of resources and promoting British goods over Indian products.  |
Card: 14 / 48 |
|
What was the primary economic structure of India during British colonial rule? |
Card: 15 / 48 |
|
India was primarily an agrarian economy with about 85% of the population living in villages and relying on agriculture.  |
Card: 16 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blanks: The Zamindari System was introduced in the ___ presidency and primarily benefited the ___ instead of the cultivators. |
Card: 17 / 48 |
|
True or False: The zamindars were motivated to improve agricultural conditions for the cultivators. |
Card: 19 / 48 |
|
False. The zamindars were primarily interested in collecting rent, which did not improve agricultural conditions. |
Card: 20 / 48 |
|
What were the consequences of the revenue settlement system implemented by the colonial government? |
Card: 21 / 48 |
|
The fixed dates for revenue payment led zamindars to exploit farmers, causing further distress among cultivators. |
Card: 22 / 48 |
|
Riddle: I am characterized by manual labor, lack of machines, and low technology. What am I? |
Card: 23 / 48 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
What factors contributed to the low agricultural productivity in India under British rule? |
Card: 25 / 48 |
|
Primitive production techniques, low levels of technology, lack of irrigation, and negligible use of fertilizers.  |
Card: 26 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The commercialization of agriculture during British rule led to ___ for the cultivators. |
Card: 27 / 48 |
|
What was the impact of the Zamindari System on the social conditions of cultivators? |
Card: 29 / 48 |
|
It caused immense misery and social tension among cultivators due to the exploitation by zamindars. |
Card: 30 / 48 |
|
What is the primary economic impact of British colonial policies on Indian agriculture? |
Card: 31 / 48 |
|
The British promoted the production of cash crops over food crops, which did not improve the economic conditions of farmers.  |
Card: 32 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The lack of investment in irrigation systems such as ___ and ___ contributed to the challenges faced by Indian agriculture. |
Card: 33 / 48 |
|
True or False: The shift from food crops to cash crops during British rule led to a significant increase in the economic stability of all Indian farmers. |
Card: 35 / 48 |
|
False. The shift did not improve the economic conditions of farmers, particularly for small farmers and sharecroppers.  |
Card: 36 / 48 |
|
What were some reasons for the lack of investment in agriculture by both the government and farmers in India? |
Card: 37 / 48 |
|
Many farmers lacked resources, technology, and incentives to invest in agriculture, leading to inadequate improvements in agricultural practices. |
Card: 38 / 48 |
|
Riddle: I am grown for profit, not for food, and during British rule, my cultivation was often pursued. What am I? |
Card: 39 / 48 |
|
Which crops were emphasized by British policies that diverted farmers from food production? |
Card: 41 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The agricultural policies during British rule encouraged the production of ___ crops, leading to a decline in food security. |
Card: 43 / 48 |
|
What was the primary aim of the systematic deindustrialisation policy implemented by the British government in India? |
Card: 45 / 48 |
|
To reduce India to the status of a mere exporter of raw materials and to create a large market for British finished products. |
Card: 46 / 48 |
|
The decline of indigenous handicraft industries in India during British rule led to massive unemployment and increased imports of manufactured goods from Britain. This phenomenon was primarily due to which policy? |
Card: 47 / 48 |