|
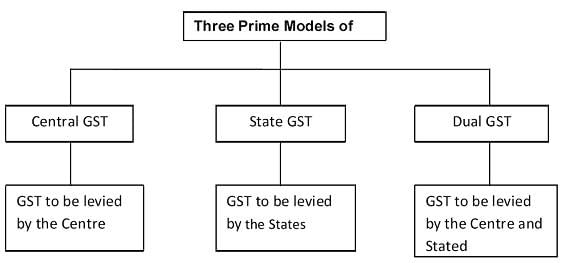
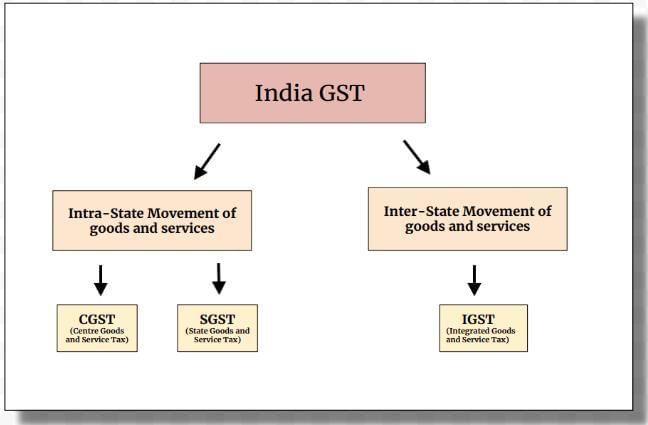
The Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) is part of a ___ model of taxation in India. |
Card: 1 / 46 |
|
True or False: Under the previous tax system, only the states had the authority to levy taxes on inter-state trade. |
Card: 3 / 46 |
|
The Central Sales Tax Act, 1956, was designed to regulate ___ trade or commerce. |
Card: 5 / 46 |
|
Fill in the blank: The main issue with the Central Sales Tax (CST) was that it was collected by the ___ state, not the destination state. |
Card: 7 / 46 |
|
CST led to cascading tax effects, increased compliance costs, and did not allow Input Tax Credit for buyers.  |
Card: 10 / 46 |
|
True or False: Indirect taxes are ideally supposed to accrue to the origin state where the goods are produced. |
Card: 11 / 46 |
|
False. Indirect taxes should ideally accrue to the destination state where the consumer is located.  |
Card: 12 / 46 |
|
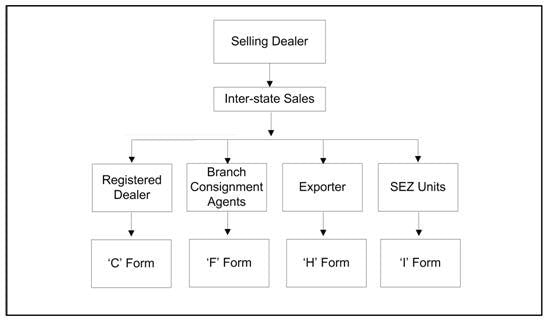
Fill in the blank: The requirement of various accountal forms in CST increased ___ for businesses. |
Card: 13 / 46 |
|
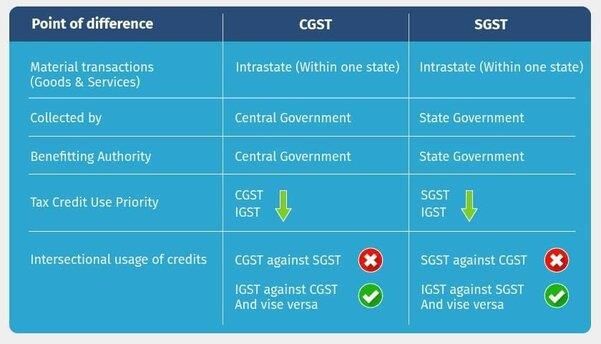
True or False: The IGST rate is always equal to the sum of CGST and SGST rates. |
Card: 17 / 46 |
|
IGST is levied by the ___ Government on all inter-State transactions of taxable goods or services. |
Card: 19 / 46 |
|
True or False: Inter-State supply includes the supply of goods from one Union territory to another Union territory. |
Card: 21 / 46 |
|
The purpose of the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act, 2017 is to impose a ___ cess aimed at compensating States. |
Card: 23 / 46 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
What is the duration initially set for the Compensation cess under the GST framework? |
Card: 25 / 46 |
|
Fill in the blank: Compensation Cess is not applicable to goods exported by an exporter under ___ . |
Card: 27 / 46 |
|
True or False: Compensation Cess is applicable to supplies made by a taxable person who opts for the composition levy. |
Card: 29 / 46 |
|
The Compensation cess came into effect on ___ coinciding with the enforcement of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act. |
Card: 31 / 46 |
|
What is the primary feature of the Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) in India's GST framework? |
Card: 33 / 46 |
|
IGST is a multi-stage value-added tax that is levied by both the Centre and States on every supply of goods or services, aiming to streamline taxation in line with India's federal structure. |
Card: 34 / 46 |
|
The Central Sales Tax Act, 1956, was established to regulate ___ and was based on ___ of the Constitution of India. |
Card: 35 / 46 |
|
True or False: The Central Sales Tax (CST) was collected and retained by the destination state where the consumer is located. |
Card: 37 / 46 |
|
The ITC of CST was not allowed to the buyer, which led to cascading tax effects, meaning tax was levied on tax within the supply chain. |
Card: 40 / 46 |
|
Fill in the blank: The requirement of various accountal forms under the CST increased ___ for businesses. |
Card: 41 / 46 |
|
Explain the rationale behind transitioning from the Central Sales Tax Act to the IGST model. |
Card: 43 / 46 |
|
The rationale was to address the shortcomings of the CST, such as its collection by the origin state instead of the destination state, the lack of ITC for buyers leading to cascading taxes, and the cumbersome compliance due to multiple accountal forms. |
Card: 44 / 46 |
|
What constitutional article prohibited states from levying sales tax on transactions outside their jurisdiction? |
Card: 45 / 46 |