|
Card: 5 / 48 |
True or False: The arithmetic mean is a good basis for comparing two or more groups of data. |
|
Card: 9 / 48 |
Fill in the blank: Averages help in ___ by condensing the information into a single value. |
|
Card: 17 / 48 |
True or False: The arithmetic mean can undergo further algebraic manipulation. |
|
Card: 19 / 48 |
What does the arithmetic mean provide that enhances its utility in statistical analysis? |
|
Card: 20 / 48 |
It provides a comprehensive representation of the distribution by considering all values. |
|
Card: 21 / 48 |
The arithmetic mean cannot be computed for ___ frequency distributions without making assumptions. |
|
Card: 23 / 48 |
True or False: The arithmetic mean can be calculated for qualitative characteristics such as intelligence. |
|
Card: 27 / 48 |
Riddle: I require all data points, but extreme values can twist my fate. What am I? |
|
Card: 31 / 48 |
What is a potential absurd result when calculating the arithmetic mean of a set of data? |
|
Card: 35 / 48 |
In calculating the simple arithmetic mean, what does 'N' represent in the formula? |
|
Card: 37 / 48 |
Fill in the blank: Unlike median or mode, the arithmetic mean cannot be determined through ___ of the series. |
|
Card: 39 / 48 |
What are the three methods for calculating the mean in frequency distribution? |
|
Card: 40 / 48 |
The three methods are the Direct Method, Short-cut Method, and Step-deviation Method. |
|
Card: 41 / 48 |
The formula for the Short-cut Method of estimating the mean involves finding the ___ of each class interval. |
|
Card: 43 / 48 |
True or False: The Step-deviation Method is used when deviations from the assumed mean have different factors. |
|
Card: 44 / 48 |
False. The Step-deviation Method is adopted when deviations from the assumed mean have a common factor. |
|
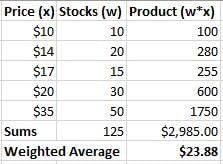
Card: 45 / 48 |
Fill in the blank: The Weighted Arithmetic Mean is calculated by dividing the ___ of the weighted items by the ___ of the weights. |
|
Card: 48 / 48 |
The mean can be affected significantly by extreme values, leading to misleading conclusions. |