Flow of Control | Computer Science for Grade 11 PDF Download
Introduction
The order of execution of the statements in a program is known as flow of control. The flow of control can be implemented using control structures. Python supports two types of control structures—Selection and Repetition.
Indentation
- Leading whitespace (spaces and tabs) at the beginning of a statement is called indentation.
- Python uses indentation for block as well as for nested block structures.
- In Python, the same level of indentation associates statements into a single block of code. The interpreter checks indentation levels very strictly and throws up syntax errors if indentation is not correct. It is a common practice to use a single tab for each level of indentation.
Types of Flow of Control
There are three types of flow of control –
a) Sequential flow of control
In Sequential flow of control execution of statement takes place in a sequence i.e. top to bottom approach.
num = int (input ("Enter Number " ))
num = num * 5
print (num)
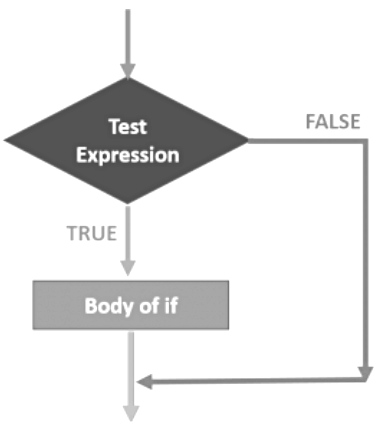
b) Conditional flow of control
Conditional flow of control is use to execute set of statements on the basis of the conditions.
num = int(input("Enter a number : "))
if num % 5 == 0:
print(num, "is divisible by 5")
else:
print(num, "is not divisible by 5")
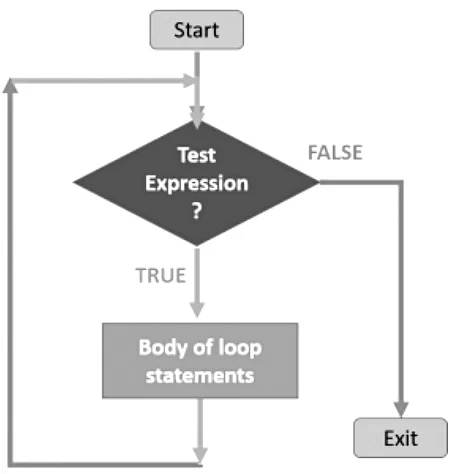
c) Iterative flow of control
iterative flow of control means repetition. It execute the set of statements till the condition is true.
Conditional statements
- An if statement tests a particular condition; if the condition evaluates to true, then set of statements executed otherwise does not.
if <conditional expression > :
statement
[statements]
# Write a program to check given character is an alphabet ‘A’.
ch = input("Enter a character : ")
if ch == 'A' :
print("You entered alphabet A")
if ch != 'A' :
print("You entered alphabet A")
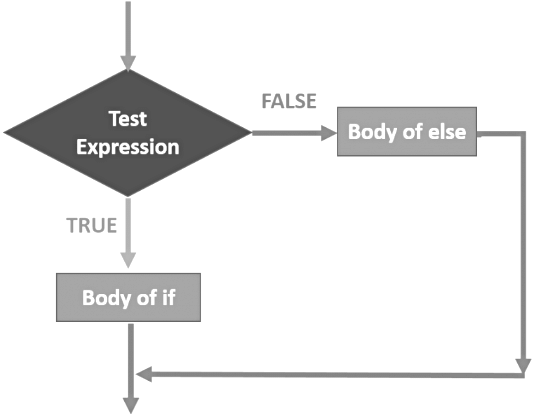
The if-else Statement
- An if statement tests a particular condition; if the condition evaluates to true, then it carries out the statements indented below if and in case condition evaluate to false, it carries out statements indented below else.
if <conditional expression > :
statement
[statements]
else :
statement
[statements]
# Write a program to check given character is an upper alphabet.
ch = input("Enter a character : ")
if ch >= 'A' and ch <= 'Z':
print("You have entered Upper alphabet")
else:
print("You have entered other than Upper Alphabet")
The if-elif-else
- An if-elif statement provide a facility to tests a condition with else ;
Syntax – 1
if <conditional expression > :
statement
[statements]
elif <conditional-expression> :
statement
[statements]
Syntax – 2
if <conditional expression > :
statement
[statements]
elif <conditional-expression>:
statement
[statements]
else:
statement
[statements]
# Write a program to check given character is an upper alphabet, lower alphabet, digits or other symbol.
ch = input("Enter a character : ")
if ch >= 'A' and ch <= 'Z':
print("You have entered Upper alphabet")
elif ch >= 'a' and ch <= 'z':
print("You have entered Lower alphabet")
elif ch >= '0' and ch <= '9':
print("You have entered Digit")
else:
print("You have entered Symbol")
Nested if statements
- An if inside the another if, called Nested if’s statement.
- An if-else inside the another if or else called nested if-else.
if <conditional expression > :
if <condition>:
statements
else:
statements
else :
if <condition>:
statements
else:
statements
Sample Programs :
# Absolute value
num = int(input("Enter a Number : "))
if num > 0 :
print("Absolute Value is ", num)
elif num < 0:
print("Absolute Value is ", num * -1)
else:
print("You have entered ", num)
# Sort 3 numbers
num1 = int(input("Enter a Number 1 : "))
num2 = int(input("Enter a Number 2 : "))
num3 = int(input("Enter a Number 3 : "))
if num1 < num2 and num1 < num3:
if num2 < num3:
print(num1, num2, num3)
else:
print(num1, num3, num2)
elif num2 < num1 and num2 < num3:
if num1 < num3:
print(num2, num1, num3)
else:
print(num2, num3, num1)
else:
if num2 < num1:
print(num3, num2, num1)
else:
print(num3, num1, num2)
# Divisibility of a number
num1 = int(input("Enter a Number 1 : "))
num2 = int(input("Enter a Number 2 : "))
if num1 % num2 == 0 :
print(num1 "is divisible by", num2)
elif num2 % num1 == 0:
print(num2, "is divisible by", num1)
else:
print(num1, 'and', num2,'neighter factor nor multiples')
Iterative / Repetitive Statements / Looping
range() function
for loop
while loop,
Flow Charts
Nested loops,
Suggested Programs:
# Python programs for generating pattern
Pattern-1
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
# Python Programs for summation of series.
# Finding the factorial of a positive number.
|
84 videos|19 docs|5 tests
|
|
Explore Courses for Grade 11 exam
|

|
















