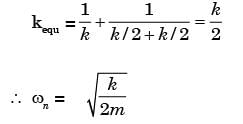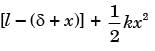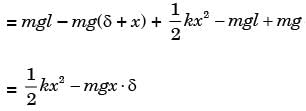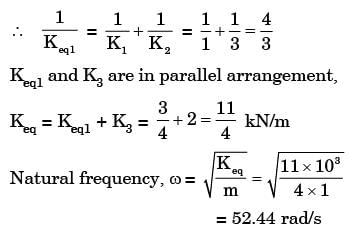Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
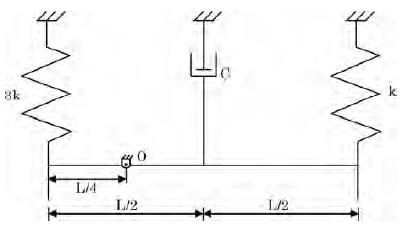
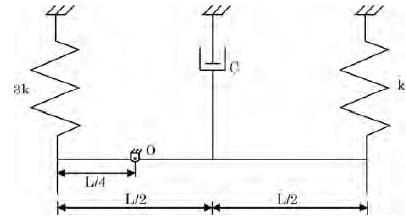
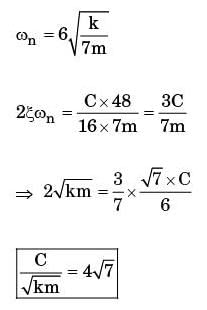
Try yourself:A slender uniform rigid bar of mass mis hinged at O an d supported by two springs, with stiffnesses 3k and k, and a damper with damping coefficient c, as shown in the figure. For the system to be critically damped, the ratio c√km should be

Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
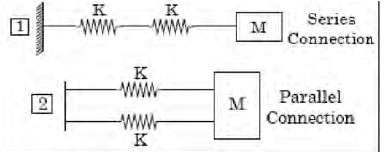
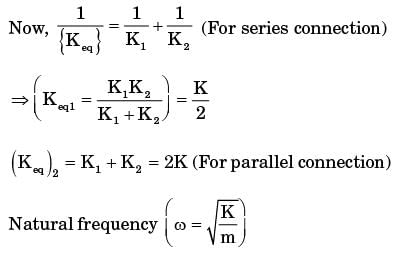
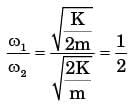
Try yourself:The natural frequencies corresponding to the spring-mass system I an d II are ωI an d ωII , respectively. The ratio  is
is

Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
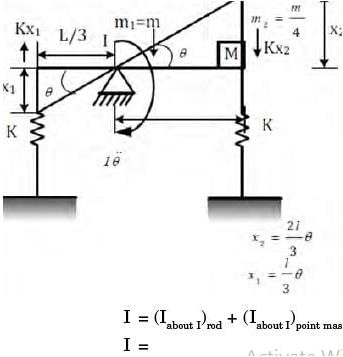
Try yourself:A thin uniform rigid bar of length L and M is hinged at point O, located at a distance of L/3 from one of its ends. The bar is further supported using springs, each of stiffness k located at the two ends. A particle of mass m = M/4 is fixed at one end of the bar, as shown in the figure. For small rotations of the bar about O, the natural frequency of the system is

[2017]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
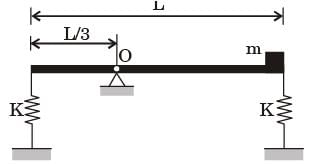
Try yourself:A mass m is attached to two identical springs having constant k as shown in the figure. The natural frequency w of this single degree of freedom system is

[2017]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
Try yourself:Considering mass less rigid rod small oscillations, the natural frequency (in rad/s) of vibration of the system shown in the figure is

[2015]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
Try yourself:What is the natural frequency of the spring mass system shown below? The contact between the block and the inclined plane is frictionless.The mass of the block is denoted by m and the spring constants are denoted by k1 and k2 as shown below
Explanation
It is parallel,

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
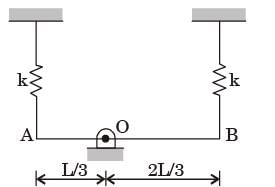
Try yourself:A rigid uniform rod AB of length L and mass m is hinged at C such that AC = L/3, CB = 2L/3.
Ends A and B are supported by springs of spring constant k. The natural frequency of the system is given by

[2014]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
Try yourself:A concentrated mass m is attached at the centre of a rod of Iength 2L as shown in the figure.
The rod is kept in a horizontal equilibrium position by a spring of stiffness k. For very small amplitude of vibration, neglecting the weights of the rod and spring, the undamped natural frequency of the system is

[2012]
Explanation

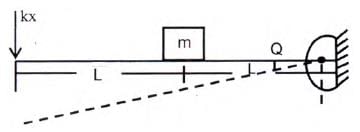
Equation of motion, is

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
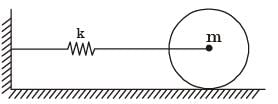
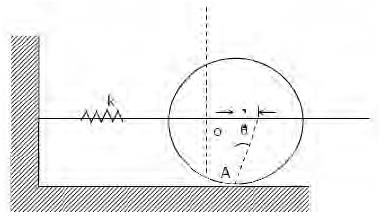
Try yourself:A disc of mass m is attached to a spring of stiffness k as shown in the fig. The disc rolls without slipping on a horizontal surface. The natural frequency of vibration of the system is

Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
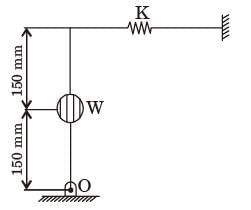
Try yourself:The natural frequency of a spring-mass system on earth is wn. The natural frequency of this system on the moon
[2010]
Explanation
 It depend s only on mass but not on weight .Therefore it is independent of gravity of a system, so it will remain ωn.
It depend s only on mass but not on weight .Therefore it is independent of gravity of a system, so it will remain ωn.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
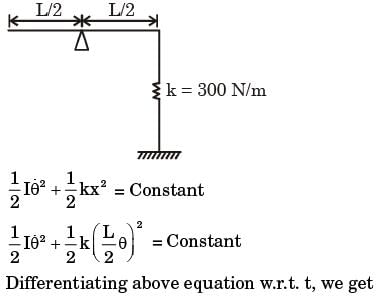
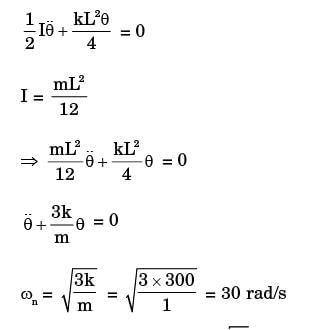
Try yourself:A uniform rigid rod of mass m = 1 kg and length L = 1 m is hinged at its centre & laterally supported at one end by a spring of spring constant k = 300 N/m. The natural frequency wn in rad/s is
[2008]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
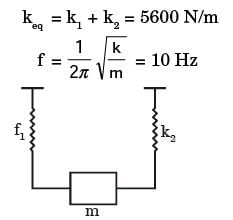
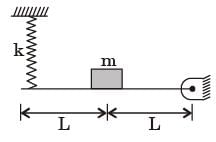
Try yourself:The natural frequency of the spring mass system shown in the figure is closest to
[2008 : 2 Marks]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
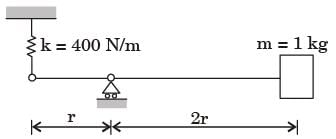
Try yourself: The natural frequency of the system shown below

Explanation
Equivalent k,

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
Try yourself:For an under damped harmonic oscillator, resonance
[2007]
Explanation
For underdamped harmonic oscillator,

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
Try yourself:A uniform stiff rod of length 300 mm and having a weight of 300 N is pivoted at one end and connected to a spring at the other end. For keeping the rod vertical in a stable position the minimum value of spring constant K needed is

[2004]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
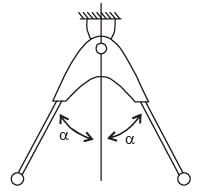
Try yourself:The assembly shown in the figure is composed of two massless rods of length l with two particles, each of mass m. The natural frequency of this assembly for small oscillations is

[2001]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
Try yourself:In the figure shown, the spring deflects by d to position A (the equilibrium position) when a mass m is kept on it. During free vibration, the mass is at position B at some instant. The change in potential energy of the spring mass system from position A to position B is
Explanation
Potential energy at A = mg (l – s)
Total energy at B = mg 
therefore, change in energy

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
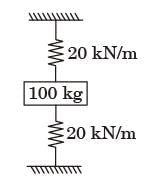
Try yourself:As shown in figure, a mass of 100 kg is held between two springs. The natural frequency of vibration of the system in cycle/s, is

[2000]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
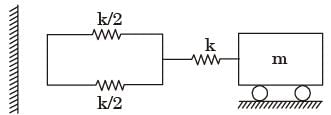
Try yourself:Consider the system of two wagons shown in figure. The natural frequencies of this system are
[1999]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Damped & Undamped Vibration
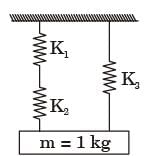
Try yourself:A mass of 1 kg is suspended by means of 3 springs as shown in figure. The spring constant K1, K2 and K3 are respectively 1 kN/m, 3 kN/m and 2 kN/m. The natural frequency of the system is approximately

[1996]
Explanation
K1 and K2 are in series,

Report a problem
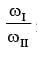 is
is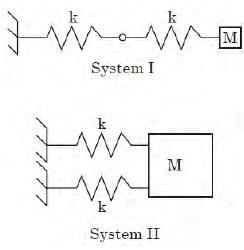








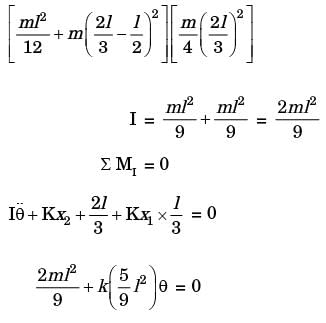
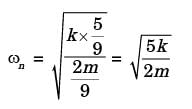
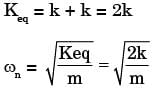
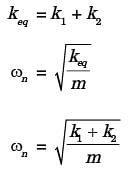
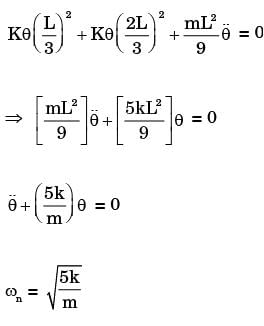
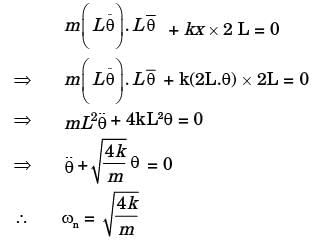
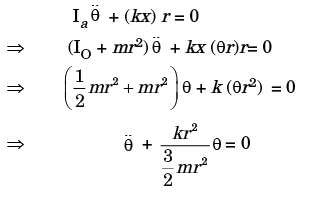
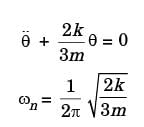
 It depend s only on mass but not on weight .Therefore it is independent of gravity of a system, so it will remain ωn.
It depend s only on mass but not on weight .Therefore it is independent of gravity of a system, so it will remain ωn.