Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
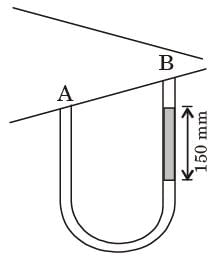
Try yourself:A U-tube manometer with a small quantity of mercury is used to measure the static pressure difference between two locations A and B in a conical section through which an incompressible fluid flows. At a particular flow rate, the mercury column appears as shown in the figure. The density of mercury is 13600 kg/ m3 and g - 9.81 m/s2. Which of the following is correct?

[2005]
Explanation

PA – PB = rg . Dh
= 13600 x 9.81 x .15
= 20 kPa
As pressure is decreasing from A to B, so flow direction is A to B.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
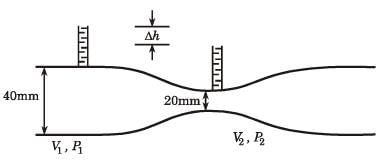
Try yourself:A venturimeter of 20 mm throat diameter is used to measure the velocity of water in a horizontal pipe of 40 mm diameter. If the pressure difference between the pipe and throat sections is found to be 30 kPa then, neglecting frictional losses, the flow velocity is
[2005]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
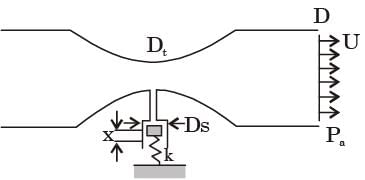
Try yourself:Air flows through a venturi and into atmosphere. Air density is ρa; atmospheric pressure is ρa; throat diameter is Dt; exit diameter is D and exit velocity is U. The throat is connected to a cylinder containing a frictionless piston attached to a spring. The spring constant is k. The bottom surface of the piston is exposed to atmosphere. Due to the flow, the piston moves by distance x. Assuming incompressible frictionless flow, x is

[2003]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
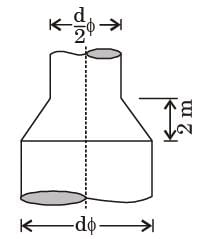
Try yourself:Water flows though a vertical contraction from a pipe of diameter d to another of diameter d/2 (see fig.) The flow velocity at the inlet to the contraction is 2 m/s and pressure 200 kN/m2. If the height of the contraction measures 2m,then pressure at the exit of the contraction will be very nearly

[1999]
Explanation
From continuity equation,
A1 v1 = A2 v2
or π/4 × d2 × 2 = π/4(d/2)2 × v2
or v2 = 8 m/s.
Applying Bernoulli's theorem,

or p2 =150.38 kN/m2.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
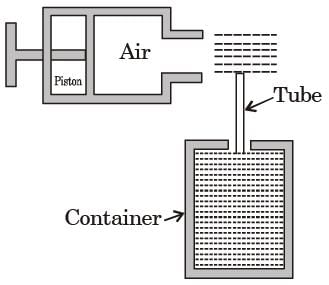
Try yourself:In a hand operated liquid sprayer (figure shown below) the liquid from the container rises to the top of the tube because of

[1990]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
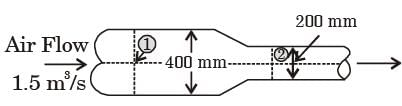
Try yourself:Air flows at the rate of 1.5 m3/s through a horizontal pipe with a gradually reducing crosssection as shown in the figure. The two crosssections of the pipe have diameters of 400 mm and 200 mm. Take the air density as 1.2 kg/m3 and assume inviscid incompressible flow. The change in pressure (p2 – p1) (in kPa) between sections 1 and 2 is

[2018, Set-2]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
Try yourself:Within a boundary layer for a steady incompressible flow, the Bernoulli equation
[2015,Set-2]
Explanation
Bernoulli equation does not hold because the flow is frictional.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
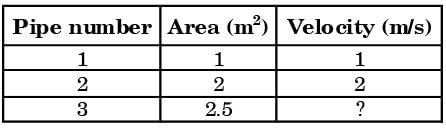
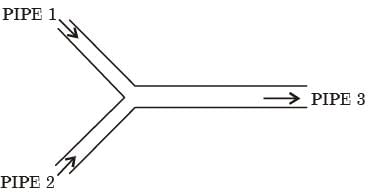
Try yourself:Consider steady flow of water in a situation where two pipe lines (pipe 1 and pipe 2) combine into a single pipe line (pipe 3) as shown in figure.
The cross-sectional'area of all three pipelines are constant. The following data is given


Assuming the water properties and the velocities to be uniform across the cross-section of the inlets and the outlet, the exit velocity (in m/s) in pipe 3 is
[2009]
Explanation
Q1 + Q2 = Q3
A1V1 + A2V3 = A3V3
1 + 4 = 2.5 V3
or V3 = 2 m/s
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
Try yourself:Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa and a specific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3/s) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation is
[2009]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
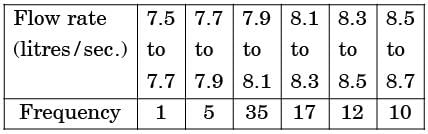
Try yourself:The following data about the flow of liquid was observed in a continuous Chemical process plant:

Mean flow rate of the liquid is
[2004]
Explanation

∴ Mean flow rate = = 8.16.
= 8.16.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics
Try yourself:Navier Stoke's equation represents the conservation of
[2000]








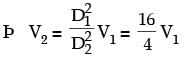
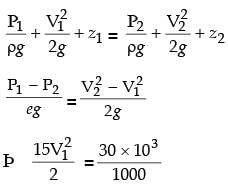
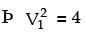




















 = 8.16.
= 8.16.
















