Glossary and Important Information: India - Size And Location | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
Glossary and Important Information
1. Equator: An imaginary line that splits the earth into two equal parts: the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere.
2. Prime Meridian: The primary meridian that runs through Greenwich, near London, and is used as the reference for measuring longitude.
3. Latitude: The angle that indicates how far a location is from the equator, measured in degrees.
4. Tropic of Cancer: An imaginary line parallel to the equator located at 23°30'N latitude.
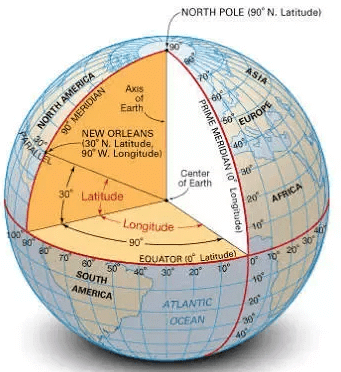 Fig: Latitudinal and longitudinal view
Fig: Latitudinal and longitudinal view
5. Subcontinent:. large land area that is smaller than a continent but larger than a country.
6. Standard Meridian of India: The meridian at 82°30’E, which determines the standard time for the entire country.
7. Local Time: The time determined by the position of the sun at midday in a specific location.
8. Standard Time: The time at the Standard Meridian of India (82°30'E), which serves as the official time nationwide.
9. Indian Union:. federation made up of 28 states and 7 Union Territories.
10. Indian mainland: The continuous landmass from Jammu and Kashmir to Kanyakumari and from Gujarat to Arunachal Pradesh.
11. Peninsula:. landmass surrounded by water on three sides.
12. Geographical Significance: India's central position at the head of the Indian Ocean is of great importance.
13. Latitudinal Extent: The mainland stretches from 8°04'N to 37°06'N latitude and from 68°07'E to 97°25'E longitude.
14. Southernmost Point: Indira Point is the southernmost point of the Indian Union and was submerged during the tsunami in 2004.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Glossary and Important Information: India - Size And Location - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What is the size of India and where is it located? |  |
| 2. What are the major geographical features of India? |  |
| 3. What is the climate of India like? |  |
| 4. What is the population of India? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of India's location in South Asia? |  |

















