Glossary and Important Information - Population | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
Glossary and Important Information
1. Census: The official counting of people living in a specific area, along with some economic and social details, usually done every ten years.
2. Migration: The movement of people from one place to another. This can be within a country (internal) or between countries (international). Internal migration affects where people live but not the total population size.
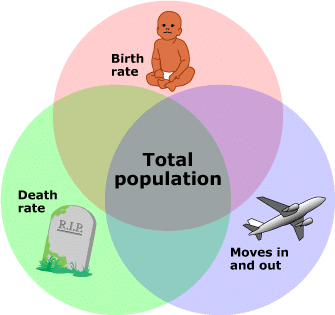
3. Population: The total number of people living in a country or area at a certain time.
4. Birth Rate: The number of babies born each year for every 1,000 people.
5. Death Rate: The number of deaths each year for every 1,000 people.
6. Density of Population: The average number of people living in a specific area. For example, India had a population density of 382 people per square kilometre in 2011.
7. Natural Increase of Population: The difference between the number of births and the number of deaths in a population.
8. Dependency Ratio: The ratio of people who are too young (under 15) or too old (over 60) to those who are of working age (15-59).
9. Demography: The study of population statistics, trends, and changes over time, including birth rates, death rates, and fertility rates.
10. Age Composition: The distribution of people across different age groups in a country.
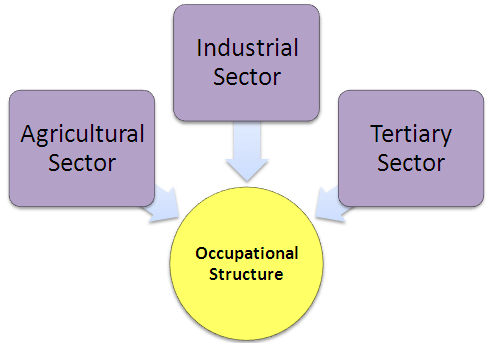
11. Occupational Structure: The way people in a country are distributed according to their jobs.
12. Population Growth: The change in the number of people living in a country over a certain time, shown as both total numbers and percentage increase per year.
13. Literate:. person aged 7 years and older who can read and write with understanding in any language is considered literate, according to the 2001 census.
14. Adolescence: This is the stage when a person is no longer a child but not yet an adult, typically ages 10 to 19.
15. Infant Mortality Rate: This measures the number of infants who die before their first birthday per 1,000 live births in a specific population during a certain time.
16. Annual Growth Rate: The rate at which a population increases, expressed as a percentage each year.
17. National Population Policy: The NPP 2000 is a framework aimed at achieving various objectives, such as providing free education up to age 14, reducing infant mortality, ensuring universal vaccination against preventable diseases, encouraging delayed marriage for girls, and focusing on family welfare.
18. Population Change: This refers to changes in the size, composition, or distribution of a population over time, caused by factors like birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration.
19. Population Density: This is the number of people living in a specific area, measured per unit of area.
|
55 videos|635 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Glossary and Important Information - Population - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What is the definition of population in a biological context? |  |
| 2. How is population density calculated? |  |
| 3. What factors can influence population growth? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of population distribution? |  |
| 5. Why is studying population important for ecology? |  |

















